Abstract
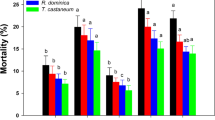
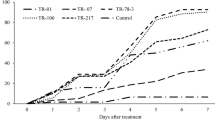
The stored grain insects cause great damage to grains under storage conditions. Synthetic insecticides and fumigants are considered as key measures to control these stored grain insect pests. However, the major issue with these chemicals is grain contamination with chemical residues and development of resistance by insect pests to these chemicals. Biological control is considered as a potential alternative to chemical control especially with the use of pathogens, alone or in combination with selective insecticides. The present study was conducted to evaluate the synergism of Metarhizium anisopliae with diatomaceous earth (DE) and thiamethoxam against four insect pests on the stored wheat grains. In the first bioassay, the M. anisopliae was applied at 1.4 × 104 and 1.4 × 106conidia/ml alone and in integration with two concentrations (250 and 500 ppm) of tested DE. The tested fungus when combined with DE and thiamethoxam possessed synergistic impact as compared to their individual efficacy. Adult mortality increased with respect to increased exposure interval and doses. In the second bioassay, M. anisopliae was applied at 1.4 × 104 conidia/ml individually and in combination with three concentrations (0.50, 0.75, and 1.00 ppm) of thiamethoxam. Results concluded that M. anisopliae integrated with DE and thiamethoxam provides more effective control of stored grain insect pests.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott W (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
Akbar W, Lord JC, Nechols JR, Howard RW (2004) Diatomaceous earth increases the efficacy of Beauveria bassiana against Tribolium castaneum larvae and increases conidia attachment. J Econ Entomol 97:273–280
Allen S (2000) Integration of inert dust into control of storage pests in bulk grain in storage in Australia. In: proceedings of the international conference controlled atmosphere and fumigation in stored products, Fresno, CA. pp 279–284
Arthur FH (2000) Toxicity of diatomaceous earth to red flour beetles and confused flour beetles (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae): effects of temperature and relative humidity. J Econ Entomol 93:526–532
Arthur FH, Yue B, Wilde GE (2004) Susceptibility of stored-product beetles on wheat and maize treated with thiamethoxam: effects of concentration, exposure interval, and temperature. J Stored Prod Res 40:527–546
Athanassiou C, Kavallieratos N (2005) Insecticidal effect and adherence of PyriSec® in different grain commodities. Crop Prot 24:703–710
Athanassiou CG, Kavallieratos NG, Vayias BJ, Tsakiri JB, Mikeli NH, Meletsis CM, Tomanović Ž (2008) Persistence and efficacy of Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschnikoff) Sorokin (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) and diatomaceous earth against Sitophilus oryzae (L.)(Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and Rhyzopertha dominica (F.)(Coleoptera: Bostrychidae) on wheat and maize. Crop Prot 27:1303–1311
Baier AH, Webster BD (1992) Control of Acanthoscelides obtectus Say (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in Phaseolus vulgaris L. seed stored on small farms—I. Evaluation of damage. J Stored Prod Res 28:289–293
Banks J, Fields P (1995) Physical methods for insect control in stored-grain ecosystems vol 353. Marcel Dekker, New York
Bittencourt SET, de Castro LA, Farias SE, Bao SN, Schrank A, Vainstein MH (2004) Purification and ultrastructural localization of a copper–zinc superoxide dismutase (CuZnSOD) from the entomopathogenic and acaricide fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Res Microbiol 155:681–687
Brito ES, de Paula AR, Vieira LP, Dolinski C, Samuels RI (2008) Combining vegetable oil and sub-lethal concentrations of Imidacloprid with Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae against adult guava weevil Conotrachelus psidii (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Biocontrol Sci Tech 18:665–673
Cherry A, Abalo P, Hell K (2005) A laboratory assessment of the potential of different strains of the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillemin and Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschnikoff) to control Callosobruchus maculatus (F.)(Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in stored cowpea. J Stored Prod Res 41:295–309
Dal Bello G, Padin S, Lastra CL, Fabrizio M (2000) Laboratory evaluation of chemical-biological control of the rice weevil (Sitophilus oryzae L.) in stored grains. J Stored Prod Res 37:77–84
Fields P, Korunic Z (2000) The effect of grain moisture content and temperature on the efficacy of diatomaceous earths from different geographical locations against stored-product beetles. J Stored Prod Res 36:1–13
Furlong M, Groden E (2001) Evaluation of synergistic interactions between the Colorado potato beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) pathogen Beauveria bassiana and the insecticides, imidacloprid, and cyromazine. J Econ Entomol 94:344–356
Garraway MO, Evans RC (1984) Fungal nutrition and physiology. In: Griffin DH (ed) Fungal Physiology. Wiley New York, p 104
Golob P (1997) Current status and future perspectives for inert dusts for control of stored product insects. J Stored Prod Res 33:69–79
Greenspan L (1977) Humidity fixed points of binary saturated aqueous solutions. J Res Nat Bur Standards 81:89–96
Hasan M, Ali Q, Zaman S, Rehman H (2016) Entomocidal effect of diatomaceous earth and thiamethoxam alone and in combination against Tribolium castaneum. Pp. 472–476. In: Navarro S, Jayas DS, Alagusundaram K, (Eds.) Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Controlled Atmosphere and Fumigation in Stored Products (CAF2016), CAF Permanent Committee Secretariat, Winnipeg
Jaramillo J, Borgemeister C, Ebssa L, Gaigl A, Tobón R, Zimmermann G (2005) Effect of combined applications of Metarhizium anisopliae (Metsch.) Sorokin (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) strain CIAT 224 and different dosages of imidacloprid on the subterranean burrower bug Cyrtomenus bergi Froeschner (Hemiptera: Cydnidae). Biol Control 34:12–20
Kassa A, Zimmermann G, Stephan D, Vidal S (2002) Susceptibility of Sitophilus zeamais (Motsch.)(Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and Prostephanus truncatus (Horn)(Coleoptera: Bostrichidae) to entomopathogenic fungi from Ethiopia. Biocontrol Sci Tech 12:727–736
Kavallieratos N et al (2006) Effect of the combined use of Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschinkoff) Sorokin and diatomaceous earth for the control of three stored-product beetle species. Crop Prot 25:1087–1094
Kavallieratos NG, Athanassiou CG, Vayias BJ, Mihail SB, Tomanović Ž (2009) Insecticidal efficacy of abamectin against three stored-product insect pests: influence of dose rate, temperature, commodity, and exposure interval. J Econ Entomol 102:1352–1359
Khashaveh A (2011) The use of entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. in assays with storage grain beetles J Agric Sci Tech 13
Korunic Z (1998) Review Diatomaceous earths, a group of natural insecticides. J Stored Prod Res 34:87–97
Lawson D, Dunbar D, White S, Ngo N (1999) Actara 25WG: control of cotton pests with a new Neonicotinoid insecticide, thiamethoxam. In: proceedings Beltwide cotton Conf. Memphis, Tenn. pp 1106–1109
Lord JC (2001) Desiccant dusts synergize the effect of Beauveria bassiana (Hyphomycetes: Moniliales) on stored-grain beetles. J Econ Entomol 94:367–372
Luz C, Rodrigues J, Rocha LF (2012) Diatomaceous earth and oil enhance effectiveness of Metarhizium anisopliae against Triatoma infestans. Acta Trop 122:29–35
Maienfisch P et al (2001) The discovery of thiamethoxam: a second-generation neonicotinoid. Pest Manag Sci 57:165–176
Menge D, Makobe M, Shomari S, Tiedemann AV (2013) Effect of environmental conditions on the growth of Cryptosporiopsis spp. causing leaf and nut blight on cashew (Anacardium occidentale Linn.) J Yeast Fung Res 4:12–20
Michalaki MP, Athanassiou CG, Kavallieratos NG, Batta YA, Balotis GN (2006) Effectiveness of Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschinkoff) Sorokin applied alone or in combination with diatomaceous earth against Tribolium confusum Du Val larvae: influence of temperature, relative humidity and type of commodity. Crop Prot 25:418–425
Minitab I (2000) MINITAB statistical software Minitab Release:13
Moore D, Lord JC, Smith S (2000) Pathogens. In: Subramanyam B, Hagstrum DW (eds) Alternatives to pesticides in stored-product IPM. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 193–227
Neves PM, Hirose E, Tchujo PT, Moino A Jr (2001) Compatibility of entomopathogenic fungi with neonicotinoid insecticides. Neotrop Entomol 30:263–268
Pimentel D (1991) World resources and food losses to pests Ecol Manag Food-industry Pests:5–12
Purwar J, Sachan G (2006) Synergistic effect of entomogenous fungi on some insecticides against Bihar hairy caterpillar Spilarctia obliqua (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Microbiol Res 161:38–42
Quintela ED, Mccoy CW (1997) Pathogenicity enhancement of Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana to first instars of Diaprepes abbreviatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) with sublethal doses of imidacloprid. Environ Entomol 26:1173–1182
Quintela ED, McCoy CW (1998) Synergistic effect of imidacloprid and two entomopathogenic fungi on the behavior and survival of larvae of Diaprepes abbreviatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in soil. J Econ Entomol 91:110–122
Ramakrishnan R, Suiter DR, Nakatsu CH, Humber RA, Bennett GW (1999) Imidacloprid-enhanced Reticulitermes flavipes (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) susceptibility to the entomopathogen Metarhizium anisopliae. J Econ Entomol 92:1125–1132
Riasat T, Wakil W, Ashfaq M, Sahi ST (2011) Effect of Beauveria bassiana mixed with diatomaceous earth on mortality, mycosis and sporulation of Rhyzopertha dominica on stored wheat. Phytoparasitica 39:325–331
Russell CW, Ugine TA, Hajek AE (2010) Interactions between imidacloprid and Metarhizium brunneum on adult Asian longhorned beetles (Anoplophora glabripennis (Motschulsky))(Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J Invertebr Pathol 105:305–311
Sabbour M, Abd-El-Aziz S, Sherief M (2012) Efficacy of three entomopathogenic fungi alone or in combination with diatomaceous earth modifications for the control of three pyralid moths in stored grains. J Plant Prot Res 52:359–363
Salunke B, Kotkar H, Mendki P, Upasani S, Maheshwari V (2005) Efficacy of flavonoids in controlling Callosobruchus chinensis (L.)(Coleoptera: Bruchidae), a post-harvest pest of grain legumes. Crop Prot 24:888–893
Shafighi Y, Ziaee M, Ghosta Y (2014) Diatomaceous earth used against insect pests, applied alone or in combination with Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana. J Plant Prot Res 54:62–66
Shakeel M et al. (2017) Environment polluting conventional chemical control compared to an environmentally friendly IPM approach for control of diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.), in China: a review Environ Sci Pol Res:14537–14550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8996-3
Sheeba G, Seshadri S, Raja N, Janarthanan S, Ignacimuthu S (2001) Efficacy of Beauveria bassiana for control of the rice weevil Sitophilus oryzae (L.)(Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Appl Entomol Zool 36:117–120
Subramanyam B, Roesli R (2000) Inert dusts. In: Alternatives to pesticides in stored-product IPM. Springer, pp 321–380
Tefera T, Pringle K (2003) Effect of exposure method to Beauveria bassiana and conidia concentration on mortality, mycosis, and sporulation in cadavers of Chilo partellus (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Invertebr Pathol 84:90–95
Timlick B, Fields P (2010) A comparison of the effect of two diatomaceous earth formulations on Plodia interpunctella (Hübner) and the effect of different commodities on diatomaceous earth efficacy. In: Carvalho OM et al. (eds) Proceedings of the10th international working conference on stored product protection, 27 June - 2 July, 2010, Estoril, Protugal, Julius-Kühn-Archiv, Berlin. pp 839–843
Ugine TA, Wraight SP, Brownbridge M, Sanderson JP (2005) Development of a novel bioassay for estimation of median lethal concentrations (LC50) and doses (LD50) of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana, against western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis. J Invertebr Pathol 89:210–218
Vandenberg JD (1992) Bioassay of the chalkbrood fungus Ascosphaera aggregata on larvae of the alfalfa leafcutting bee Megachile rotundata. J Invertebr Pathol 60:159–163
Vayias BJ, Athanassiou CG, Kavallieratos NG, Tsesmeli CD, Th Buchelos C (2006) Persistence and efficacy of two diatomaceous earth formulations and a mixture of diatomaceous earth with natural pyrethrum against Tribolium confusum Jacquelin du Val (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) on wheat and maize. Pest Manag Sci 62:456–464
Wakil W, Ghazanfar MU, Yasin M, Jung Kwon Y (2015) Efficacy of Metarhizium anisopliae combined with diatomaceous earth against Sitophilus oryzae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) under laboratory conditions Revista Colombiana de Entomología 41:81-86
Wakil W, Riasat T, Lord JC (2013) Effects of combined thiamethoxam and diatomaceous earth on mortality and progeny production of four Pakistani populations of Rhyzopertha dominica (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae) on wheat, rice and maize. J Stored Prod Res 52:28–35
Zhang L, Greenberg SM, Zhang Y, Liu TX (2011) Effectiveness of thiamethoxam and imidacloprid seed treatments against Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) on cotton. Pest Manag Sci 67:226–232
Acknowledgements
Author(s) are highly thankful to Muhammad Yasin, Muhammad Tahir and Abdul Qayyum for their contribution during course of study. Author(s) would also like to pay special tribute to Dr. Anjum Suhail (Late), Chairman, Department of Entomology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad for his passionate support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Our work confirms to the legal requirements of the country in which it was carried out.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashraf, M., Farooq, M., Shakeel, M. et al. Influence of entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae, alone and in combination with diatomaceous earth and thiamethoxam on mortality, progeny production, mycosis, and sporulation of the stored grain insect pests. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 28165–28174 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0383-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0383-6