Abstract
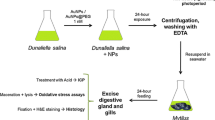
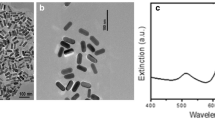
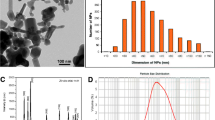
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are being developed and produced for a wide variety of industrial and biomedical applications, which raises the concern about their release and potential effects in the environment. In this study, we aim to assess the effects of PEGylated AuNPs and ionic gold on the freshwater bivalve Corbicula fluminea. As NP bioavailability is conditioned by many factors of variability, we focused on the determination of biodynamic parameters which control AuNP uptake and elimination in bivalves. Three experiments were conducted: (1) a waterborne exposure (0–24 mg/L for AuNPs and 0–12 mg/L for ionic gold), (2) a dietborne exposure (0–48 mg/L for AuNPs and 0–24 mg/L for ionic gold), and (3) an elimination phase (after waterborne exposure to 12 mg/L for AuNPs and 24 mg/L for ionic gold), to calculate rate constants for uptake from water(kuw), from food (kuf), and for the physiological elimination (ke) for AuNPs and AuCl(OH)3−. Jointly, the relative expression of several genes was investigated in the hemolymph cells to relate AuNPs and gold ion exposures to detoxification, oxidative stress, immune, and apoptosis responses in C. fluminea. Results show that kuw and kuf were around 10 and 30 times higher for AuNPs compared to AuCl(OH)3−, respectively. The ke was also faster in clams exposed to AuNPs meaning that they also had greater excretion capacities in comparison to gold ions. Water seems to be the main exposure pathway for C. fluminea according to kuw and kuf values for AuNPs and AuCl(OH)3− (kuw = 0.28 and 0.03, kuf = 0.009 and 0.001, respectively). The gene analyses pointed out important responses against oxidative stress, strong activations of genes of the immunity, and apoptosis after the waterborne exposure to AuNPs and to a lesser extent after exposure to gold ions. Very few responses were observed after the dietary exposure to both forms of gold, probably due to valve closure in response to contamination. While some studies suggest that the toxicity of nanoparticles may come from the release of metal ions, our results showed that the AuNPs we used were very stable (less than 1% of ion release) and generated more effects at the gene level than ionic gold. Therefore these results highlight the strong potential of toxicity of AuNPs compared to ionic gold and raise new concerns about the toxicity inherent to NPs in the environment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiard J-C, Amiard-Triquet C, Barka S, Pellerin J, Rainbow P (2006) Metallothioneins in aquatic invertebrates: their role in metal detoxification and their use as biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 76:160–202
Arini A, Baudrimont M, Feurtet-Mazel A, Coynel A, Blanc G, Coste M, Delmas F (2011) Comparison of periphytic biofilm and filter-feeding bivalve metal bioaccumulation (Cd and Zn) to monitor hydrosystem restoration after industrial remediation: a year of biomonitoring. J Environ Monit 13:3386–3398
Arini A, Daffe G, Gonzalez P, Feurtet-Mazel A, Baudrimont M (2014) Detoxification and recovery capacities of Corbicula fluminea after an industrial metal contamination (Cd and Zn): a one-year depuration experiment. Environ Pollut 192:74–82
Baudrimont M, Andres S, Durrieu G, Boudou A (2003) The key role of metallothioneins in the bivalve Corbicula fluminea during the depuration phase, after in situ exposure to Cd and Zn. Aquat Toxicol 63:89–102
Buffet P-E, Pan J-F, Poirier L, Amiard-Triquet C, Amiard J-C, Gaudin P, Risso-de Faverney C, Guibbolini M, Gilliland D, Valsami-Jones E (2013) Biochemical and behavioural responses of the endobenthic bivalve Scrobicularia plana to silver nanoparticles in seawater and microalgal food. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 89:117–124
Burchardt AD, Carvalho RN, Valente A, Nativo P, Gilliland D, Garcìa CP, Passarella R, Pedroni V, Rossi O, Lettieri T (2012) Effects of silver nanoparticles in diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana and Cyanobacterium synechococcus sp. Environ Sci Technol 46:11336–11344
Cajaraville MP, Pal SG (1995) Morphofunctional study of the haemocytes of the bivalve mollusc Mytilus galloprovincialis with emphasis on the endolysosomal compartment. Cell Struct Funct 20:355–367
Canesi L, Ciacci C, Fabbri R, Marcomini A, Pojana G, Gallo G (2012) Bivalve molluscs as a unique target group for nanoparticle toxicity. Mar Environ Res 76:16–21
Conner SD, Schmid SL (2003) Regulated portals of entry into the cell. Nature 422:37–44
Croteau M-N, Misra SK, Luoma SN, Valsami-Jones E (2011) Silver bioaccumulation dynamics in a freshwater invertebrate after aqueous and dietary exposures to Nanosized and ionic Ag. Environ Sci Technol 45:6600–6607. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200880c
Croteau M-N, Misra SK, Luoma SN, Valsami-Jones E (2014) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of CuO nanoparticles by a freshwater invertebrate after waterborne and dietborne exposures. Environ Sci Technol 48:10929–10937
Dai Q, Walkey C, Chan WC (2014) Polyethylene glycol backfilling mitigates the negative impact of the protein corona on nanoparticle cell targeting. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:5093–5096
Daniel M-C, Astruc D (2004) Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293–346
Diegoli S, Manciulea AL, Begum S, Jones IP, Lead JR, Preece JA (2008) Interaction between manufactured gold nanoparticles and naturally occurring organic macromolecules. Sci Total Environ 402:51–61
Doherty GJ, McMahon HT (2009) Mechanisms of endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem 78:857–902
García-Negrete C, Blasco J, Volland M, Rojas T, Hampel M, Lapresta-Fernández A, De Haro MJ, Soto M, Fernández A (2013) Behaviour of Au-citrate nanoparticles in seawater and accumulation in bivalves at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ Pollut 174:134–141
Giljohann DA, Seferos DS, Daniel WL, Massich MD, Patel PC, Mirkin CA (2010) Gold nanoparticles for biology and medicine. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:3280–3294
Gordon D, Rice J (1988) Opsonin-dependent and independent surface phagocytosis of S. aureus proceeds independently of complement and complement receptors. Immunology 64:709
Hull MS, Chaurand P, Rose J, Auffan M, Bottero JY, Jones JC, Schultz IR, Vikesland PJ (2011) Filter-feeding bivalves store and biodeposit colloidally stable gold nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 45:6592–6599
Jimeno-Romero A, Izagirre U, Gilliland D, Warley A, Cajaraville MP, Marigómez I, Soto M (2017) Lysosomal responses to different gold forms (nanoparticles, aqueous, bulk) in mussel digestive cells: a trade-off between the toxicity of the capping agent and form, size and exposure concentration. Nanotoxicology 11:658–670
Joubert Y, Pan J-F, Buffet P-E, Pilet P, Gilliland D, Valsami-Jones E, Mouneyrac C, Amiard-Triquet C (2013) Subcellular localization of gold nanoparticles in the estuarine bivalve Scrobicularia plana after exposure through the water. Gold Bull 46:47–56
Katsumiti A, Gilliland D, Arostegui I, Cajaraville MP (2015) Mechanisms of toxicity of Ag nanoparticles in comparison to bulk and ionic Ag on mussel hemocytes and gill cells. PLoS One 10:e0129039
Katsumiti A, Arostegui I, Oron M, Gilliland D, Valsami-Jones E, Cajaraville MP (2016) Cytotoxicity of Au, ZnO and SiO2 NPs using in vitro assays with mussel hemocytes and gill cells: relevance of size, shape and additives. Nanotoxicology 10:185–193
Kimling J, Maier M, Okenve B, Kotaidis V, Ballot H, Plech A (2006) Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle synthesis revisited. J Phys Chem B 110:15700–15707
Lapresta-Fernández A, Fernández A, Blasco J (2012) Nanoecotoxicity effects of engineered silver and gold nanoparticles in aquatic organisms. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 32:40–59
Levy R, Shaheen U, Cesbron Y, See V (2010) Gold nanoparticles delivery in mammalian live cells: a critical review. Nanotechnol Rev 1:4889
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Luoma SN (2008) Silver nanotechnologies and the environment : old problems or new challenges The Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies Report 15
Luoma SN, Rainbow PS (2005) Why is metal bioaccumulation so variable? Biodynamics as a unifying concept. Environ Sci Technol 39:1921–1931
Navarro E, Piccapietra F, Wagner B, Marconi F, Kaegi R, Odzak N, Sigg L, Behra R (2008) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Sci Technol 42:8959–8964
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Paciotti GF, Myer L, Weinreich D, Goia D, Pavel N, McLaughlin RE, Tamarkin L (2004) Colloidal gold: a novel nanoparticle vector for tumor directed drug delivery. Drug Deliv 11:169–183
Pelaz B, del Pino P, Maffre P, Hartmann R, Gallego M, Rivera-Fernandez S, de la Fuente JM, Nienhaus GU, Parak WJ (2015) Surface functionalization of nanoparticles with polyethylene glycol: effects on protein adsorption and cellular uptake. ACS Nano 9:6996–7008
Perrier F (2017) Nanocontamination d’organismes aquatiques par des particules inorganiques : transfert trophique et impacts toxiques Biodiversité et Ecologie. Université de Bordeaux
Praharaj S, Panigrahi S, Basu S, Pande S, Jana S, Ghosh SK, Pal T (2007) Effect of bromide and chloride ions for the dissolution of colloidal gold. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 187:196–201
Renault S, Baudrimont M, Mesmer-Dudons N, Gonzalez P, Mornet S, Brisson A (2008) Impacts of gold nanoparticle exposure on two freshwater species: a phytoplanktonic alga (Scenedesmus subspicatus) and a benthic bivalve (Corbicula fluminea). Gold Bull 41:116–126
Tedesco S, Doyle H, Redmond G, Sheehan D (2008) Gold nanoparticles and oxidative stress in Mytilus edulis. Mar Environ Res 66:131–133
Teles M, Soares A, Tort L, Guimarães L, Oliveira M (2017) Linking cortisol response with gene expression in fish exposed to gold nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 584:1004–1011
Volland M, Hampel M, Martos-Sitcha JA, Trombini C, Martínez-Rodríguez G, Blasco J (2015) Citrate gold nanoparticle exposure in the marine bivalve Ruditapes philippinarum: uptake, elimination and oxidative stress response. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:17414–17424
Wang W-X (2013) Dietary toxicity of metals in aquatic animals: recent studies and perspectives. Chin Sci Bull 58:203–213
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Marie-Noëlle Croteau for her valuable help on the application and interpretation of the biodynamic model on Corbicula fluminea and Anthony Bertucci for his help on the choice of relevant genes in the hemolymph. We also thank Bruno Etcheverria for his help in field and lab work.
Funding
This work was supported by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) in the CITTOXIC-Nano program (ANR-14-CE21-0001-01) and the Investments for the Future Program, within the Cluster of Excellence COTE (ANR-10-LABX-45).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Cinta Porte
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arini, A., Pierron, F., Mornet, S. et al. Bioaccumulation dynamics and gene regulation in a freshwater bivalve after aqueous and dietary exposures to gold nanoparticles and ionic gold. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 3637–3650 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4009-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4009-4