Abstract
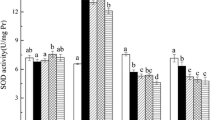
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are a class of man-made organic compounds ubiquitously present in the biosphere. In this study, we evaluated the toxic effects of different concentrations of PCBs in two natural soils (i.e. red soil and fluvo-aquic soil) on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. The parameters investigated included anti-oxidative response, genotoxic potential, weight variation and biochemical responses of the earthworm exposed to two different types of soils spiked with PCBs after 7 or 14 days of exposure. Earthworms had significantly lower weights in both soils after PCB exposure. PCBs significantly increased catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and guaiacol peroxidase (POD) activity in earthworms exposed to either soil type for 7 or 14 days and decreased the malondialdehyde (MDA) content in earthworms exposed to red soil for 14 days. Of the enzymes examined, SOD activity was the most sensitive to PCB stress. In addition, PCB exposure triggered dose-dependent coelomocyte DNA damage, even at the lowest concentration tested. This response was relatively stable between different soils. Three-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed that the weight variation, anti-oxidant enzyme activities, and MDA contents were significantly correlated with exposure concentration or exposure duration (P < 0.01). Furthermore, weight variation, CAT activity, and SOD activity were significantly affected by soil type (P < 0.01). Therefore, the soil type and exposure time influence the toxic effects of PCBs, and these factors should be considered when selecting responsive biomarkers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belmeskine H, Haddad S, Vandelac L, Sauvé S, Fournier M (2012) Toxic effects of PCDD/Fs mixtures on Eisenia andrei earthworms. Ecotox Environ Safe 80:54–59. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.02.008
Bonnard M, Devin S, Leyval C, Morel JL, Vasseur P (2010) The influence of thermal desorption on genotoxicity of multipolluted soil. Ecotox Environ Safe 73:955–960. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.02.023
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brown SAE, McKelvie JR, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2010) 1H-NMR metabolomics of earthworm exposure to sub-lethal concentrations of phenanthrene in soil. Environmen Pollut 158:2117–2123. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2010.02.023
Chen X, Wang XR, Gu XY, Jiang Y, Ji R (2017) Oxidative stress responses and insights into the sensitivity of the earthworms Metaphire guillelmi and Eisenia fetida to soil cadmium. Sci Total Environ 574:300–306. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.059
Coteur G, Danis B, Fowler SW, Teyssié JL, Dubois P, Warnau M (2001) Effects of PCBs on reactive oxygen species (ROS) production by the immune cells of Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata). Mar Pollut Bull 42(8):667–672. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00063-7
Delannoy M, Fournier A, Dan-Badjo AT, Schwarz J, Lerch S, Rychen G, Feidt C (2015) Impact of soil characteristics on relative bioavailability of NDL-PCBs in piglets. Chemosphere 139:393–401. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.06.098
DeRosa C, Richter P, Pohl H, Jones DE (1998) Environmental exposures that affect the endocrine system: public health implications. J Toxicol Env Heal B 1(1):3–26
Duan X, Xu L, Song J, Jiao JG, Liu MQ, Hu F, Li HX (2015) Effects of benzo[a]pyrene on growth, the antioxidant system, and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) in 2 different soil types under laboratory conditions. Environmen Toxicol Chem 34(2):283–290. doi:10.1002/etc.2785
Espinosa-Reyes G, Ilizaliturri CA, González-Mille DJ, Costilla R, Díaz-Barriga F, Cuevas MDC, Martínez MÁ, Mejía-Saavedra J (2010) DNA damage in earthworms (spp.) as an indicator of environmental stress in the industrial zone of Coatzacoalcos, Veracruz, Mexico. J Environ Sci Health A 45(1):49–55
Eyambe GS, Goven AJ, Fitzpatrick L, Venables BJ, Cooper EL (1991) A non-invasive technique for sequential collection of earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) leukocytes during subchronic immunotoxicity studies. Lab Anim-UK 25(1):61–67. doi:10.1258/002367791780808095
Gonzalez Flecha B, Repetto M, Evelson P, Boveris A (1991) Inhibition of microsomal lipid peroxidation by α-tocopherol and α-tocopherol acetate. Xenobiotica 21(8):1013–1022
González-Mille D, Ilizaliturri-Hernández C, Espinosa-Reyes G, Costilla-Salazar R, Díaz-Barriga F, Ize-Lema I, Mejía-Saavedra J (2010) Exposure to persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and DNA damage as an indicator of environmental stress in fish of different feeding habits of Coatzacoalcos, Veracruz, Mexico. Ecotoxicology 19(7):1238–1248. doi:10.1007/s10646-010-0508-x
Han C, Fang S, Cao H, Lu Y, Ma Y, Wei D, Xie X, Liu X, Li X, Fei D, Zhao C (2013) Molecular interaction of PCB153 to human serum albumin: insights from spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies. J Hazard Mater 248:313–321. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.12.056
Hao X, Ling Q, Hong F (2014) Effects of dietary selenium on the pathological changes and oxidative stress in loach (Paramisgurnus dabryanus). Fish physiol and biochem 40(5):1313–1323. doi:10.1007/s10695-014-9926-7
Hecker M, Murphy MB, Giesy JP, Hopkins WA (2006) Induction of cytochrome P4501A in African brown house snake (Lamprophis fuliginosus) primary hepatocytes. Environ Toxicol Chem 25(2):496–502. doi:10.1897/05-348R.1
Hofman J, Rhodes A, Semple KT (2008) Fate and behaviour of phenanthrene in the natural and artificial soils. Environmen Pollut 152(2):468–475. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.05.034
Hou H, Zhao L, Zhang J, Xu YF, Yan ZG, Bai LP, Li FS (2013) Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in soils surrounding the Tanggu Chemical Industrial District of Tianjin, China. Environmen Sci Pollut R 20(5):3366–3380. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-1260-y
Kavlock RJ, Daston GP, DeRosa C, FennerCrisp P, Gray LE, Kaattari S, Lucier G, Luster M, Mac MJ, Maczka C, Miller R, Moore J, Rolland R, Scott G, Sheehan DM, Sinks T, Tilson HA (1996) Research needs for the risk assessment of health and environmental effects of endocrine disruptors: a report of the US EPA-sponsored workshop. Environ Health Persp 104:715–740. doi:10.2307/3432708
Khan MI, Cheema SA, Tang X, Shen C, Sahi ST, Jabbar A, Park J, Chen Y (2012) Biotoxicity assessment of pyrene in soil using a battery of biological assays. Arch Environ Con Tox 63(4):503–512. doi:10.1007/s00244-012-9793-0
Koivula MJ, Eeva T (2010) Metal-related oxidative stress in birds. Environmen Pollu 158(7):2359–2370. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2010.03.013
Końca K, Lankoff A, Banasik A, Lisowska H, Kuszewski T, Góźdź S, Koza Z, Wojcik A (2003) A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 534(1–2):15–20. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(02)00251-6
Li YF, Harner T, Liu L, Zhang Z, Ren NQ, Jia H, Ma J, Sverko E (2010) Polychlorinated biphenyls in global air and surface soil: distributions, air-soil exchange, and fractionation effect. Environ Sci Technol 4(4):2784–2790 http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/es901871e
Li ZH, Li D, Ren JL, Wang LB, Yuan LJ, Liu YC (2012) Optimization and application of accelerated solvent extraction for rapid quantification of PCBs in food packaging materials using GC-ECD. Food Control 27(2):300–306. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.04.006
Liu S, Zhou Q, Wang Y (2011) Ecotoxicological responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to soil contaminated with HHCB. Chemosphere 83(8):1080–1086. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.01.046
Lokke H, Gestel CAMV (1998) Handbook of soil invertebrate toxicity tests. Wiley, New Jersey,
Marabini L, Calò R, Fucile S (2011) Genotoxic effects of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB 153, 138, 101, 118) in a fish cell line (RTG-2). Toxicol in Vitro 25(5):1045–1052. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2011.04.004
Martin-Diaz L, Franzellitti S, Buratti S, Valbonesi P, Capuzzo A, Fabbri E (2009) Effects of environmental concentrations of the antiepilectic drug carbamazepine on biomarkers and cAMP-mediated cell signaling in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat Toxicol 94(3):177–185. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.06.015
Mohebbi-Nozar SL, Ismail WR, Zakaria MP, Mortazavi MS, Zahed MA, Jahanlu A (2013) Health risk of PCBs and DDTs in seafood from Southern Iran. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 20(5):1164–1176. doi:10.1080/10807039.2013.838121
Mosleh YY, Paris-Palacios S, Couderchet M, Vernet G (2003) Effects of the herbicide isoproturon on survival, growth rate, and protein content of mature earthworms (Lumbricus terrestris) and its fate in the soil. Appl Soil Ecol 23(1):69–77. doi:10.1016/S0929-1393(02)00161-0
OECD (1984) Guideline for testing of chemicals
Parolini M, Pedriali A, Binelli A (2013) Chemical and biomarker responses for site-specific quality assessment of the Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy). Environ Sci Pollut R 20(8):5545–5557. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1556-6
Sanchez E, Santiago MF, Lopez-Aparicio P, Recio MN, Perez-Albarsanz MA (2000) Selective fatty acid release from intracellular phospholipids caused by PCBs in rat renal tubular cell cultures. Chem Biol Interact 125(2):117–131. doi:10.1016/S0009-2797(00)00142-3
Schmitt CJ, Whyte JJ, Roberts AP, Annis ML, May TW, Tillitt DE (2007) Biomarkers of metals exposure in fish from lead-zinc mining areas of Southeastern Missouri, USA. Ecotox Environ Safe 67(1):31–47. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.12.011
Sforzini S, Moore MN, Boeri M, Bencivenga M, Viarengo A (2015) Effects of PAHs and dioxins on the earthworm Eisenia andrei: a multivariate approach for biomarker interpretation. Environmen Pollut 196:60–71. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2014.09.015
Shi ZM, Xu L, Wang N, Zhang W, Li HX, Hu F (2013) Pseudo-basal levels of and distribution of anti-oxidant enzyme biomarkers in Eisenia fetida and effect of exposure to phenanthrene. Ecotox Environ Safe 95:33–38. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.05.009
Šmídová K, Hofman J (2014) Uptake kinetics of five hydrophobic organic pollutants in the earthworm Eisenia fetida in six different soils. J Hazard Mater 267:175–182. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.063
Song Y, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Liu W, Xie H (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by atrazine. Soil Biol Biochem 41(5):905–909. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.09.009
Teng YG, Li J, Wu J, Lu SJ, Wang YY, Chen HY (2015) Environmental distribution and associated human health risk due to trace elements and organic compounds in soil in Jiangxi province, China. Ecotox Environ Safe 122:406–416. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.09.005
Vlčková K, Hofman J (2012) A comparison of POPs bioaccumulation in Eisenia fetida in natural and artificial soils and the effects of aging. Environ Pollut 160:49–56. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2011.08.049
Wågman N, Strandberg B, Tysklind M (2001) Dietary uptake and elimination of selected polychlorinated biphenyl congeners and hexachlorobenzene in earthworms. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1778–1784. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2001)020<1778:DUAEOS>2.0.CO;2
Whitfield Åslund M, Simpson A, Simpson M (2011) H-1 NMR metabolomics of earthworm responses to polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) exposure in soil. Ecotoxicology 20(4):836–846. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0638-9
Wu S, Wu E, Qiu L, Zhong W, Chen J (2011) Effects of phenanthrene on the mortality, growth, and anti-oxidant system of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 83(4):429–434. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.082
Xue Y, Gu X, Wang X, Sun C, Xu X, Sun J, Zhang B (2009) The hydroxyl radical generation and oxidative stress for the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to tetrabromobisphenol A. Ecotoxicology 18(6):693–699. doi:10.1007/s10646-009-0333-2
Yang G, Chen C, Wang Y, Cai L, Kong X, Qian Y, Wang Q (2015) Joint toxicity of chlorpyrifos, atrazine, and cadmium at lethal concentrations to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut R 22(12):9307–9315. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4097-3
Zhang L, Qiu L, Wu H, Liu X, You L, Pei D, Chen L, Wang Q, Zhao J (2012) Expression profiles of seven glutathione S-transferase (GST) genes from Venerupis philippinarum exposed to heavy metals and benzo[a]pyrene. Comp Biochem Phys C 155(3):517–527. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2012.01.002
Zhang Q, Ye J, Chen J, Xu H, Wang C, Zhao M (2014) Risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in soils of an abandoned e-waste site in China. Environ Pollut 185:258–265. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2013.11.003
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 41371469), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYZ201626), Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (No. 201503121-01), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (No. 2016M591856), Anhui Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (No. 2015B057), Science and Technology Project of Anhui Province (1604a0702006), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD). We are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and Ms. Kathleen Farquharson for the language improvement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Markus Hecker
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
(DOC 113 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, X., Fu, X., Song, J. et al. Physiological and molecular responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida to polychlorinated biphenyl contamination in soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 18096–18105 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9383-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9383-9