Abstract
Introduction
Initial geosmin degradation was closely related to water temperature and natural geosmin concentration of sampling environment. Here, for the first time, we evaluated the biodegradation of geosmin by microorganisms in biofilm from biological treatment unit of actual potable water treatment plant.
Materials and methods
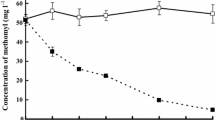
At an initial geosmin concentration of 2,500 ng/l, efficient geosmin removal was confirmed throughout the year. Furthermore, in the presence of mixed musty odor compounds (geosmin and MIB) as carbon source, geosmin degradation was enhanced compared to sole carbon source (geosmin alone).
Results and discussion
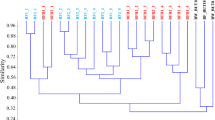
PCR-DGGE analysis revealed a rich community structure within the biofilm during rapid geosmin removal period, April. PCA revealed that the significant change in bacterial communities occurred from day 1 to day 2. Two novel geosmin-degrading bacteria were isolated from the biofilm of the biological treatment unit of Kasumigaura Water Purification, Waterworks Department, Japan. They belong to Methylobacterium sp. and Oxalobacteraceae bacterium, respectively.
Conclusions
These studies provide further insights into the unknown microbiological processes that occur during the biological removal of geosmin through water treatment and could facilitate the geosmin bioremediation in contaminated habitats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cook D, Newcombe G, Sztajnbok P (2001) The application of powdered activated carbon for MIB and geosmin removal: predicting PAC doses in four raw waters. Water Res 35:1325–1333
Decho AW (2000) Microbial biofilms in intertidal systems: an overview, Cont. Shelf Res 20:1257–1273
Eaton RW, Sandusky P (2009) Biotransformations of 2-methylisoborneol by camphor-degrading bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:583–588
Eaton RW, Sandusky P (2010) Biotransformations of (+/−)-geosmin by terpene-degrading bacteria. Biodegradation 21:71–79
Gerber NN (1979) Volatile substances from actinomycetes: their role in the odor pollution of water. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol 7:191–214
Glaze WH, Zarnoch JJ, Ruth EC, Chauncey W, Schep R (1990) Evaluating oxidants for the removal of model taste and odor compounds from a municipal water supply. J Am Water Works Assoc 82:79–84
Ho L, Newcombe G, Croue JP (2002) Influence of the character of NOM on the ozonation of MIB and geosmin. Water Res 36:511–518
Ho L, Croue JP, Newcombe G (2004) The effect of water quality and NOM character on the ozonation of MIB and geosmin. Water Sci Technol 49:249–255
Ho L, Hoefel D, Bock F, Saint CP, Newcombe G (2007) Biodegradation rates of 2-methylisoborneol (MIB) and geosmin through sand filters and in bioreactors. Chemosphere 66:2210–2218
Hoefel D, Monis PT, Grooby WL, Andrews S, Saint CP (2005) Profiling bacterial survival through a water treatment process and subsequent distribution system. J Appl Microbiol 99:175–186
Hoefel D, Ho L, Aunkofer W, Monis PT, Keegan A, Newcombe G, Saint CP (2006) Cooperative biodegradation of geosmin by a consortium comprising three gram-negative bacteria isolated from the biofilm of a sand filter column. Lett Appl Microbiol 43:417–423
Hoefel D, Ho L, Monis PT, Newcombe G, Saint CP (2009) Biodegradation of geosmin by a novel Gram-negative bacterium; isolation, phylogenetic characterisation and degradation rate determination. Water Res 43:2927–2935
Juttner F, Watson SB (2007) Biochemical and ecological control of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in source waters. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4395–4406
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 9:299–306
Lalezary S, Pirbazari M, McGuire MJ (1986) Oxidation of five earthy-musty taste and odor compounds. J Am Water Works Assoc 78:62–69
Lawrence JR, Kopf G, Headley JV, Neu TR (2001) Sorption and metabolism of selected herbicides in river biofilm communities. Can J Microbiol 47:634–641
McDowall B, Hoefel D, Newcombe G, Saint CP, Ho L (2009) Enhancing the biofiltration of geosmin by seeding sand filter columns with a consortium of geosmin-degrading bacteria. Water Res 43:433–440
Namkung E, Rittman BE (1987) Removal of taste- and odorcausing compounds by biofilms grown on humic substances. J Am Water Works Assoc 79:107–112
Narayan LV, Nunez WJ (1974) Biological control: isolation and bacterial oxidation of the taste and odor compound geosmin. J Am Water Works Assoc 66:532–536
Pusch M, Fiebig D, Brettar I, Eisenmann H, Ellis BK, Kaplan LA, Lock MA, Naegeli MW, Traunspurger W (1998) The role of micro-organisms in the ecological connectivity of running waters. Freshw Biol 40:453–495
Saadoun I, El-Migdadi F (1998) Degradation of geosmin-like compounds by selected species of gram-positive bacteria. Lett Appl Microbiol 26:98–100
Saito A, Tokuyama T, Tanaka A, Oritani T, Fuchigami K (1999) Microbiological degradation of (−)-geosmin. Water Res 33(13):3033–3036
Silvey JKG, Henley AW, Nunez WJ, Cohen RC (1970) Biological Control: Control of Naturally Occurring Taste and Odors by Microorganisms. Proceedings of the National Biological Congress, Detroit, USA
Sugiura N, Iwami N, Inamori Y, Nishimura O, Sudo R (1998) Significance of attached cyanobacteria relevant to the occurrence of musty odor in Lake Kasumigaura. Water Res 32:3549–3554
Sugiura N, Isoda H, Takaaki M (2003) Degradation potential of musty odor in a dinking water source by a biofilm method. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology –. AQUA 52:181–187
Sutherland IW (2001) The biofilm matrix — an immobilized but dynamic microbial environment. Trends Microbiol 9:222–227
Xue Q, Utsumi M, Shimizu K, Chen H, Li M, Xu C, Zhang Z, Zhang Q, Sugiura N (2011a) Biodegradation of geosmin by biofilm from water treatment plant in winter season. Int J Integ Biol 11:30–34
Xue Q, Chen G, Shimizu K, Sakharkar MK, Utsumi M, Chen H, Li M, Zhang Z, Sugiura N (2011b) Isolation and identification of novel geosmin-degrading bacteria. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 3:830–833
Young WF, Horth H, Crane R, Ogden T, Arnott M (1996) Taste and odor threshold concentrations of potential potable water contaminants. Water Res 30:331–340
Zhou B, Yuan R, Shi C, Yu L, Gu J, Zhang C (2011) Biodegradation of geosmin in drinking water by novel bacteria isolated from biologically active carbon. J Environ Sci 23(5):816–823
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the assistance of the Kasumigaura Water Purification Works Department. This research was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (21310049) from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), Sumitomo Electronic Industries Group CSR Foundation and the Water Pollution Control and Management Project of China (2008ZX07313-001, 2009ZX07318-008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Q., Shimizu, K., Sakharkar, M.K. et al. Geosmin degradation by seasonal biofilm from a biological treatment facility. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19, 700–707 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0613-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0613-2