Abstract
Few studies were conducted to evaluate health effects of acute exposure to PM2.5 and daily mortality in Asian countries due to lack of large-scale PM2.5 monitoring data. We conducted a time-series study to examine the associations of short-term exposure to four common air pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, NO2, and SO2) and daily mortality in Ningbo, Zhejiang, China. We used generalized addictive model (GAM) to estimate relative risks (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the association of these four air pollutants with daily mortality. The study included 9365 people in the 2-year study period from 2014 to 2015. SO2 were significantly associated with risk of NAD, RD, and CD mortality with RRs of 1.034 (95% CI 1.004, 1.064), 1.067 (95% CI 1.010, 1.127), and 1.049 (95% CI 1.001, 1.098), respectively.PM2.5 and PM10 were significantly associated with risk of death from NAD mortality in warm season. Similar associations were observed for PM10 (RR = 1.056, 95% CI 1.004, 1.111) and risk of CD mortality. The study provides further evidence that short-term exposure to PM2.5, PM10, NO2, and SO2 are associated with increased risk of daily mortality.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson RW, Kang S, Anderson HR, Mills IC, Walton HA (2014) Epidemiological time series studies of PM2.5 and daily mortality and hospital admissions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 69:660–665
Bhaskaran K, Gasparrini A, Hajat S, Smeeth L, Armstrong B (2013) Time series regression studies in environmental epidemiology. Int J Epidemiol 42:1187–1195
Brook RD, Rajagopalan S, Pope CA, Brook JR, Bhatnagar A, Diez-Roux AV, Holguin F, Hong YL, Luepker RV, Mittleman MA, Peters A, Siscovick D, Smith SC, Whitsel L, Kaufman JD (2010) Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease an update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 121:2331–2378
Brunekreef B, Forsberg B (2005) Epidemiological evidence of effects of coarse airborne particles on health. Eur Respir J 26:309–318
China MOEP (2012): Ambient air quality standards. http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/dqhjbh/dqhjzlbz/201203/t20120302_224165.shtml
China MOEP (2013): Technical regulation for selection of ambient air quality monitoring stations(on trial). http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/dqhjbh/jcgfffbz/201309/t20130925_260810.shtml
China NBOS (2010): Population Census in China (2010) (in Chinese). http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/pcsj/rkpc/6rp/indexch.htm
Chow JC, Watson JG, Mauderly JL, Costa DL, Wyzga RE, Vedal S, Hidy GM, Altshuler SL, Marrack D, Heuss JM, Wolff GT, Pope CA, Dockery DW (2006) Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: lines that connect. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 56:1368–1380
Dai LZ, Zanobetti A, Koutrakis P, Schwartz JD (2014) Associations of fine particulate matter species with mortality in the United States: a multicity time-series analysis. Environ Health Perspect 122:837–842
Faustini A, Rapp R, Forastiere F (2014) Nitrogen dioxide and mortality: review and meta-analysis of long-term studies. Eur Respir J 44:744–753
Feng SXZSZG (2012) Use the capture-recapture method to evaluate the information integrity of the registration report of the all death causes (in Chinese). Chin Health Stat 29:229–230
Franklin M, Zeka A, Schwartz J (2007) Association between PM2.5 and all-cause and specific-cause mortality in 27 US communities. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 17:279–287
Goldberg MS, Burnett RT, Stieb DM, Brophy JM, Daskalopoulou SS, Valois MF, Brook JR (2013) Associations between ambient air pollution and daily mortality among elderly persons in Montreal, Quebec. Sci Total Environ 463:931–942
Graff DW, Cascio WE, Rappold A, Zhou HB, Huang Y, Devlin RB (2009) Exposure to concentrated coarse air pollution particles causes mild cardiopulmonary effects in healthy young adults. Environ Health Perspect 117:1089–1094
Hu J, Wang L, Yang G (2007) A study on the accuracy evaluation of the statistical data of the death causes of urban residents in China (in Chinese). Chin J Health Stat 24:2
Kan HD, London SJ, Chen GH, Zhang YH, Song GX, Zhao NQ, Jiang LL, Chen BH (2008) Season, sex, age, and education as modifiers of the effects of outdoor air pollution on daily mortality in Shanghai, China: The Public Health and Air Pollution in Asia (PAPA) study. Environ Health Perspect 116:1183–1188
Katsouyanni K, Touloumi G, Spix C, Schwartz J, Balducci F, Medina S, Rossi G, Wojtyniak B, Sunyer J, Bacharova L, Schouten JP, Ponka A, Anderson HR (1997) Short term effects of ambient sulphur dioxide and particulate matter on mortality in 12 European cities: results from time series data from the APHEA project. BMJ 314:1658–1663
Kim H, Lee JT, Hong YC, Yi SM, Kim Y (2004) Evaluating the effect of daily PM10 variation on mortality. Inhal Toxicol 161:55–58
Krzyzanowski M, Cohen A (2008) Update of WHO air quality guidelines. Air Qual Atmos Health 1:7–13
Lee H, Honda Y, Hashizume M, Guo YL, Wu CF, Kan HD, Jung K, Lim YH, Yi S, Kim H (2015a) Short-term exposure to fine and coarse particles and mortality: a multicity time-series study in East Asia. Environ Pollut 207:43–51
Lee YG, Jeong JY, Raftis J, Cho WS (2015b) Determination of adsorption affinity of nanoparticles for interleukin-8 secreted from A549 cells by in vitro cell-free and cell-based assays. J Toxicol Environ Health A 78:185–195
Levy JI, Hammitt JK, Spengler JD (2000) Estimating the mortality impacts of particulate matter: what can be learned from between-study variability? Environ Health Perspect 108:109–117
Liang KY, Zeger SL (1986) Longitudinal data-analysis using generalized linear-models. Biometrika 73:13–22
Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, AlMazroa MA, Amann M, Anderson HR, Andrews KG, Aryee M, Atkinson C, Bacchus LJ, Bahalim AN, Balakrishnan K, Balmes J, Barker-Collo S, Baxter A, Bell ML, Blore JD, Blyth F, Bonner C, Borges G, Bourne R, Boussinesq M, Brauer M, Brooks P, Bruce NG, Brunekreef B, Bryan-Hancock C, Bucello C, Buchbinder R, Bull F, Burnett RT, Byers TE, Calabria B, Carapetis J, Carnahan E, Chafe Z, Charlson F, Chen H, Chen JS, Cheng ATA, Child JC, Cohen A, Colson KE, Cowie BC, Darby S, Darling S, Davis A, Degenhardt L, Dentener F, Des Jarlais DC, Devries K, Dherani M, Ding EL, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Edmond K, Ali SE, Engell RE, Erwin PJ, Fahimi S, Falder G, Farzadfar F, Ferrari A, Finucane MM, Flaxman S, Fowkes FGR, Freedman G, Freeman MK, Gakidou E, Ghosh S, Giovannucci E, Gmel G, Graham K, Grainger R, Grant B, Gunnell D, Gutierrez HR, Hall W, Hoek HW, Hogan A, Hosgood HD III, Hoy D, Hu H, Hubbell BJ, Hutchings SJ, Ibeanusi SE, Jacklyn GL, Jasrasaria R, Jonas JB, Kan H, Kanis JA, Kassebaum N, Kawakami N, Khang YH, Khatibzadeh S, Khoo JP, Kok C, Laden F, Lalloo R, Lan Q, Lathlean T, Leasher JL, Leigh J, Li Y, Lin JK, Lipshultz SE, London S, Lozano R, Lu Y, Mak J, Malekzadeh R, Mallinger L, Marcenes W, March L, Marks R, Martin R, McGale P, McGrath J, Mehta S, Memish ZA, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Micha R, Michaud C, Mishra V, Hanafiah KM, Mokdad AA, Morawska L, Mozaffarian D, Murphy T, Naghavi M, Neal B, Nelson PK, Nolla JM, Norman R, Olives C, Omer SB, Orchard J, Osborne R, Ostro B, Page A, Pandey KD, Parry CDH, Passmore E, Patra J, Pearce N, Pelizzari PM, Petzold M, Phillips MR, Pope D, Pope CA III, Powles J, Rao M, Razavi H, Rehfuess EA, Rehm JT, Ritz B, Rivara FP, Roberts T, Robinson C, Rodriguez-Portales JA, Romieu I, Room R, Rosenfeld LC, Roy A, Rushton L, Salomon JA, Sampson U, Sanchez-Riera L, Sanman E, Sapkota A, Seedat S, Shi P, Shield K, Shivakoti R, Singh GM, Sleet DA, Smith E, Smith KR, Stapelberg NJC, Steenland K, Stöckl H, Stovner LJ, Straif K, Straney L, Thurston GD, Tran JH, van Dingenen R, van Donkelaar A, Veerman JL, Vijayakumar L, Weintraub R, Weissman MM, White RA, Whiteford H, Wiersma ST, Wilkinson JD, Williams HC, Williams W, Wilson N, Woolf AD, Yip P, Zielinski JM, Lopez AD, Murray CJL, Ezzati M (2012) A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380:2224–2260
Liu SY, Zhang K (2015) Fine particulate matter components and mortality in Greater Houston: did the risk reduce from 2000 to 2011? Sci Total Environ 538:162–168
Lv BL, Liu Y, Yu P, Zhang B, Bai YQ (2015) Characterizations of PM2.5 pollution pathways and sources analysis in four large cities in China. Aerosol Air Qual Res 15:1836–1843
Meng X, Wang CC, Cao DC, Wong CM, Kan HD (2013) Short-term effect of ambient air pollution on COPD mortality in four Chinese cities. Atmos Environ 77:149–154
Milojevic A, Wilkinson P, Armstrong B, Bhaskaran K, Smeeth L, Hajat S (2014) Short-term effects of air pollution on a range of cardiovascular events in England and Wales: case-crossover analysis of the MINAP database, hospital admissions and mortality. Heart 100:1093–1098
Peng RD, Chang HH, Bell ML, McDermott A, Zeger SL, Samet JM, Dominici F (2008) Coarse particulate matter air pollution and hospital admissions for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases among medicare patients. JAMA-J Am Med Assoc 299:2172–2179
Peng RD, Bell ML, Geyh AS, McDermott A, Zeger SL, Samet JM, Dominici F (2009) Emergency admissions for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases and the chemical composition of fine particle air pollution. Environ Health Perspect 117:957–963
Qian Z, He QC, Lin HM, Kong LL, Liao D, Yang NN, Bentley CM, Xu SQ (2007) Short-term effects of gaseous pollutants on cause-specific mortality in Wuhan, China. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 57:785–793
Rodopoulou S, Samoli E, Chalbot M, Kavouras IG (2015) Air pollution and cardiovascular and respiratory emergency visits in Central Arkansas: a time-series analysis. Sci Total Environ 536:872–879
Samet JM, Dominici F, Curriero FC, Coursac I, Zeger SL (2000) Fine particulate air pollution and mortality in 20 US cities, 1987–1994. New Engl J Med 343:1742–1749
Samoli E, Stafoggia M, Rodopoulou S, Ostro B, Declercq C, Alessandrini E, Diaz J, Karanasiou A, Kelessis AG, Le Tertre A, Pandolfi P, Randi G, Scarinzi C, Zauli-Sajani S, Katsouyanni K, Forastiere F (2013) Associations between fine and coarse particles and mortality in Mediterranean cities: results from the MED-PARTICLES project. Environ Health Perspect 121:932–938
Samoli E, Stafoggia M, Rodopoulou S, Ostro B, Alessandrini E, Basagana X, Diaz J, Faustini A, Martina G, Karanasiou A, Kelessis AG, Le Tertre A, Linares C, Ranzi A, Scarinzi C, Katsouyanni K, Forastiere F (2014) Which specific causes of death are associated with short term exposure to fine and coarse particles in Southern Europe ? Results from the MED-PARTICLES project. Environ Int 67:54–61
Schwartz J, Dockery DW, Neas LM (1996) Is daily mortality associated specifically with fine particles? J Air Waste Manage Assoc 46:927–939
Suh HH, Zanobetti A, Schwartz J, Coull BA (2011) Chemical properties of air pollutants and cause-specific hospital admissions among the elderly in Atlanta, Georgia. Environ Health Perspect 119:1421–1428
Touloumi G, Katsouyanni K, Zmirou D, Schwartz J, Spix C, DeLeon AP, Tobias A, Quennel P, Rabczenko D, Bacharova L, Bisanti L, Vonk JM, Ponka A (1997) Short-term effects of ambient oxidant exposure on mortality: a combined analysis within the APHEA project. Am J Epidemiol 146:177–185
Vonesh EF, Chinchilli VP, Pu KW (1996) Goodness-of-fit in generalized nonlinear mixed-effects models. Biometrics 52:572–587
Wang HB, Shooter D (2005) Source apportionment of fine and coarse atmospheric particles in Auckland, New Zealand. Sci Total Environ 340:189–198
Wilson WE, Suh HH (1997) Fine particles and coarse particles: concentration relationships relevant to epidemiologic studies. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 47:1238–1249
Wong CM, Vichit-Vadakan N, Kan HD, Qian ZM (2008) Public Health and Air Pollution in Asia (PAPA): a multicity study of short-term effects of air pollution on mortality. Environ Health Perspect 116:1195–1202
Yorifuji T, Kashima S, Doi H (2016) Associations of acute exposure to fine and coarse particulate matter and mortality among older people in Tokyo, Japan. Sci Total Environ 542:354–359
Funding
This study was supported and funded by Air Pollution and Health Research Center, Zhejiang University (14.585302-001) and Yinzhou Special Foundation for Agricultural and Social Development (YZ-STB-2015-96).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
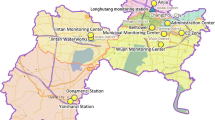
The distribution of monitor sites, health services and monitor factories in Yinzhou distric (GIF 295 kb)
High Resolution Image
(TIFF 4083 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Wang, Jb., Zhang, Zy. et al. Association between short-term exposure to ambient air pollution and daily mortality: a time-series study in Eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 16135–16143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1759-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1759-y