Abstract
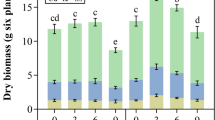
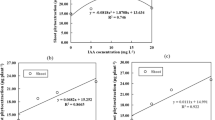
Plant uptake of cadmium (Cd) is affected by soil and environmental conditions. In this study, hydroponic experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of elevated CO2 coupled with inoculated endophytic bacteria M002 on morphological properties, gas exchange, photosynthetic pigments, chlorophyll fluorescence, and Cd uptake of S. alfredii. The results showed that bio-fortification processes (elevated CO2 and/or inoculated with endophytic bacteria) significantly (p < 0.05) promoted growth patterns, improved photosynthetic characteristics and increased Cd tolerance of both ecotypes of S. alfredii, as compared to normal conditions. Net photosynthetic rate (Pn) in intact leaves of hyperaccumulating ecotype (HE) and non-hyperaccumulating ecotype (NHE) were increased by 73.93 and 32.90%, respectively at the low Cd (2 μM), 84.41 and 57.65%, respectively at the high Cd level (10 μM). Superposition treatment increased Cd concentration in shoots and roots of HE, by 50.87 and 82.12%, respectively at the low Cd and 46.75 and 88.92%, respectively at the high Cd level. Besides, superposition treatment declined Cd transfer factor of NHE, by 0.85% at non-Cd rate, 17.22% at the low Cd and 22.26% at the high Cd level. These results indicate that elevated CO2 coupled with endophytic bacterial inoculation may effectively improve phytoremediation efficiency of Cd-contaminated soils by hyperaccumulator, and alleviate Cd toxicity to non-hyperaccumulator ecotype of Sedum alfredii.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzal M, Khan QM, Sessitsch A (2014) Endophytic bacteria: prospects and applications for the phytoremediation of organic pollutants. Chemosphere 117:232–242
Ainsworth EA, Rogers A (2007) The response of photosynthesis and stomatal conductance to rising [CO2]: mechanisms and environmental interactions. Plant Cell Environ 30:258–270
Ashraf S, Afzal M, Rehman K, Naveed M, Zahir ZA (2018) Plant-endophyte synergism in constructed wetlands enhances the remediation of tannery effluent. Water Sci Techn 77:1262–1270
Baker NR, Rosenqvist E (2004) Applications of chlorophyll fluorescence can improve crop production strategies: an examination of future possibilities. J Exp Bot 55:1607–1621
Barton CVM, Duursma RA, Medlyn BE, Ellsworth DS, Eamus D, Tissue DT, Adams MA, Conroy J, Crous KY, Liberloo M (2012) Effects of elevated atmospheric [CO2] on instantaneous transpiration efficiency at leaf and canopy scales in Eucalyptus saligna. Glob Change Biol 18:585–595
Belimov AA, Hontzeas N, Safronova VI, Demchinskaya SV, Piluzza G, Bullitta S, Glick BR (2005) Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with the roots of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.). Soil Biol Biochem 37:241–250
Bernacchi CJ, Morgan PB, Ort DR, Long SP (2005) The growth of soybean under free air [CO2] enrichment (FACE) stimulates photosynthesis while decreasing in vivo Rubisco capacity. Planta 220:434–446
Cao L, Bala G, Caldeira K, Nemani R, Ban-Weiss G (2009) Climate response to physiological forcing of carbon dioxide simulated by the coupled community atmosphere model (CAM3.1) and community land model (CLM3.0). Geophys Res Lett 36:L10402
Chen B, Shen JG, Zhang XC, Pan FS, Yang XE, Feng Y (2014a) The Endophytic bacterium, Sphingomonas SaMR12, improves the potential for zinc phytoremediation by its host, Sedum alfredii. PLoS One 9:e106826
Chen B, Zhang YB, Rafiq MT, Khan KY, Pan FS, Yang XE, Feng Y (2014b) Improvement of cadmium uptake and accumulation in Sedum alfredii by endophytic bacteria Sphingomonas SaMR12: effects on plant growth and root exudates. Chemosphere 117:367–373
Croonenborghs S, Ceusters J, Londers E, De Proft MP (2009) Effects of elevated CO2 on growth and morphological characteristics of ornamental bromeliads. Sci Hortic 121:192–198
Donohue RJ, Roderick ML, McVicar TR, Yang YT (2017) A simple hypothesis of how leaf and canopy-level transpiration and assimilation respond to elevated CO2 reveals distinct response patterns between disturbed and undisturbed vegetation. J Geophys Res-Biogeo 122:168–184
Drennan PM, Nobel PS (2000) Responses of CAM species to increasing atmospheric CO2 concentrations. Plant Cell Environ 23:767–781
Ehsan M, Lara Viveros FM, Hernández VE, Barakat MA, Ortega AR, Maza AV, Monter JV (2015) Zinc and cadmium accumulation by Lupinus uncinatus Schldl. grown in nutrient solution. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:307–316
Guo BH, Dai SX, Wang RG, Guo JK, Ding YZ, Xu YM (2015) Combined effects of elevated CO2 and Cd-contaminated soil on the growth, gas exchange, antioxidant defense, and Cd accumulation of poplars and willows. Environ Exp Bot 115:1–10
Haldimann P, Strasser RJ (1999) Effects of anaerobiosis as probed by the polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence rise kinetic in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Photosynth Res 62:67–83
Hamid Y, Tang L, Yaseen M, Hussain B, Zehra A, Aziz MZ, He ZL, Yang XE (2019) Comparative efficacy of organic and inorganic amendments for cadmium and lead immobilization in contaminated soil under rice - wheat cropping system. Chemosphere 214:259–268
Houshmandfar A, Fitzgerald GJ, Tausz M (2015) Elevated CO2 decreases both transpiration flow and concentrations of Ca and Mg in the xylem sap of wheat. J Plant Physiol 174:157–160
Hussain Z, Arslan M, Malik MH, Mohsin M, Iqbal S, Afzal M (2018) Integrated perspectives on the use of bacterial endophytes in horizontal flow constructed wetlands for the treatment of liquid textile effluent: phytoremediation advances in the field. J Environ Manag 224:387–395
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, New York
Jaffrin A, Bentounes N, Joan AM, Makhlouf S (2003) Landfill biogas for heating greenhouses and providing carbon dioxide supplement for plant growth. Biosyst Eng 86:113–123
Jia Y, Tang SR, Wang RG, Ju XH, Ding YZ, Tu SX, Smith DL (2010) Effects of elevated CO2 on growth, photosynthesis, elemental composition, antioxidant level, and phytochelatin concentration in Lolium mutiforum and Lolium perenne under cd stress. J Hazard Mater 180:384–394
Jing YX, Yan JL, He HD, Yang DJ, Xiao L, Zhong T, Yuan M, Cai XD, Li SB (2014) Characterization of bacteria in the rhizosphere soils of Polygonum pubescens and their potential in promoting growth and Cd, Pb, Zn uptake by Brassica napus. Int J Phytoremed 16:321–333
Khan MU, Sessitsch A, Harris M, Fatima K, Imran A, Arslan M, Shabir G, Khan QM, Afzal M (2015) Cr-resistant rhizo- and endophytic bacteria associated with Prosopis juliflora and their potential as phytoremediation enhancing agents in metal-degraded soils. Front Plant Sci 5:755
Kolbas A, Kidd P, Guinberteau J, Jaunatre R, Herzig R, Mench M (2015) Endophytic bacteria take the challenge to improve cu phytoextraction by sunflower. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:5370–5382
Kuffner M, Puschenreiter M, Wieshammer G, Gorfer M, Sessitsch A (2008) Rhizosphere bacteria affect growth and metal uptake of heavy metal accumulating willows. Plant Soil 304:35–44
Küpper H, Parameswaran A, Leitenmaier B, Trtilek M, Setlik I (2007) Cadmium-induced inhibition of photosynthesis and long-term acclimation to cadmium stress in the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. New Phytol 175:655–674
Li TQ, Di ZZ, Han X, Yang XE (2012) Elevated CO2 improves root growth and cadmium accumulation in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. Plant Soil 354:325–334
Li TQ, Tao Q, Han X, Yang XE (2013) Effects of elevated CO2 on rhizosphere characteristics of Cd/Zn hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. Sci Total Environ 454:510–516
Li TQ, Tao Q, Di ZZ, Lu F, Yang XE (2015) Effect of elevated CO2 concentration on photosynthetic characteristics of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii under cadmium stress. J Integr Plant Biol 57:653–660
Liu L, Hu L, Tang J, Li Y, Zhang Q, Chen X (2012) Food safety assessment of planting patterns of four vegetable-type crops grown in soil contaminated by electronic waste activities. J Environ Manag 93:22–30
Long SP, Ainsworth EA, Rogers A, Ort DR (2004) Rising atmospheric carbon dioxide: plants face the future. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:591–628
Long XX, Chen XM, Chen YG, Woon-Chung WJ, Wei ZB, Wu QT (2011) Isolation and characterization endophytic bacteria from hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance and their potential to promote phytoextraction of zinc polluted soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:1197–1207
Luo S, Chen L, Chen J, Xiao X, Xu T, Wan Y, Rao C, Liu C, Liu Y, Lai C, Zeng G (2011) Analysis and characterization of cultivable heavy metal resistant bacterial endophytes isolated from Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. and their potential use for phytoremediation. Chemosphere 85:1130–1138
Pan FS, Meng Q, Luo S, Shen J, Chen B, Khan KY, Japenga J, Ma XX, Yang XE, Feng Y (2017) Enhanced Cd extraction of oilseed rape (Brassica napus) by plant growth-promoting bacteria isolated from cd hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance. Int J Phytoremed 19:281–289
Pietrini F, Iannelli MA, Pasqualini S, Massacci A (2003) Interaction of cadmium with glutathione and photosynthesis in developing leaves and chloroplasts of Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex steudel. Plant Physiol 133:829–837
Redondo-Gómez S, Mateos-Naranjo E, Andrades-Moreno L (2010) Accumulation and tolerance characteristics of cadmium in a halophytic Cd-hyperaccumulator, Arthrocnemum macrostachyum. J Hazard Mater 184:299–307
Rehman K, Imran A, Amin I, Afzal M (2018) Inoculation with bacteria in floating treatment wetlands positively modulates the phytoremediation of oil field wastewater. J Hazard Mater 349:242–251
Singh SK, Reddy VR, Fleisher DH, Timlin DJ (2017) Relationship between photosynthetic pigments and chlorophyll fluorescence in soybean under varying phosphorus nutrition at ambient and elevated CO2. Photosynthetica 55:421–433
Solti A, Gaspar L, Meszaros I, Szigeti Z, Levai L, Sarvari E (2008) Impact of iron supply on the kinetics of recovery of photosynthesis in Cd-stressed poplar (Populus glauca). Ann Bot 102:771–782
Song NN, Ma YB, Zhao YJ, Tang SR (2015) Elevated ambient carbon dioxide and Trichoderma inoculum could enhance cadmium uptake of Lolium perenne explained by changes of soil pH, cadmium availability and microbial biomass. Appl Soil Ecol 85:56–64
Tang L, Luo WJ, Tian SK, He ZL, Stoffella PJ, Yang XE (2016) Genotypic differences in cadmium and nitrate co-accumulation among the Chinese cabbage genotypes under field conditions. Sci Hortic 201:92–100
Tang L, Luo WJ, Chen WK, He ZL, Gurajala HK, Hamid Y, Deng MH, Yang XE (2017) Field crops (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk. and Brassica chinensis L.) for phytoremediation of cadmium and nitrate co-contaminated soils via rotation with Sedum alfredii Hance. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19293–19305
Tang L, Luo WJ, He ZL, Gurajala HK, Hamid Y, Khan KY, Yang XE (2018) Variations in cadmium and nitrate co-accumulation among water spinach genotypes and implications for screening safe genotypes for human consumption. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol) 19:147–158
Tao Q, Hou DD, Yang XE, Li TQ (2016) Oxalate secretion from the root apex of Sedum alfredii contributes to hyperaccumulation of Cd. Plant Soil 398:139–152
Wu HB, Tang SR, Zhang XM, Guo JK, Song ZG, Tian SA, Smith DL (2009) Using elevated CO2 to increase the biomass of a Sorghum vulgare × Sorghum vulgare var. sudanense hybrid and Trifolium pratense L. and to trigger hyperaccumulation of cesium. J Hazard Mater 170:861–870
Xia C, Li NN, Zhang XX, Feng Y, Christensen MJ, Nan ZB (2016) An Epichloe endophyte improves photosynthetic ability and dry matter production of its host Achnatherum inebrians infected by Blumeria graminis under various soil water conditions. Fungal Ecol 22:26–34
Yadav SK (2010) Heavy metals toxicity in plants: an overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. S Afr J Bot 76:167–179
Yang XE, Long XX, Ye HB, He ZL, Calvert DV, Stoffella PJ (2004) Cadmium tolerance and hyperaccumulation in a new Zn-hyperaccumulating plant species (Sedum alfredii Hance). Plant Soil 259:181–189
Zheng JM, Wang HY, Li ZQ, Tang SR, Chen ZY (2008) Using elevated carbon dioxide to enhance copper accumulation in Pteridium revolutum, a copper-tolerant plant, under experimental conditions. Int J Phytoremed 10:161–172
Zhou WB, Qiu BS (2005) Effects of cadmium hyperaccumulation on physiological characteristics of Sedum alfredii Hance (Crassulaceae). Plant Sci 169:737–745
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Key Projects from Ministry of Science and Technology of China (#2016YFD0800805), Zhejiang Provincial Science and Technology Bureau (#2015C02011-3; #2015C03020-2), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the Funding from Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Ecosystem Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Yi-ping Chen
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 141 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, L., Hamid, Y., Gurajala, H.K. et al. Effects of CO2 application and endophytic bacterial inoculation on morphological properties, photosynthetic characteristics and cadmium uptake of two ecotypes of Sedum alfredii Hance. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 1809–1820 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3680-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3680-9