Abstract
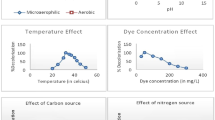
Aeromonas veronii GRI (KF964486), isolated from acclimated textile effluent after selective enrichment on azo dye, was assessed for methyl orange biodegradation potency. Results suggested the potential of this bacterium for use in effective treatment of azo-dye-contaminated wastewaters under static conditions at neutral and alkaline pH value, characteristic of typical textile effluents. The strain could tolerate higher doses of dyes as it was able to decolorize up to 1000 mg/l. When used as microbial surfactant to enhance methyl orange biodecolorization, Bacillus subtilis SPB1-derived lipopeptide accelerated the decolorization rate and maximized slightly the decolorization efficiency at an optimal concentration of about 0.025 %. In order to enhance the process efficiency, a Taguchi design was conducted. Phytotoxicity bioassay using sesame and radish seeds were carried out to assess the biotreatment effectiveness. The bacterium was able to effectively decolorize the azo dye when inoculated with an initial optical density of about 0.5 with 0.25 % sucrose, 0.125 % yeast extract, 0.01 % SPB1 biosurfactant, and when conducting an agitation phase of about 24 h after static incubation. Germination potency showed an increase toward the nonoptimized conditions indicating an improvement of the biotreatment. When comparing with synthetic surfactants, a drastic decrease and an inhibition of orange methyl decolorization were observed in the presence of CTAB and SDS. The nonionic surfactant Tween 80 had a positive effect on methyl orange biodecolorization. Also, studies ensured that methyl orange removal by this strain could be due to endocellular enzymatic activities. To conclude, the addition of SPB1 bioemulsifier reduced energy costs by reducing effective decolorization period, biosurfactant stimulated bacterial decolorization method may provide highly efficient, inexpensive, and time-saving procedure in treatment of textile effluents.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadulla E, Tzanov T, Costa S, Robra KH, Cavaco-Paulo A, Gubitz GM (2000) Decolourization and detoxification of textile dyes with a laccase from Trametes hirsute. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3357–3362
Adedayo O, Javadpour S, Taylor C, Anderson WA, Moo-Young M (2004) Decolourization and detoxification of methyl red by aerobic bacteria from a wastewater treatment plant. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:545–550
An S-Y, Min S-K, Cha I-H, Choi Y-L, Cho Y-S, Kim C-H, Lee Y-C (2002) Decolorization of triphenylmethane and azo dyes by Citrobacter sp. Biotechnol Lett 24:1037–1040
Arun Prasad AS, Bhaskara Rao KV (2012) Aerobic biodegradation of Azo dye by Bacillus cohnii MTCC 3616; an obligately alkaliphilic bacterium and toxicity evaluation of metabolites by different bioassay systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4492-3
Asad S, Amoozegar MA, Pourbabaee AA, Sarbolouki MN, Dastgheib SMM (2007) Decolorization of textile azo dyes by newly isolated halophilic and halotolerant bacteria. Bioresour Technol 98:2082–2088
Ayed L, Khelifi E, Ben Jannet H, Miladi H, Cheref A, Achour S, Bakhrouf A (2010) Response surface methodology for decolorization of azo dye methyl orange by bacterial consortium: produced enzymes and metabolites characterization. Chem Eng J 165:200–208
Ayed L, Mahdhi A, Cheref A, Bakhrouf A (2011) Decolorization and degradation of azo dye methyl red by an isolated Sphingomonas paucimobilis: biotoxicity and metabolites characterization. Desalination 274:272–277
Bautista FL, Sanz R, Molina MC, Gonzalez N, Sanchez D (2009) Effect of different non-ionic surfactants on the biodegradation of PAHs by diverse aerobic bacteria. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63:913–922
Ben Mansour H, Boughzala O, Dridi D, Barillier D, Chekir-Ghedira L, Mosrati R (2011a) Les colorants textiles sources de contamination de l’eau : criblage de la toxicité et des méthodes de traitement. J Water Sci 24(3):209–238
Ben Mansour H, Mechri B, Ayed-Ajmi Y, Ghedira K, Barillier D, Hammami M, Mosrati R, Chekir L (2011b) Treatment of Olive Mill wastewaters by Pseudomonas putida mt-2: toxicity assessment of the untreated and treated effluent. Environ Eng Sci 28(12):835–841
Ben Mansour H, Mosrati R, Ghedira K, Chekir L (2011c) Decolorization of textiles finishing wastewater by Pseudomonas putida: toxicity assessment. Environ Eng Sci. doi:10.1089/ees.2010.0225
Ben Mansour H, Dellai A, Ayed Y (2012) Toxicities effects of pharmaceutical, olive mill and textile wastewaters before and after degradation by Pseudomonas putida mt-2. Cancer Cell Int 12(4):1–4
Bhatt N, Patel KC, Keharia H, Madamwar D (2005) Decolorization of diazo-dye Reactive Blue 172 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa NBAR12. J Basic Microbiol 45:407–418
Carmen Z, Daniela S (2012) Textile organic dyes – characteristics, polluting effects and separation/elimination procedures from industrial effluents – a critical overview. organic pollutants ten years after the stockholm convention - environmental and analytical update, Dr. Tomasz Puzyn (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-307-917-2, In Tech
Champagne P-P, Nesheim ME, Ramsay JA (2010) Effect of a non-ionic surfactant, Merpol, on dye decolorization of Reactive blue 19 by laccase. Enzym Microb Technol 46:147–152
Chou DK, Krishnamurthy R, Randolph TW, Carpenter JF, Manning MC (2005) Effects of Tween 20 and Tween 80 on the stability of Albutropin during agitation. J Pharm Sci 94(6):1368–1381
Das SK, Shome I, Guha AK (2012) Biotechnological potential of soil isolate, Flavobacterium mizutaii for removal of azo dyes: kinetics, isotherm, and microscopic study. Sep Sci Technol 47:1913–1925
Dawkar VV, Jadhav UU, Jadhav SU, Govindwar SP (2008) Biodegradation of disperse textile dye Brown 3REL by newly isolated Bacillus sp VUS. J Appl Microbiol 105:14–24
Dayeh VR, Chow SL, Schirmer K, Bols NC (2004) Evaluating the toxicity of Triton X-100 to protozoan, fish, and mammalian cells using fluorescent dyes as indicators of cell viability. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 57:375–382
Erden E, Kaymaz Y, Pazarlioglu NK (2011) Biosorption kinetics of a direct azo dye Sirius Blue K-CFN by Trametes versicolor. Elect J Biotechnol 14 (2)
Franciscon E, Grossman MJ, Rizzato Paschoal JA, Reyes Reyes FG, Durrant LR (2012) Decolorization and biodegradation of reactive sulfonated azo dyes by a newly isolated Brevibacterium sp. strain VN-15. Springer Plus 1:2–10
Ghodake G, Jadhav U, Tamboli D, Kagalkar A, Govindwar S (2011) Decolorization of textile dyes and degradation of mono-azo dye Amaranth by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus NCIM 2890. Indian J Microbiol 51:501–508
Ghribi D, Abdelkefi-Mesrati L, Mnif I, Kammoun R, Ayadi I, Saadaoui I, Maktouf S, Chaabouni-Ellouze S (2012) Investigation of antimicrobial activity and statistical optimization of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant production in solid-state fermentation. J Biomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1155/2012/373682
Gopalakrishnan R, Sellappa S (2011) Decolourisation of methyl orange and methyl red by live and dead biomass of fungi. Asian J Exp Biol Sci 2(4):569–574
Gopinath SM, Kalleshappa TK, Narasimhamurthy TP, Ashwinipathil GM (2013) Isolation and screening of fungi for decolourization of azo dye. Int J Res Sci Technol 2(2):95–97
Gul UD, Donmez G (2010) Effect of a cationic surfactant on dye biosorption properties of Aspergillus versicolor, Communications de la Faculté des Sciences de l'Université d'Ankara, Séries C 22:1–13
Gul UD, Donmez G (2011) Effect of surfactants on Remazol Blue bioremoval capacity of Rhizopus Arrhizus strain growing in molasses medium. Fresenius Environ Bull 20:2677–2683
Gül UD, Dönmez G (2012) Effects of dodecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide surfactant on decolorization of Remazol Blue by a living Aspergillus versicolor strain. J Surfactant Deterg 15:797–803
Hadibarata T, Adnan LA, MohdYusoff AR, Yuniarto A, Meor R, Ahmad Zubir MF, Khudhair AB, Teh ZC, Naser MA (2013) Microbial decolorization of an azo dye reactive black 5 using white-rot fungus Pleurotus eryngii F032. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1595
Hakimelahi M, Moghaddam MRA, Hashemi SH (2012) Biological treatment of wastewater containing an azo dye using mixed culture on alternating anaerobic/aerobic sequencing batch reactors. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 17:875–880
Hayasen N, Kouno K, Ushio K (2000) Isolation and characterization of Aeromonas sp. B-5 capable of decolorizing various dyes. J Biosci Bioeng 90:570–573
Helle SS, Duff JBS, Cooper DG (1993) Effect of surfactants on cellulosehydrolysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 42:611–617
Hsueh C-C, Chen B-Y, Yen C-Y (2009) Understanding effects of chemical structure on azo dye decolorization characteristics by Aeromonas hydrophila. J Hazard Mater 167:995–1001
Jadhav DJP, Parshetti GK, Kalme SD, Govindwar SP (2007) Decolourization of azo dye methyl red by Saccharomyces cerevisiae MTCC 463. Chemosphere 68:394–400
Jadhav M, Kalme S, Tamboli D, Govindwar S (2011) Rhamnolipid from Pseudomonas desmolyticum NCIM-2112 and its role in the degradation of Brown 3REL. J Basic Microbiol 51:385–396
Ji G, Zhang H, Huang F, Huang X (2009) Effects of nonionic surfactant Triton X-100 on the laccase-catalyzed conversion of bisphenol A. J Environ Sci 21:1486–1490
Joshi T, Iyengar I, Singh K, Garg S (2008) Isolation, identification and application of novel bacterial consortium TJ-1 for the decolourization of structurally different azo dyes. Bioresour Technol 99:7115–7121
Junnarkar N, Srinivas Murty D, Bhatt NS, Madamwar D (2006) Decolorization of diazo dye Direct Red 81 by a novel bacterial consortium. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:163–168
Kalme SD, Parshetti GK, Jadhav SU, Govindwar SP (2007) Biodegradation of benzidine based dye Direct Blue-6 by Pseudomonas desmolyticum NCIM 2112. Bioresour Technol 98:1405–1410
Kang SW, Kim YB, Shin JD, Kim EK (2010) Enhanced biodegradation of hydrocarbons in soil by microbial biosurfactant, sophorolipid. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:780–790
Kapadia Sanket G, Yagnik BN (2013) Current trend and potential for microbial biosurfactants. Asian J Exp Biol Sci 4:1–8
Kristensen JB, Borjesson J, Bruun MH, Tjerneld F, Jørgensen H (2007) Use of surface active additives in enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat straw lignocellulose. Enzym Microb Technol 40:888–895
Kumar Praveen GN, Sumangala KB (2012) Fungal degradation of azo dye- red 3bn and optimization of physico-chemical parameters. J Biol Sci 1(2):17–24
Kumar A, Bisht BS, Joshi VD, Dhewa T (2011) Review on bioremediation of polluted environment: a management tool. Int J Environ Sci 1(6):1079–1093
Lade SH, Waghmode TR, Kadam AA, Govindwar SP (2012) Enhanced biodegradation and detoxification of disperse azo dye rubine gfl and textile industry effluent by defined fungal-bacterial consortium. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 72:94–107
Liang Y-S, Yuan X-Z, Zeng G-M, Hu C-L, Zhong H, Huang D-L, Tang L, Zhao J-J (2010) Biodelignification of rice straw by Phanerochaete chrysosporium in the presence of dirhamnolipid. Biodegradation. doi:10.1007/s10532-010-9329-0
Liu J, Yuan X, Zeng G, Shi J, Chen S (2006) Effect of biosurfactant on cellulase and xylanase production by Trichoderma viride in solid substrate fermentation. Process Biochem 41:2347–2351
Liu X-L, Zeng G-M, Tang L, Zhong H, Wang R-Y, Fu H-Y, Liu Z-F, H-l H, Zhang J-C (2008) Effects of dirhamnolipid and SDS on enzyme production by Phanerochaete chrysosporium in submerged fermentation. Process Biochem 43:1300–1303
Liu Z-F, Zeng G-M, Zhong H, Yuan X-Z, Fu H-Y, Zhou M-F, Ma X-L, Li H, Li J-B (2012) Effect of dirhamnolipid on the removal of phenol catalyzed by laccase in aqueous solution. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:175–181
Mnif I, Ghribi D (2015) Lipopeptides biosurfactants main classes and new insights for industrial; biomedical and environmental applications. Biopolymers: Pept Sci. doi:10.1002/bip.22630
Mnif I, Ellouze-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2012a) Response surface methodological approach to optimize the nutritional parameters for enhanced production of lipopeptide biosurfactant in submerged culture by B. subtilis SPB1. J Adv Sci Res 3(1):87–94
Mnif I, Ellouze-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2012b) Economic production of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant using local agro-industrial wastes and its application in enhancing solubility of diesel. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88(5):779–787
Mnif I, Sahnoun R, Ellouze-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2013) Evaluation of B. subtilis SPB1 biosurfactants' potency for diesel-contaminated soil washing: optimization of oil desorption using Taguchi design. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1894-4
Mnif I, Ayedi Y, Ellouze-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2014) Treatment of diesel- and kerosene-contaminated water by B. subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant-producing strain. Water Environ Res 86(8):707–716
Mnif I, Mnif S, Sahnoun R, Ayedi Y, Ellouze-Chaabouni S, Ghribi D (2015) Biodegradation of diesel oil by a novel microbial consortium: comparison between co-inoculation with biosurfactant-producing strain and exogenously added biosurfactants. Env Sci Pollut Res
Moosvi S, Keharia H, Madamwar D (2005) Decolourization of textile dye Reactive Violet 5 by a newly isolated bacterial consortium RVM 11.1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:667–672
Moosvi S, Kher X, Madamwar D (2007) Isolation, characterization and decolorization of textile dyes by a mixed bacterial consortium JW-2. Dyes Pigments 74:723–729
Mukerjee P, Mysels KJ (1971) Critical micelle concentration of aqueous surfactant systems. NSRDS-NBS 36. US. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C
Ogugbue CJ, Sawidis T, Oranusi NA (2012) Bioremoval of chemically different synthetic dyes by Aeromonas hydrophila in simulated wastewater containing dyeing auxiliaries. Ann Microbiol 62:1141–1153
Owsianiak M, Chrzanowski L, Szulc A, Staniewski J, Olszanowski A, Olejnik-Schmidt AK, Heipieper HJ (2009) Biodegradation of diesel/biodiesel blends by a consortium of hydrocarbon degraders: effect of the type of blend and the addition of biosurfactants. Bioresour Technol 100:1497–1500
Parra E, Moleiro LH, López-Montero I, Cruz A, Monroy F, Pérez-Gil J (2011) A combined action of pulmonary surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C modulates permeability and dynamics of phospholipid membranes. Biochem J 438:555–564
Parshetti GK, Kalme SD, Gomare SS, Govindwar SP (2007) Biodegradation of reactive blue-25 by Aspergillus ochraceus NCIM-1146. Bioresour Technol 98:3638–3642
Parshetti GK, Telke AA, Kalyani DC, Govindwar SP (2010) Decolorization and detoxification of sulfonated azo dye methyl orange by Kocuria rosea MTCC 1532. J Hazard Mater 176:503–509
Pavlic Z, Cifrek ZV, Puntaric D (2005) Toxicity of surfactants to green microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata and Scenedesmus subspicatus and to marine diatoms Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Skeletonema costatum. Chemosphere 61:1061–1068
Peace Stuart G (1995) Taguchi methods, a hands-on approach to quality engineering. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Reading
Phadke MS (1989) Quality engineering using robust design. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Radhakrishin JS, Saraswati PN (2015) Microbial decolorization of methyl orange by Klebsiella spp. DA26. Int J Res Biosci 4(3):29–38
Ratna Padhi BS (2012) Pollution due to synthetic dyes toxicity & carcinogenicity studies and remediation. Int J Environ Sci 3(3):940–955
Ren S, Guo J, Zeng G, Sun G (2006) Decolorization of triphenylmethane, azo, and anthraquinone dyes by a newly isolated Aeromonas hydrophila strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:1316–1321
Ruta IG, Juozas K (2013) Effects of rhamnolipid biosurfactant JBR425 and synthetic surfactant Surfynol465 on the peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of 2-naphthol. J Environ Sci 25(7):1431–1440
Saeki H, Sasaki M, Komatsu K, Miura A, Matsuda H (2009) Oil spill remediation by using the remediation agent JE1058BS that contains a biosurfactant produced by Gordonia sp. strain JE-1058. Bioresour Technol 100:572–577
Salihu A, Abdulkadir I, Almustapha MN (2009) An investigation for potential development on biosurfactants. Biotechnol Mol Biol Rev 4:111–117
Saratale RG, Saratale GD, Chang JS, Govindwar SP (2011) Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: a review. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 42(1):138–157
Seesuriyachan P, Takenaka S, Kuntiya A, Klayraung S, Murakami S, Aoki K (2007) Metabolism of azo dyes by Lactobacillus casei TISTR 1500 and effects of various factors on decolorization. Water Res 41:985–992
Selvam K, Shanmuga Priya M (2012) Biological treatment of Azo dyes and textile industry effluent by newly isolated White rot fungi Schizophyllum commune and Lenzites eximia. Int J Environ Sci 2
Seyis I, Subasioglu T (2008) Comparison of live and dead biomass of fungi on decolorization of methyl orange. Afr J Biotechnol 7(13):2212–2216
Shah MP (2014) Isolation and screening of dye decolorizing bacteria. J Appl Environ Microbiol 2(5):244–248
Shah MP, Patel KA, Nair SS, Darji AM (2013a) Microbial decolorization of methyl orange dye by Pseudomonas spp ETL-M. Int J Environ Bioremed Biodegrad 1(2):54–59
Shah MP, Patel KA, Nair SS, Darji AM (2013b) Selection of bacterial strains efficient in decolourisation of Remazol Black-B. Open Access Biotechnol 2:14
Shah MP, Patel KA, Nair SS, Darji AM, Maharaul S (2013c) Exploiting Application of Pseudomonas spp. ETL-2013 in microbial degradation and decolorization of disperse orange. J Bioremed Biodegrad 4:6
Sharma S, Saxena R, Gaur G (2014) Study of removal techniques for azo dyes by biosorption: a review. J Appl Chem 7(10):06–21
Shedbalkar U, Jadhav JP (2011) Detoxification of malachite green and textile industrial effluent by Penicillium ochrochloron. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 16(1):196–204
Shoeb E, Akhlaq F, Badar U, Akhter J, Imtiaz S (2013) Classification and industrial applications of biosurfactants. Part-I: Nat Appl Sci 4(3):243–252
Solis M, Solis A, Perez HI, Mnjarrez N, Flores M (2012) Microbial decolouration of azo dyes: a review. Process Biochem 47:1723–1748
Tantiwa N, Seesuriyachan P, Kuntiya A (2013) Strategies to decolorize high concentrations of methyl orange using growing cells of Lactobacillus casei TISTR 1500. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77(10):2030–2037
Tastan BE, Ertugrul S, Donmez G (2010) Effective bioremoval of reactive dye and heavy metals by Aspergillus versicolor. Bioressour Technol 101:870–876
Tehrani-Bagha R, Holmberg K (2013) Solubilization of hydrophobic dyes in surfactant solutions. Mater 6:580–608
Umesh UJ, Vishal VD, Gajanan SG, Sanjay PG (2008) Biodegradation of Direct Red 5B, a textile dye by newly isolated Comamonas sp UVS. J Hazard Mater 158:507–516
Urum K, Pekdemir T, Gopur M (2003) Optimum conditions for washing of contaminated soil with biosurfactant solutions. Inst Chem Eng 81(3):203–209
Vaidyanathan S, Orr BG, Banaszak Holl MM (2014) Detergent Induction of HEK 293A cell membrane permeability measured under quiescent and superfusion conditions using whole cell patch clamp. J Phys Chem B 118:2112–2123
Yaofeng W (2009) Encapsulation of myoglobin in a cetyl trimethylammonium bromide micelle in vacuo: a simulation study. Biochemistry 48(5):1006–1015
Zeng G-M, Shi J-G, Yuan X-Z, Liu J, Zhang Z-B, Huang G-H, Li J-B, Xi B-D, Liu H-L (2006) Effects of Tween 80 and rhamnolipid on the extracellular enzymes of Penicillium simplicissimum isolated from compost. Enz Microbial Technol 39:1451–1456
Zhang Q, He G, Wang J, Cai W, Xu Y (2009) Mechanisms of the stimulatory effects of rhamnolipid biosurfactant on rice straw hydrolysis. Appl Energy 86:233–237
Zhang Y, Zeng Z, Zeng G, Liud X, Liu Z, Chen M, Liu L, Lie J, Xie G (2012) Effect of Triton X-100 on the removal of aqueous phenol by laccase analyzed with a combined approach of experiments and molecular docking. Colloids Surf B 97:7–12
Zhou M-F, Yuan X-Z, Zhong H, Liu Z-F, Li H, Jiang L-L, Zeng GM (2011) Effect of biosurfactants on laccase production and phenol biodegradation in solid-state fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 164:103–114
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by grants from the “Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research and Technology.”
Ethical statement
The experimental protocols were conducted in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals issued by the University of Sfax, Tunisia, and approved by the Tunisia Committee of Animal Ethics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mnif, I., Maktouf, S., Fendri, R. et al. Improvement of methyl orange dye biotreatment by a novel isolated strain, Aeromonas veronii GRI, by SPB1 biosurfactant addition. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 1742–1754 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5294-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5294-9