Abstract
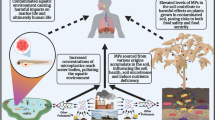
The effects of two formulations (emulsifiable concentrate (EC) and granule (G)) on the distribution, degradation, sorption, and residue risk of chlorpyrifos (CHP) were investigated in two producing areas of bamboo shoot. The results showed that CHP was mainly distributed in the topsoil (0–5 cm, P < 0.05), with the proportion of CHP in the total quantity ranging from 76.0 to 100.0 % (G) and 12.0 to 98.1 % (EC), respectively. The degradation of CHP-EC in soils (half-life 27.7–36.4 days) was faster than that of CHP-G in soils (half life above 120–150 days). The main metabolite of CHP, 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol (TCP), was found in soil samples. CHP showed good sorption ability in the two tested soils, with the sorption coefficient (KF) of 43.76 and 94.43 mg/kg. The terminal residues of CHP in bamboo shoots were in the range of 15.2–75.6 (G) and 10.4–35.7 μg/kg (EC), respectively. The soil type had a notable effect on the CHP behaviors in soil (P < 0.05, especially for CHP-G), but it did not affect the metabolite of CHP. Although some positive bamboo shoot samples (CHP residue exceeding maximum residue limits) were found, the hazard quotients did not exceed 7 %, which meant there was a negligible risk associated with the exposure to CHP via the consumption of bamboo shoots.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alekseeva T, Kolyagin Y, Sancelme M, Besse-Hoggan P (2014) Effect of soil properties on pure and formulated mesotrione adsorption onto vertisol (Limagne plane, Puy-de-Dome, France). Chemosphere 111:177–183
Alvarez M, du Mortier C, Cirelli AF (2013) Behavior of Insecticide Chlorpyrifos on Soils and Sediments with Different Organic Matter Content from Provincia de Buenos Aires, Republica Argentina. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1453–1459
Awasthi MD, Prakash NB (1997) Persistence of chlorpyrifos in soils under different moisture regimes. Pestic Sci 50:1–4
Bending GD, Lincoln SD, Edmondson RN (2006) Spatial variation in the degradation rate of the pesticides isoproturon, azoxystrobin and diflufenican in soil and its relationship with chemical and microbial properties. Environ Pollut 139:279–287
Berenstein GA, Hughes EA, March H, Rojic G, Zalts A, Montserrat JM (2014) Pesticide potential dermal exposure during the manipulation of concentrated mixtures at small horticultural and floricultural production units in Argentina: the formulation effect. Sci Total Environ 472:509–516
Brun EM, Garces-Garcia M, Puchades R, Maquieira AN (2005) Highly sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for chlorpyrifos. Application to olive oil analysis. J Agric Food Chem 53:9352–9360
Chen LZ, Li YL, Wang T, Jiang YL, Li K, Yu YL (2014) Microencapsulated chlorpyrifos: degradation in soil and influence on soil microbial community structures. J Environ Sci (China) 26:2322–2330
Chinese Society of Nutrition (2007) Chinese dietary guide. The Tibet people's publishing house
Fernandez-Perez M, Garrido-Herrera FJ, Gonzalez-Pradas E (2011) Alginate and lignin-based formulations to control pesticides leaching in a calcareous soil. J Hazard Mater 190:794–801
Gamiz B, Celis R, Hermosin MC, Cornejo J (2012) Soil clay modification with spermine and its effect on the behavior of the herbicide fluometuron. Soil Sci Soc Am J 76:432–440
Holeckova B, Sivikova K, Dianovsky J, Galdikova M (2013) Effect of triazole pesticide formulation on bovine culture cells. J Environ Sci Health Part B-Pestic Contam Agric Wastes 48:1080–1088
Huang YF, Liu ZZ, He Y, Li YL (2015) Impact of soil primary size fractions on sorption and desorption of atrazine on organo-mineral fractions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4396–4405
Joly P, Bonnemoy F, Charvy JC, Bohatier J, Mallet C (2013) Toxicity assessment of the maize herbicides S-metolachlor, benoxacor, mesotrione and nicosulfuron, and their corresponding commercial formulations, alone and in mixtures, using the Microtox (R) test. Chemosphere 93:2444–2450
Langeron J, Sayen S, Couderchet M, Guillon E (2014) Leaching potential of phenylurea herbicides in a calcareous soil: comparison of column elution and batch studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:4906–4913
Liang Y, Wang W, Shen Y, Liu Y, Liu XJ (2012) Dynamics and residues of chlorpyrifos and dichlorvos in cucumber grown in greenhouse. Food Control 26:231–234
Liu YH, Xu ZZ, Wu XG, Gui WJ, Zhu GN (2010) Adsorption and desorption behavior of herbicide diuron on various Chinese cultivated soils. J Hazard Mater 178:462–468
Liu CY, Wang SL, Li L, Ge J, Jiang SR, Liu FM (2011) Dissipation and residue of cyprodinil in strawberry and soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:323–325
Liu YH, Shen DY, Zhong DL, Mo RH, Ni ZL, Tang FB (2014) Time-dependent movement and distribution of chlorpyrifos and its metabolism in bamboo forest under soil surface mulching. J Agric Food Chem 62:6565–6570
Mandal K, Singh B (2013) Persistence of fipronil and its metabolites in sandy loam and clay loam soils under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 91:1596–1603
Narayanani N, Gajbhiye VT, Gupta S, Manjaiah KM (2014) Adsorption-desorption of chlorothalonil, chlorpyrifos and pendimethalin in soils: effect of soil organic matter and clay. Agrochimica 58:165–177
Oukali-Haouchine O, Barriuso E, Mayata Y, Moussaoui KM (2013) Factors affecting metribuzin retention in Algerian soils and assessment of the risks of contamination. Environ Monit Assess 185:4107–4115
Paradelo M, Soto-Gomez D, Perez-Rodriguez P, Pose-Juan E, Lopez-Periago JE (2014) Predicting release and transport of pesticides from a granular formulation during unsaturated diffusion in porous media. J Contam Hydrol 158:14–22
Paramasivam M, Chandrasekaran S (2013) Dynamics and residues of mixed formulation of fenamidone and mancozeb in gherkin field ecosystem. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:292–296
Potter TL, Gerstl Z, White PW, Cutts GS, Webster TM, Truman CC, Strickland TC, Bosch DD (2010) Fate and efficacy of metolachlor granular and emulsifiable concentrate formulations in a conservation tillage system. J Agric Food Chem 58:10590–10596
Prado B, Duwig C, Hidalgo C, Muller K, Mora L, Raymundo E, Etchevers JD (2014) Transport, sorption and degradation of atrazine in two clay soils from Mexico: andosol and vertisol. Geoderma 232:628–639
Racke KD, Lubinski RN, Fontaine DD, Miller JR, McCall PJ, Oliver GR (1993) Comparative fate of chlorpyrifos insecticide in urban and agricultural environments. ACS Symp Ser 522:70–85
Raszewski G, Lemieszek MK, Lukawski K, Juszczak M, Rzeski W (2015) Chlorpyrifos and cypermethrin induce apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 116:158–167
Redondo MJ, Ruiz MJ, Font G, Boluda R (1997) Dissipation and distribution of atrazine, simazine, chlorpyrifos, and tetradifon residues in citrus orchard soil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 32:346–352
Sai LL, Li XX, Liu YZ, Guo QM, Xie L, Yu GC, Bo CX, Zhang ZL, Li L (2014) Effects of chlorpyrifos on reproductive toxicology of male rats. Environ Toxicol 29:1083–1088
Syed JH, Alamdar A, Mohammad A, Ahad K, Shabir Z, Ahmed H, Ali SM, Sani S, Bokhari H, Gallagher KD, Ahmad I, Eqani S (2014) Pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables from Pakistan: a review of the occurrence and associated human health risks. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:13367–13393
Tiwari MK, Guha S (2012) Role of soil organic matter on the sorption and cosorption of endosulfan and chlorpyrifos on agricultural soils. J Environ Eng-ASCE 138:426–435
Tureli FC, Ok SS, Goldberg S (2015) Specific surface area effect on adsorption of chlorpyrifos and TCP by soils and modelling. Soil Sediment Contam 24:64–75
Undabeytia T, Recio E, Maqueda C, Sanchez-Verdejo T, Balek V (2012) Slow diuron release formulations based on clay-phosphatidylcholine complexes. Appl Clay Sci 55:53–61
Wlodarczyk M (2014) Influence of formulation on mobility of metazachlor in soil. Environ Monit Assess 186:3503–3509
Yang DB, Li GX, Yan XJ, Yuan HZ (2014) Controlled release study on microencapsulated mixture of fipronil and chlorpyrifos for the management of white grubs (Holotrichia parallela) in peanuts (Arachis hypogaea L.). J Agric Food Chem 62:10632–10637
Zhang X, Shen Y, Yu XY, Liu XJ (2012) Dissipation of chlorpyrifos and residue analysis in rice, soil and water under paddy field conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:276–280
Zhou Y, Wang K, Yan C, Li WS, Li H, Zhang N, Zhang ZX (2014) Effect of two formulations on the decline curves and residue levels of rotenone in cabbage and soil under field conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 104:23–27
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Applied Research Project in the Public Interest of Zhejiang Province (2015C32071) and the Special Fund for Forestry Scientific Research in the Public Interest (201304705).
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Mo, R., Tang, F. et al. Influence of different formulations on chlorpyrifos behavior and risk assessment in bamboo forest of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 20245–20254 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5272-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5272-2