Abstract
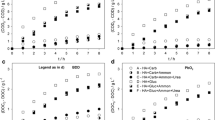
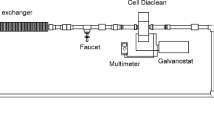
Electrochemical oxidation (ELOX) with boron-doped diamond (BDD) anodes was successfully applied to degrade a model aqueous solution of a mixture of commercial naphthenic acids (NAs). The model mixture was prepared resembling the NA and salt composition of oil sands process-affected water (OSPW) as described in the literature. The initial concentration of NAs between 70 and 120 mg/L did not influence the electrooxidation kinetics. However, increasing the applied current density from 20 to 100 A/m2 and the initial chloride concentration from 15 to 70 and 150 mg/L accelerated the rate of NA degradation. At higher chloride concentration, the formation of indirect oxidative species could contribute to the faster oxidation of NAs. Complete chemical oxygen demand removal at an initial NA concentration of 120 mg/L, 70 mg/L of chloride and applied 50 A/m2 of current density was achieved, and 85% mineralization, defined as the decrease of the total organic carbon (TOC) content, was attained. Moreover, after 6 h of treatment and independently on the experimental conditions, the formation of more toxic species, i.e. perchlorate and organochlorinated compounds, was not detected. Finally, the use of ELOX with BDD anodes produced a 7 to 11-fold reduction of toxicity (IC50 towards Vibrio fischeri) after 2 h of treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Pugliese CE, Marriaga-Cabrales N, Machuca-Martínez F (2014) A patent review of technologies for wastewater treatment by electrochemical oxidation with boron doped diamond electrodes. In: Peralta-Hernández JM, Rodrigo-Rodrigo MA, Martínez-Huitle CA (eds) Evaluation of electrochemical reactors as a new way to environmental protection. Research Signpost, India, pp 79–95
Anglada A, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I (2009a) Contributions of electrochemical oxidation to waste-water treatment: fundamentals and review of applications. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84(12):1747–1755. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2214
Anglada A, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I (2009b) Pilot scale performance of the electro-oxidation of landfill leachate at boron-doped diamond anodes. Environ Sci Technol 43(6):2035–2040. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802748c
Anglada A, Urtiaga AM, Ortiz I (2010) Laboratory and pilot plant scale study on the electrochemical oxidation of landfill leachate. J Hazard Mater 15:729–735
Anglada A, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I, Mantzavinos D, Diamadopoulos E (2011) Boron-doped diamond anodic treatment of landfill leachate: evaluation of operating variables and formation of oxidation by-products. Water Res 45(2):828–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.017
Bezerra-Rocha JH, Soares-Gomes MM, Nedja Suely-Fernandes N, Ribeiro da Silva D, Martínez-Huitle CA (2012) Application of electrochemical oxidation as alternative treatment of produced water generated by Brazilian petrochemical industry. Fuel Process Technol 96:80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.12.011
Cabeza A, Urtiaga AM, Ortiz I (2007) Electrochemical treatment of landfill leachates using a boron-doped diamond anode. Ind Eng Chem Res 46(5):1439–1446. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie061373x
Clemente JS, Fedorak PM (2005) A review of the occurrence, analyses, toxicity, and biodegradation of naphthenic acids. Chemosphere 60(5):585–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.065
Cotillas S, Martín de Vidales MJ, Llanos J, Sáez C, Cañizares P, Rodrigo MA (2016) Electrolytic and electro-irradiated processes with diamond anodes for the oxidation of persistent pollutants and disinfection of urban treated wastewater. J Hazard Mater 319:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.050
Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the quality of water intended for human consumption (1998) Official Journal of the European Communities OJ L 330 41: 32–54
Del Rio LF, Hadwin AKM, Pinto LJ, MacKinnon MD, Moore MM (2006) Degradation of naphthenic acids by sediment micro-organisms. J Appl Microbiol 101(5):1049–1061
Díaz V, Ibáñez R, Gómez P, Urtiaga AM, Ortiz I (2011) Kinetics of electro-oxidation of ammonia-N, nitrites and COD from a recirculating aquaculture saline water system using BDD anodes. Water Res 45(1):125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.020
Frank RA, Kavanagh R, Burnison BK, Arsenault G, Headley JV, Peru KM, Van Der Kraak G, Solomon KR (2008) Toxicity assessment of collected fractions from an extracted naphthenic acid mixture. Chemosphere 72(9):1309–1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.04.078
Gomez-Ruiz B, Gómez-Lavín S, Diban N, Boiteux V, Colin A, Dauchy X, Urtiaga A (2017a) Efficient electrochemical degradation of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) from the effluents of an industrial wastewater treatment plant. Chem Eng J 322:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.040
Gomez-Ruiz B, Gómez-Lavín S, Diban N, Boiteux V, Colin A, Dauchy X, Urtiaga A (2017b) Boron doped diamond electrooxidation of 6:2 fluorotelomers and perfluorocarboxylic acids. Application to industrial wastewaters treatment. J Electroanal Chem 798:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.05.033
Han X, MacKinnon MD, Martin JW (2009) Estimating the in situ biodegradation of naphthenic acids in oil sands process waters by HPLC/HRMS. Chemosphere 76(1):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.02.026
Holowenko FM, MacKinnon MD, Fedorak PM (2002) Characterization of naphthenic acids in oil sands wastewaters by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Water Res 36(11):2843–2855. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00492-4
Kannel PR, Gan TY (2013) Application of WASP for modelling and management of naphthenic acids along Athabasca River, Alberta, Canada. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1764-1
Khan MK, Riaz A, Yi M, Kim J (2017) Removal of naphthenic acids from high acid crude via esterification with methanol. Fuel Process Technol 165:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.05.015
Leshuk T, Livera DO, Peru KM, Headley JV, Vijayaraghavan S, Wong T, Gu F (2016a) Photocatalytic degradation kinetics of naphthenic acids in oil sands process-affected water: multifactorial determination of significant factors. Chemosphere 144:1854–1861
Leshuk T, Wong T, Linley S, Peru KM, Headley JV, Gua F (2016b) Solar photocatalytic degradation of naphthenic acids in oil sands process-affected water. Chemosphere 144:1854–1861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.10.073
Li C, Fu L, Stafford J, Belosevic M, Gamal El-Din M (2017) The toxicity of oil sands process-affected water (OSPW): a critical review. Sci Total Environ 601:1785–1802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.024
MacKinnon MD, Boerger H (1986) Description of two treatment methods for detoxifying oil sands tailings pond water. Water Pollut Res J Can 21:496–512
Marentette JR, Frank RA, Bartlett AJ, Gillis PL, Hewitt LM, Peru KM, Headley JV, Brunswick P, Shang D, Parrott JL (2015) Toxicity of naphthenic acid fraction components extracted from fresh and aged oil sands process-affected waters, and commercial naphthenic acid mixtures, to fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) embryos. Aquat Toxicol 164:108–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.04.024
Martín de Vidales MJ, Cotillas S, Perez-Serrano JF, Llanos J, Sáez C, Cañizares P, Rodrigo MA (2016) Scale-up of electrolytic and photoelectrolytic processes for water reclaiming: a preliminary study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:19713–19722
Martin JW, Barri T, Han X, Fedorak PM, Amalel-Din MG, Perez L, Scott AC, Jiang JT (2010) Ozonation of oil sands process-affected water accelerates microbial bioremediation. Environ Sci Technol 44(21):8350–8356. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101556z
Medel A, Bustos E, Esquivel K, Godínez LA, Meas Y (2012) Electrochemical incineration of phenolic compounds from the hydrocarbon industry using boron-doped diamond electrodes. Int J Photoenergy 2012, Article ID 681875, 6 pages. doi:https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/681875, 6
Meshref MNA, Klamerth N, Islam Md S, McPhedran KN, Gamal El-Din M (2017) Understanding the similarities and differences between ozone and peroxone in the degradation of naphthenic acids: comparative performance for potential treatment. Chemosphere 180:149–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.113
Panizza M, Michaud PA, Cerisola G, Comninellis C (2001) Anodic oxidation of 2-naphtol at boron doped diamond electrodes. J Electroanal Chem 507(1-2):206–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(01)00398-9
Pérez G, Saiz J, Ibañez R, Urtiaga AM, Ortiz I (2012) Assessment of the formation of inorganic oxidation by-products during the electrocatalytic treatment of ammonium from landfill leachates. Water Res 46(8):2579–2590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.02.015
Pourrezaei P, Alpatova A, Khosravi K, Drzewicz P, Chen Y, Chelme-Ayala P, Gamal El-Din M (2014) Removal of organic compounds and trace metals from oil sands process-affected water using zero valent iron enhanced by petroleum coke. J Environ Manag 139:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.03.001
Radjenovic J, Sedlak DL (2015) Challenges and opportunities for electrochemical processes as next-generation technologies for the treatment of contaminated water. Environ Sci Technol 49(19):11292–11302. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02414
Schaefer CE, Lavorgna GM, Webster TS, Deshusses MA, Andaya C, Urtiaga A (2017) Pilot-scale electrochemical disinfection of surface water: assessing disinfection by-product and free chlorine formation. Water Sci Tech Water Supply 17(2):526–536. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2016.165
Scott AC, Zubot W, MacKinnon MD, Smith DW, Fedorak PM (2008) Ozonation of oil sands process water removes naphthenic acids and toxicity. Chemosphere 71(1):156–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.10.051
Sohrabi V, Ross MS, Martin JW, Barker JF (2013) Potential for in situ chemical oxidation of acid extractable organics in oil sands process affected groundwater. Chemosphere 93(11):2698–2703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.08.072
Soriano A, Gorri D, Urtiaga A (2017) Efficient treatment of perfluorohexanoic acid by nanofiltration followed by electrochemical degradation of the NF concentrate. Water Res 112:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.043
Souza RBA, Ruotolo LAM (2013) Electrochemical treatment of oil refinery effluent using boron-doped diamond anodes. J Environm Chem Eng 1:544–551
Sprague JB, Ramsay BA (1965) Lethal levels of mixed copper-zinc solutions for juvenile salmon. J Fish Res Board Can 22(2):425–432. https://doi.org/10.1139/f65-042
Urtiaga A, Rueda A, Anglada A, Ortiz I (2009) Integrated treatment of landfill leachates including electrooxidation at pilot plant scale. J Hazard Mater 166(2-3):1530–1534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.037
Urtiaga A, Ortiz I, Anglada A, Mantzavinos D, Diamadopoulos E (2012) Kinetic modeling of the electrochemical removal of ammonium and COD from landfill leachates. J Appl Electrochem 54:779–786
Urtiaga AM, Pérez G, Ibáñez R, Ortiz I (2013) Removal of pharmaceuticals from a WWTP secondary effluent by ultrafiltration/reverse osmosis followed by electrochemical oxidation of the RO concentrate. Desalination 331:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.10.010
Urtiaga A, Fernández-Castro P, Gómez P, Ortiz I (2014a) Remediation of wastewaters containing tetrahydrofuran. Study of the electrochemical mineralization on BDD electrodes. Chem Eng J 239:341–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.11.028
Urtiaga A, Gómez P, Arruti A, Ortiz I (2014b) Electrochemical removal of tetrahydrofuran from industrial wastewaters: anode selection and process scale-up. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89(8):1243–1250. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4384
Urtiaga A, Fernández-González C, Gómez-Lavín S, Ortiz I (2015) Kinetics of the electrochemical mineralization of perfluorooctanoic acid on ultrananocrystalline boron doped conductive diamond electrodes. Chemosphere 129:20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.05.090
Wang C, Klamerth N, Messele SA, Singh A, Belosevic M, Gamal El-Din M (2013) Comparison of UV/hydrogen peroxide, potassium ferrate(VI), and ozone in oxidizing the organic fraction of oil sands process-affected water (OSPW). Water Res 100:476–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.037
WHO (2005) Chlorite and chlorate in drinking-water. Background document for preparation of WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organisation, Geneva (WHO/SDE/WSH/05.08/86)
Zhang Y, Klamerth N, Chelme-Ayala P, Gamal El-Din M (2017) Comparison of classical fenton, nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA)-Fenton, UV-Fenton, UV photolysis of Fe-NTA, UV-NTA-Fenton, and UV-H2O2 for the degradation of cyclohexanoic acid. Chemosphere 175:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.058
Acknowledgements
The financial support from the project CTM2016-75509-R (MINECO, Spain) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Angeles Blanco
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diban, N., Urtiaga, A. Electrochemical mineralization and detoxification of naphthenic acids on boron-doped diamond anodes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 34922–34929 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1124-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1124-6