Abstract
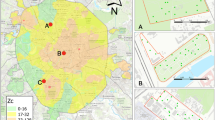
One super city leading and supported by surrounding smaller cities, towns, and countries is a typical regional development pattern in China. To study the metal enrichment differences in environment among these regions, 91 urban surface dust and rural surface soil samples were collected from Beijing center (BJC), Miyun town (MYT), and Miyun county (MYC). Cu and Sb concentrations in urban surface dust of BJC were much higher than the less crowded MYT which stood out as a good indicator for brake system wear. Cd, Cu, Hg, Pb, Sb, and Zn concentrations in urban surface dust were 1.48, 1.57, 2.73, 1.58, 6.20, and 1.98 times higher than rural surface soils on average, respectively. Aerosol sedimentation was shown to mainly contribute to Cd and Pb in urban surface dust in parks and forest soils. Hospitals and clinics were found to contribute much Hg to the surrounding environment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino O, Aceto M, Malandrino M, Mentasti E, Sarzanini C, Petrella F (2002) Heavy metals in agricultural soils from Piedmont, Italy. Distribution, speciation and chemometric data treatment. Chemosphere 49:545–557
Adachi K, Tainosho Y (2004) Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ Int 30:1009–1017
Al-Khashman OA (2007) The investigation of metal concentrations in street dust samples in Aqaba city, Jordan. Environ Geochem Health 29:197–207
Apeagyei E, Bank MS, Spengler JD (2011) Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban-rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmos Environ 45:2310–2323
Banerjee ADK (2003) Heavy metal levels and solid phase speciation in street dusts of Delhi, India. Environ Pollut 123:95–105
Beijing Statistics Bureau (2013) Beijing statistical yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Charlesworth S, Everett M, McCarthy R, Ordóñez A, de Miguel E (2003) A comparative study of heavy metal concentration and distribution in deposited street dusts in a large and a small urban area: Birmingham and Coventry, West Midlands, UK. Environ Int 29:563–573
Chen T, Zheng Y, Chen H (2004) Background concentrations of soil heavy metals in Beijing. Environ Sci 25:117–122 (in Chinese)
Chen X, Xia X, Zhao Y, Zhang P (2010) Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 181:640–646
Chester R, Stoner JH (1973) Pb in particulates from the lower atmosphere of the eastern Atlantic. Nature 245:27–28
China National Environmental Monitoring Center (1990) The Background Concentrations of Soil Elements of China. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Christoforidis A, Stamatis N (2009) Heavy metal contamination in street dust and roadside soil along the major national road in Kavala’s region, Greece. Geoderma 151:257–263
Davis AP, Shokouhian M, Ni S (2001) Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere 44:997–1009
Du Y, Gao B, Zhou H, Ju X, Hao H, Yin S (2013) Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Road Dusts in Urban Parks of Beijing, China. Procedia Environ Sci 18:299–309
Duong TTT, Lee B (2011) Determining contamination level of heavy metals in road dust from busy traffic areas with different characteristics. J Environ Manage 92:554–562
Erel Y, Veron A, Halicz L (1997) Tracing the transport of anthropogenic lead in the atmosphere and in soils using isotopic ratios. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 61:4495–4505
Ferreira-Baptista L, De Miguel E (2005) Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: a tropical urban environment. Atmos Environ 39:4501–4512
GB (1995) Soil environmental quality standard (GB15618-1995). (in Chinese)
Han Y, Du P, Cao J, Posmentier ES (2006) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci Total Environ 355:176–186
Hopke PK, Lamb RE, Natusch DFS (1980) Multielemental characterization of urban roadway dust. Environ Sci Technol 14:164–172
http://www.mlr.gov.cn/xwdt/jrxw/201404/t20140417_1312998.htm (reported by Ministry of land and resources of the People’s republic of China and Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s republic of China)
Kang J, Lee SW, Cho KH, Ki SJ, Cha SM, Kim JH (2010) Linking land-use type and stream water quality using spatial data of fecal indicator bacteria and heavy metals in the Yeongsan river basin. Water Res 44:4143–4157
Kim LH, Kayhanian M, Lau SL, Stenstrom MK (2005) A new modeling approach for estimating first flush metal mass loading. Water Sci Technol 51:159–167
Klaminder J, Farmer JG, MacKenzie AB (2011) The origin of lead in the organic horizon of tundra soils: Atmospheric deposition, plant translocation from the mineral soil or soil mineral mixing? Sci Total Environ 409:4344–4350
Lau WKY, Liang P, Man YB, Chung SS, Wong MH (2014) Human health risk assessment based on trace metals in suspended air particulates, surface dust, and floor dust from e-waste recycling workshops in Hong Kong, China. Ebviron Sci Pollut R 21:3813–3825
Li X, Poon C, Liu PS (2001) Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Appl Geochem 16:1361–1368
Li X, Liu L, Wang Y, Luo G, Chen X, Yang X, Hall MHP, Guo R, Wang H, Cui J, He X (2013a) Heavy metal contamination of urban soil in an old industrial city (Shenyang) in Northeast China. Geoderma 192:50–58
Li Z, Feng X, Li G, Bi X, Zhu J, Qin H, Dai Z, Liu J, Li Q, Sun G (2013b) Distributions, sources and pollution status of 17 trace metal/metalloids in the street dust of a heavily industrialized city of central China. Environ Pollut 182:408–416
Lu X, Wang L, Li LY, Lei K, Huang L, Kang D (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 173:744–749
Lu X, Zhang X, Li LY, Chen H (2014) Assessment of metals pollution and health risk in dust from nursery schools in Xi’an, China. Environ Res 128:27–34
Ma J, Singhirunnusorn W (2012) Distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface dusts of Maha Sarakham municipality. Procedia - Soci Behav\ Sci 50:280–293
Marković M, Cupać S, Đurović R, Milinović J, Kljajić P (2010) Assessment of heavy metal and pesticide levels in soil and plant products from agricultural area of Belgrade, Serbia. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:341–351
Micó C, Recatalá L, Peris M, Sánchez J (2006) Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 65:863–872
Niu J, Yang H, Bai D (2012) Exploration of the prevention for the mercury pollution in pharmaceutical industry. Chin Pharm Affairs 26:855–865 (in Chinese)
Robertson DJ, Taylor KG, Hoon SR (2003) Geochemical and mineral magnetic characterisation of urban sediment particulates, Manchester, UK. Appl Geochem 18:269–282
Rodríguez JA, Nanos N, Grau JM, Gil L, Lopez-Arias M (2008) Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in Spanish agricultural topsoils. Chemosphere 70:1085–1096
Romic M, Romic D (2003) Heavy metals distribution in agricultural topsoils in urban area. Environ Geol 43:795–805
Saeedi M, Li LY, Salmanzadeh M (2012) Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: pollution and ecological risk assessment in street dust of Tehran. J Hazard Mater 227–228:9–17
Shi C, Lin H, Ke Z, Jian X, Lan R (2007) Research about the contribution of medical industry sources to influent mercury of municipal wastewater. Res Environ Sci 20:129–132 (in Chinese)
Shi G, Chen Z, Xu S, Zhang J, Wang L, Bi C, Teng J (2008) Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environ Pollut 156:251–260
Smolders E, Degryse F (2002) Fate and effect of zinc from tire debris in soil. Environ Sci Technol 36:3706–3710
Sternbeck J, Sjödin Å, Andréasson K (2002) Metal emissions from road traffic and the influence of resuspension—results from two tunnel studies. Atmos Environ 36:4735–4744
Stigliani WM, Doelman P, Salomons W, Schulin R, Smidt GR, Van der Zee SEAT (1991) Chemical time bombs: predicting the unpredictable. Environment: Science and Policy for Sustainable Development 33:4–30
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ Geol 39:611–627
Wong SC, Li XD, Zhang G, Qi SH, Min YS (2002) Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Pollut 119:33–44
Xiang L, Li Y, Yang Z, Shi J (2010) Seasonal difference and availability of heavy metals in street dust in Beijing. J Environ Sci Health A 45:1092–1100
Yu Y, Li Y, Shen Z, Yang Z, Mo L, Kong Y, Lou I (2014) Occurrence and possible sources of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) along the Chao River, China. Chemosphere 114:136–143
Zahran S, Laidlaw MAS, McElmurry SP, Filippelli GM, Taylor M (2013) Linking source and effect: resuspended soil lead, air lead, and children’s blood lead levels in Detroit, Michigan. Environ Sci Technol 47:2839–2845
Zhang J, Deng H, Wang D, Chen Z, Xu S (2013) Toxic heavy metal contamination and risk assessment of street dust in small towns of Shanghai suburban area, China. Environ Sci Pollut R 20:323–332
Zhao H, Li X (2013) Risk assessment of metals in road-deposited sediment along an urban–rural gradient. Environ Pollut 174:297–304
Žibret G, Rokavec D (2010) Household dust and street sediment as an indicator of recent heavy metals in atmospheric emissions: a case study on a previously heavily contaminated area. Environ Earth Sci 61:443–453
Žibret G (2012) Impact of dust filter installation in ironworks and construction on Brownfield area on the toxic metal concentration in street and house dust (Celje, Slovenia). Ambio 41:292–301
Žibret G, Van Tonder D, Žibret L (2013) Metal content in street dust as a reflection of atmospheric dust emissions from coal power plants, metal smelters, and traffic. Environ Sci Pollut R 20:4455–4468
Zoller WH, Gladney ES, Duce RA (1974) Atmospheric concentrations and sources of trace metals at the South Pole. Science 183:198–200
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation for Innovative Research Group (Grant. 51121003), the National Science Foundation of China (Grant 51278054), and the FST Short Term PD & VF Scheme 2013 and MYRG072(Y1-L2)-FST13-LIC from University of Macao. The authors are grateful for the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Céline Guéguen
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Yu, Y., Yang, Z. et al. A comparison of metal distribution in surface dust and soil among super city, town, and rural area. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 7849–7860 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5911-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5911-7