Abstract
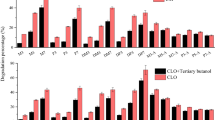
Cyclodextrins (CDs) can improve the apparent solubility and bioavailability of a variety of organic compounds through the formation of inclusion complexes; accordingly, they are suitable for application in innovative remediation technologies of contaminated soils. However, the different interactions in the tertiary system CD/contaminant/soil matrix can affect the bioavailability of the inclusion complex through the possible sorption of CD and CD complex in the soil matrix, as well as with the potential of the sorbed CD to form the complex, concurrent with the desorption processes. This work focuses in changes produced by three different CDs in soil sorption-desorption processes of chlorpyrifos (CPF), diazinon (DZN), and chlorothalonil (CTL), and their major degradation products, 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol (TCP), 2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinol, and hydroxy-chlorothalonil (OH-CTL). Cyclodextrins used were β-cyclodextrin (β-CD), methyl-β-cyclodextrin (Mβ-CD), and 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβ-CD). The studied soils belong to the orders Andisol, Ultisol, and Mollisol with different organic matter contents, mineral composition, and pH. The apparent sorption constants were significantly lower for the three pesticides in the presence of all CDs. The highest displacement of sorption equilibria was produced by the influence of Mβ-CD, with the most pronounced effect for CPF, a pesticide strongly sorbed on soils. The same was obtained for TCP and OH-CTL, highlighting the need to assess the risk of generating higher levels of groundwater contamination with polar metabolites if degradation rates are not controlled. The highest desorption efficiency was obtained for the systems CPF-β-CD, DZN-Mβ-CD, and CTL-Mβ-CD. Since the degree of adsorption of the complex is relevant to obtain an increase in the bioavailability of the contaminant, a distribution coefficient for the complexed pesticide in all CD–soil–pesticide system was estimated by using the apparent sorption coefficients, the stability constant for each CD–pesticide complex, and the distribution coefficients of free pesticide.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal V, Deng X, Tuli A, Goh KS (2013) Diazinon—chemistry and environmental fate: a California perspective. In: Whitacre DM (ed) Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology, vol 223. Springer, New York, pp 107–140
Armbrust KL (2001) Chlorothalonil and chlorpyrifos degradation products in golf course leachate. Pest Manag Sci 57:797–802
Baskaran S, Kookana RS, Naidu R (2003) Contrasting behaviour of chlorpyrifos and its primary metabolite, TCP (3, 5, 6-trichloro-2-pyridinol), with depth in soil profiles. Aust J Soil Res 41:749–760
Badr T, Hanna K, de Brauer C (2004) Enhanced solubilization and removal of naphthalene and phenanthrene by cyclodextrins from two contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 112:215–223
Baez ME, Espinoza J, Silva R, Fuentes E (2015) Sorption-desorption behavior of pesticides and their degradation products in volcanic and nonvolcanic soils: interpretation of interactions through two-way principal component analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8576–8585
Bergmark WR, Davis A, York C, Macintosh A, Jones G (1990) Dramatic fluorescence effects for coumarin laser dyes coincluded with organic solvents in cyclodextrins. J Phys Chem 94:5020–5022
Bavcon M, Trebše P, Zupančič-Kralj L (2003) Investigations of the determination and transformations of diazinon and malathion under environmental conditions using gas chromatography coupled with a flame ionisation detector. Chemosphere 50:595–601
Bian H, Chen J, Cai X, Liu P, Liu H, Qiao X, Huang L (2009) Inclusion complex of butachlor with β-cyclodextrin: characterization, solubility, and speciation-dependent adsorption. J Agric Food Chem 57:7453–7458
Brady JA, Wallender WW, Werner I, Fard BM, Zalom FG, Oliver MN, Wilson BW, Mata MM, Henderson JD, Deanovic LA, Upadhaya S (2006) Pesticide runoff from orchard floors in Davis, California, USA: a comparative analysis of diazinon and esfenvalerate. Agric Ecosyst Environ 115:56–68
Brusseau ML, Wang X, Hu Q (1994) Enhanced transport of low-polarity organic compounds through soil by cyclodextrin. Environ Sci Technol 28:952–956
Chaves A, Shea D, Cope WG (2007) Environmental fate of chlorothalonil in a Costa Rican banana plantation. Chemosphere 69:1166–1174
Chu X, Fang H, Pan X, Wang X, Shan M, Feng B, Yu Y (2008) Degradation of chlorpyrifos alone and in combination with chlorothalonil and their effects on soil microbial populations. J Environ Sci 20:464–469
Churchill D, Cheung JCF, Park YS, Smith VH, van Loon G, Buncel E (2006) Complexation of diazinon, an organophosphorus pesticide, with α-, β-, and γ-cyclodextrin. NMR and computational studies. Can J Chem 84:702–708
Coly A, Aaron J-J (1998) Cyclodextrin-enhanced fluorescence and photochemically-induced fluorescence determination of five aromatic pesticides in water. Anal Chim Acta 360:129–141
Connors KA (1997) The stability of cyclodextrin complexes in solution. Chem Rev 97:1325–1357
Del Valle EMM (2004) Cyclodextrins and their uses: a review. Process Biochem 39:1033–1046
Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2006) Highly selective sample preparation and gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of chlorpyrifos, diazinon and their major metabolites in sludge and sludge fertilized agricultural soils. J Chromatogr A 1132:21–27
Flaherty RJ, Nshime B, DeLaMarre M, DeJong S, Scott P, Lantz AW (2013) Cyclodextrins as complexation and extraction agents for pesticides from contaminated soil. Chemosphere 91:912–920
Gebremariam SY, Beutel MW, Yonge DR, Flury M, Harsh JB (2012) Adsorption and desorption of chlorpyrifos to soils and sediments. In: Whitacre DM (ed) Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology, vol 215. Springer New York, New York, pp 123–175
Hartnik T, Jensen J, Hermens JLM (2008) Nonexhaustive β-cyclodextrin extraction as a chemical tool to estimate bioavailability of hydrophobic pesticides for earthworms. Environ Sci Technol 42:8419–8425
Herrero-Hernandez E, Andrades MS, Alvarez-Martin A, Pose-Juan E, Rodriguez-Cruz MS, Sanchez-Martin MJ (2013) Occurrence of pesticides and some of their degradation products in waters in a Spanish wine region. J Hydrol 486:234–245
Humbert S, Margni M, Charles R, Salazar OMT, Quirós AL, Jolliet O (2007) Toxicity assessment of the main pesticides used in Costa Rica. Agric Ecosyst Environ 118:183–190
Imfeld G, Vuilleumier S (2012) Measuring the effects of pesticides on bacterial communities in soil: a critical review. Eur J Soil Biol 49:22–30
Köprücü SŞ, Köprücü K, Ural MŞ, İspir Ü, Pala M (2006) Acute toxicity of organophosphorous pesticide diazinon and its effects on behavior and some hematological parameters of fingerling European catfish (Silurus glanis L.) Pestic Biochem Physiol 86:99–105
Kookana R, Gerritse R, Aylmore L (1990) Effect of organic cosolvent on adsorption and desorption of linuron and simazine in soil. Aust J Soil Res 28:717–725
Kumar Singh B, Walker A, Wright DJ (2002) Persistence of chlorpyrifos, fenamiphos, chlorothalonil, and pendimethalin in soil and their effects on soil microbial characteristics. B Environ Contam Tox 69:181–188
Kumar A, Correll R, Grocke S, Bajet C (2010) Toxicity of selected pesticides to freshwater shrimp, Paratya australiensis (Decapoda: Atyidae): use of time series acute toxicity data to predict chronic lethality. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:360–369
Landy D, Mallard I, Ponchel A, Monflier E, Fourmentin S (2012) Remediation technologies using cyclodextrins: an overview. Environ Chem Lett 10:225–237
Lau EV, Gan S, Ng HK, Poh PE (2014) Extraction agents for the removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from soil in soil washing technologies. Environ Pollut 184:640–649
Leitao S, Cerejeira MJ, Van den Brink PJ, Sousa JP (2014) Effects of azoxystrobin, chlorothalonil, and ethoprophos on the reproduction of three terrestrial invertebrates using a natural Mediterranean soil. Appl Soil Ecol 76:124–131
Liu H, Cai X, Chen J (2013) Mathematical model for cyclodextrin alteration of bioavailability of organic pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 47:5835–5842
Lucas-Abellán C, Gabaldón-Hernández JA, Penalva J, Fortea MI, Núñez-Delicado E (2008) Preparation and characterization of the inclusion complex of chlorpyrifos in cyclodextrins to improve insecticide formulations. J Agric Food Chem 56:8081–8085
Magnusdottir A, Másson M, Loftsson T (2002) Self association and cyclodextrin solubilization of NSAIDs. J Incl Phenom Macrocyl Chem 44:213–218
McManus SL, Moloney M, Richards KG, Coxon CE, Danaher M (2014) Determination and occurrence of phenoxyacetic acid herbicides and their transformation products in groundwater using ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Molecules 19:20627–20649
Morillo E, Pérez-Martínez JI, Ginés JM (2001) Leaching of 2,4-D from a soil in the presence of β-cyclodextrin: laboratory columns experiments. Chemosphere 44:1065–1069
Morillo E, Sánchez-Trujillo MA, Moyano JR, Villaverde J, Gómez-Pantoja ME, Pérez-Martínez JI (2012) Enhanced solubilisation of six PAHs by three synthetic cyclodextrins for remediation applications: molecular modelling of the inclusion complexes. PLoS One 7:e44137
Morillo E, Sánchez-Trujillo MA, Villaverde J, Madrid F, Undabeytia T (2014) Effect of contact time and the use of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in the removal of fluorene and fluoranthene from contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 496:144–154
Ni Y, Liang X, Chen J, Zhang Q, Ma L, Wu W, Kettrup A (2004) Investigation on the influence of methanol on adsorption and leaching of pesticides with soil column liquid chromatography. Chemosphere 56:1137–1142
Papadopoulou ES, Karas PA, Nikolaki S, Storck V, Ferrari F, Trevisan M, Tsiamis G, Martin-Laurent F, Karpouzas DG (2016) Dissipation and adsorption of isoproturon, tebuconazole, chlorpyrifos and their main transformation products under laboratory and field conditions. Sci Total Environ 569–570:86–96
Rubio-Bellido M, Morillo E, Villaverde J (2016) Effect of addition of HPBCD on diuron adsorption–desorption, transport and mineralization in soils with different properties. Geoderma 265:196–203
Sánchez-Trujillo MA, Morillo E, Villaverde J, Lacorte S (2013) Comparative effects of several cyclodextrins on the extraction of PAHs from an aged contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 178:52–58
Shemer H, Sharpless CM, Linden KG (2005) Photodegradation of 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol in aqueous solution. Water Air Soil Pollut 168:145–155
Sinclair CJ, Boxall ABA, Parsons SA, Thomas MR (2006) Prioritization of pesticide environmental transformation products in drinking water supplies. Environ Sci Technol 40:7283–7289
Singh BK, Walker A (2006) Microbial degradation of organophosphorus compounds. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30:428–471
Sucahyo D, van Straalen NM, Krave A, van Gestel CA (2008) Acute toxicity of pesticides to the tropical freshwater shrimp Caridina laevis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 69:421–427
Sun M, Luo Y, Teng Y, Jia Z, Li Z, Deng S (2013) Remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and metal-contaminated soil by successive methyl-β-cyclodextrin-enhanced soil washing–microbial augmentation: a laboratory evaluation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:976–986
Tang T, Boenne W, Desmet N, Seuntjens P, Bronders J, van Griensven A (2015) Quantification and characterization of glyphosate use and loss in a residential area. Sci Total Environ 517:207–214
Tardioli PW, Zanin GM, de Moraes FF (2006) Characterization of Thermoanaerobacter cyclomaltodextrin glucanotransferase immobilized on glyoxyl-agarose. Enzym Microb Technol 39:1270–1278
Tomlin C (2006) The e-pesticide manual: a world compendium. 14th edition, version 4.0. British Crop Protection Council. Alton, pp 146, 150, 231, 574
Trellu C, Mousset E, Pechaud Y, Huguenot D, van Hullebusch ED, Esposito G, Oturan MA (2016) Removal of hydrophobic organic pollutants from soil washing/flushing solutions: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 306:149–174
US Environmental Protection Agency (1999). Reregistration eligibility decision (RED). Chlorothalonil, EPA738-R-99-004, Washington, DC
Villaverde J (2007) Time-dependent sorption of norflurazon in four different soils: use of beta-cyclodextrin solutions for remediation of pesticide-contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 142:184–190
Villaverde J, Posada-Baquero R, Rubio-Bellido M, Laiz L, Saiz-Jimenez C, Sanchez-Trujillo MA, Morillo E (2012) Enhanced mineralization of diuron using a cyclodextrin-based bioremediation technology. J Agric Food Chem 60:9941–9947
Villeneuve DL, Curtis LR, Jenkins JJ, Warner KE, Tilton F, Kent ML, Watral VG, Cunningham ME, Markle DF, Sethajintanin D, Krissanakriangkrai O, Johnson ER, Grove R, Anderson KA (2005) Environmental stresses and skeletal deformities in fish from the Willamette River. Oregon Environ Sci Technol 39:3495–3506
Wang H, Wang C, Chen F, Wang X (2011) Anaerobic degradation of chlorothalonil in four paddy soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1000–1005
Watts M (2012) Chlorpyrifos as a possible global persistent organic pollutant. Pesticide Action Network North America, Oakland
Wu XW, Cheng LY, Cao ZY, Yu YL (2012) Accumulation of chlorothalonil successively applied to soil and its effect on microbial activity in soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 81:65–69
Ye M, Sun M, Hu F, Kengara FO, Jiang X, Luo Y, Yang X (2014) Remediation of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) contaminated site by successive methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MCD) and sunflower oil enhanced soil washing—Portulaca oleracea L. cultivation. Chemosphere 105:119–125
Yu YL, Shan M, Fang H, Wang X, Chu XQ (2006) Responses of soil microorganisms and enzymes to repeated applications of chlorothalonil. J Agric Food Chem 54:10070–10075
Zeng Q-R, Tang H-X, Liao B-H, Zhong T, Tang C (2006) Solubilization and desorption of methyl-parathion from porous media: a comparison of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and two nonionic surfactants. Water Res 40:1351–1358
Zhang M, Teng Y, Xu Z, Wang J, Christie P, Luo Y (2016) Cumulative effects of repeated chlorothalonil application on soil microbial activity and community in contrasting soils. J. Soils Sediments 16:1754–1763
Acknowledgments
This study was financed by Project FONDECYT 1140327 from Comisión Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONICYT), Chile.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 528 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Báez, M.E., Espinoza, J., Silva, R. et al. Influence of selected cyclodextrins in sorption-desorption of chlorpyrifos, chlorothalonil, diazinon, and their main degradation products on different soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 20908–20921 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9652-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9652-7