Abstract
Background, aim, and scope
Composting is an effective treatment process to realize sludge land application. However, nitrogen loss could result in the reduction of nutrient value of the compost products and the stabilization effect of composting on heavy metal concentration and mobility in sludge has been shown to be very limited.
Materials and methods
Laboratory-scale experiments were carried out to investigate the effects of bamboo charcoal (BC) on nitrogen conservation and mobility of Cu and Zn during sludge composting.
Results
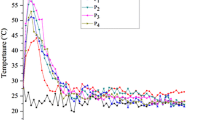
The result indicated that the incorporation of BC into the sludge composting material could significantly reduce nitrogen loss. With 9% BC amendment, total nitrogen loss at the end of composting decreased 64.1% compared with no BC amendment (control treatment). Mobility of Cu and Zn in the sludge may also have been lessened, based on the decline in diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid-extractable Cu and Zn contents of composted sludge by 44.4% and 19.3%, respectively, compared to metal extractability in the original material.
Discussion
Ammonia adsorption capability of BC might be the main reason for the retention of nitrogen in sludge composting materials. Decrease of extractable Cu2+ and Zn2+ in the composting material mainly resulted from the adsorption of both metals by BC.
Conclusions
Incorporation of BC into composting material could significantly lessen the total nitrogen loss during sludge composting. Mobility of heavy metals in the sludge composting material could also be reduced by the addition of BC.
Recommendations and perspectives
Bamboo charcoal could be an effective amendment for nitrogen conservation and heavy metal stabilization in sludge composts. Further research into the effect of BC-amended sludge compost material on soil properties, bioavailability of heavy metals, and nutrient turnover in soil needs to be carried out prior to the application of BC-sludge compost in agriculture.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BC:
-
Bamboo charcoal
- FBC:
-
Fresh bamboo charcoal
- CBC:
-
Composted bamboo charcoal
- TOM:
-
Total organic matter
- TOC:
-
Total organic carbon
References
Amir S, Hafidi M, Merlina G, Revel JC (2005) Sequential extraction of heavy metals during composting of sewage sludge. Chemosphere 5:801–810
Baddi GA, Hafidi M, Cegarra J, Alburquerque JA, Gonzálvez J, Gilard V, Revel JC (2004) Characterization of fulvic acids by elemental and spectroscopic (FTIR and 13C-NMR) analyses during composting of olive mill wastes plus straw. Bioresour Technol 9:285–290
Barrington S, Choinière D, Trigui M (2002) Effect of carbon source on compost nitrogen and carbon losses. Bioresour Technol 83(3):189–194
Bernal MP, Lopez-Real JM, Scott KM (1993) Application of narural zeolites for the reduction of ammonia emission during the composting of organic waste in a laboratory composting simulators. Bioresour Technol 43:35–39
Boehm HP (1994) Some aspects of surface chemistry of carbon blacks and other carbons. Carbon 32:759–770
Cooperband LR, Middleton JH (1996) Changes in chemical, physical and biological properties of passively-aerated cocomposted poultry litter and municipal solid waste compost. Compost Sci Util 4:24–34
Dai JY, Xu MQ, Chen JP, Yang XP, Ke ZS (2007) PCDD/F, PAH and heavy metals in the sewage sludge from six wastewater treatment plants in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 66:353–361
Fang M, Wong JWC (1999) Effects of lime amendment on availability of heavy metals and maturation in sewage sludge composting. Environ Pollut 106:83–89
Glaser B, Balashov E, Haumaier L, Guggenberger G, Zech W (2000) Black carbon in density fractions of anthropogenic soils of the Brazilian Amazon region. Org Geochem 31:669–678
Hernández T, Masciandaro G, Moreno JI, García C (2006) Changes in organic matter composition during composting of two digested sewage sludges. Waste Manage 26:1370–1376
Hiller DA, Brümmer GW (1997) Electron microprobe studies on soil samples with varying heavy metal contamination: part 2. Contents of heavy metals and other elements in aggregations of humic substances, litter residues, and charcoal particles. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 160:47–55
Hseu ZY (2006) Extractability and bioavailability of zinc over time in three tropical soils incubated with biosolids. Chemosphere 63:762–771
Illera V, Walter I, Souza P, Cala V (2000) Short-term effects of biosolid and municipal solid waste applications on heavy metals distribution in a degraded soil under a semiarid environment. Sci Total Environ 255:29–44
Iyobe T, Asada T, Kawata K, Oikawa K (2004) Comparison of removal efficiencies for ammonia and amine gases between woody charcoal and activated carbon. J Health Sci 50:148–153
Kithome M, Paul JW, Bomk AA (1999) Reducing nitrogen losses during simulated composting of poultry manure using absorbents or chemical amendments. J Environ Qual 28:194–201
Liu YH, Ma LL, Li YQ, Zheng LT (2007) Evolution of heavy metal speciation during the aerobic composting process of sewage sludge. Chemosphere 67:1025–1032
Major J, Steiner C, Ditommaso A, Falcǎo NPS, Lenmann J (2005) Weed composition and cover after three years of soil fertility management in the central Brazilian Amazon: compost, fertilizer, manure and charcoal applications. Weed Biol Manag 5:69–76
Martins O (1992) Loss of nitrogenous compounds during composting of animal wastes. Bioresour Technol 4:10–16
Nishantha Fernando WAR, Kang X, Charles WR (2005) Sorption and desorption of ammonium from liquid swine waste in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 69:1057–1065
Oliveira AS, Bocio A, Beltramini Trevilato TM, Magosso Takayanagui AM, Domingo JL, Segura-Muñoz SI (2007) Heavy metals in untreated/treated urban effluent and sludge from a biological wastewater treatment plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 14(7):483–489
Oya A, Iu WG (2002) Deodorization performance of charcoal particles loaded with orthophosphoric acid against ammonia and trimethylamine. Carbon 40:1391–1399
Pagans E, Barrena R, Font X, Sánchez A (2006) Ammonia emissions from the composting of different organic wastes-dependency on process temperature. Chemosphere 62:1534–1542
Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (1982) Method of soil analysis, part 2—chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. ASA, SSSA, Madison, WI Agronomy, no 9
Paredes C, Bernal MP, Cegarra J, Roig A (2002) Biodegradation of olive mill wastewater sludge by its co-composting with agricultural wastes. Bioresour Technol 85:1–8
Qiao L, Ho G (1997) The effects of clay amendment and composting on metal speciation in digested sludge. Water Res 31:951–964
Rao Bhamidimarri SM, Pandey SP (1996) Aerobic thermophilic composting of piggery solid wastes. Water Sci Technol 33(8):89–94
Raviv M, Medina S, Karasnovsky A (2002) Conserving nitrogen during composting. Biocycle 43(9):48–51
Scancara J, Milacica R, Straza M (2000) Total metal concentrations and partitioning of Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ni and Zn in sewage sludge. Sci Total Environ 250:9–19
Sigua GC, Adjei MB, Rechcigl JE (2005) Cumulative and residual effects of repeated sewage sludge applications: forage productivity and soil quality implications in South Florida, USA ESPR. Environ Sci Pollut Res 12(2):80–88
Steiner C, Teixeira WG, Lehmann J, Nehls T, de Macêdo JLV, Blum WEH, Zech W (2007) Long term effects of manure, charcoal and mineral fertilization on crop production and fertility on a highly weathered Central Amazonian upland soil. Plant Soil 291:275–290
Su JJ, Wan HL, Kimberley MO, Beecroft K, Magesan GN, Hu CX (2007) Fractionation and mobility of phosphorus in a sandy forest soil amended with biosolids. Environ Sci Pollut Res 14(7):529–535
Tennant MF, Mazyck DW (2007) The role of surface acidity and pore size distribution in the adsorption of 2-methylisoborneol via powdered activated carbon. Carbon 45:858–864
Udom BE, Mbagwu JSC (2004) Distribution of Zn, Cu, Cd, and Pb in a tropical ultisol after long-term disposal of sewage sludge. Environ Int 4(2):467–470
Zhang QS (2001) Prospect and utilization of bamboo resources in China, mechanism and science of bamboo charcoal and bamboo vinegar (in Chinese). China Forestry, Beijing
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by China National Natural Science Fund (40432004), Project of Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (2006C13066 and 2007C03002), and Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hailong Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, L., Wu, W., Liu, Y. et al. Reduction of nitrogen loss and Cu and Zn mobility during sludge composting with bamboo charcoal amendment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16, 1–9 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-008-0041-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-008-0041-0