Abstract
Purpose
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) can lead to increased morning blood pressure (BP). We hypothesized that high evening BP may aggravate OSA-related morning BP elevation. Additionally, this interactional effect may be modified by sex.
Methods
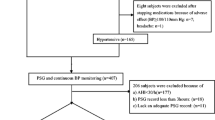
This retrospective, cross-sectional study included newly diagnosed OSA patients with an apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) ≥ 5 per hour on a full-night polysomnography. An analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was used to determine whether severe OSA (AHI ≥ 30) was associated with higher morning BP than mild-to-moderate OSA (5 ≤ AHI < 30) and whether there was an interaction between apnea severity and evening BP on morning BP. To identify the sex effects, analyses were performed separately in each sex group.
Results
A total of 1445 patients with an average age of 51.9 years (SD 11.7) (male 77.9% vs. female 22.1%; high evening BP group 22.4% vs. normal evening BP group 59.6%) were included in the study. Based on the ANCOVA, patients with severe OSA had significantly higher morning systolic BP (SBP) (p = 0.003), diastolic BP (DBP) (p < 0.001), and mean BP (MBP) (p < 0.001) than the mild-to-moderate group in male subjects. A significant interaction between apnea severity and evening BP was identified on morning DBP and MBP in male subjects. However, there were no differences in morning BP between severe and mild-to-moderate OSA groups in female subjects.
Conclusions
In male subjects, severe OSA contributed to higher morning BP than mild-to-moderate OSA. OSA-associated morning BP elevation was more prominent in the high evening BP group than in the normal BP group. Such relations were not found in female subjects.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nam H, Lim JS, Kim JS, Lee KJ, Koo DL, Lee C (2016) Sleep perception in obstructive sleep apnea: a study using polysomnography and the multiple sleep latency test. J Clin Neurol 12(2):230–235. https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2016.12.2.230
Kario K (2009) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and hypertension: ambulatory blood pressure. Hypertens Res 32(6):428–432. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2009.56
Lavie-Nevo K, Pillar G (2006) Evening-morning differences in blood pressure in sleep apnea syndrome: effect of gender. Am J Hypertens 19(10):1064–1069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjhyper.2006.02.018
Lee YJ, Jeong DU (2014) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is associated with higher diastolic blood pressure in men but not in women. Am J Hypertens 27(3):325–330. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpt280
Mokros L, Kuczynski W, Franczak L, Bialasiewicz P (2017) Morning diastolic blood pressure may be independently associated with severity of obstructive sleep apnea in non-hypertensive patients: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Sleep Med 13(7):905–910. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.6664
Logan AG, Perlikowski SM, Mente A, Tisler A, Tkacova R, Niroumand M, Leung RS, Bradley TD (2001) High prevalence of unrecognized sleep apnoea in drug-resistant hypertension. J Hypertens 19(12):2271–2277
Torres G, Sanchez-de-la-Torre M, Barbe F (2015) Relationship between OSA and hypertension. Chest 148(3):824–832. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.15-0136
Kapa S, Sert Kuniyoshi FH, Somers VK (2008) Sleep apnea and hypertension: interactions and implications for management. Hypertension 51(3):605–608. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.106.076190
Jafari B, Mohsenin V (2012) Activation of heme oxygenase and suppression of cGMP are associated with impaired endothelial function in obstructive sleep apnea with hypertension. Am J Hypertens 25(8):854–861. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajh.2012.56
Damiani MF, Zito A, Carratu P, Falcone VA, Bega E, Scicchitano P, Ciccone MM, Resta O (2015) Obstructive sleep apnea, hypertension, and their additive effects on atherosclerosis. Biochem Res Int 2015:984193. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/984193
Wang L, Cai A, Zhang J, Zhong Q, Wang R, Chen J, Zhou Y (2016) Association of obstructive sleep apnea plus hypertension and prevalent cardiovascular diseases: a cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore) 95(39):e4691. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000004691
Pratt-Ubunama MN, Nishizaka MK, Boedefeld RL, Cofield SS, Harding SM, Calhoun DA (2007) Plasma aldosterone is related to severity of obstructive sleep apnea in subjects with resistant hypertension. Chest 131(2):453–459. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.06-1442
Drager LF, Bortolotto LA, Figueiredo AC, Silva BC, Krieger EM, Lorenzi-Filho G (2007) Obstructive sleep apnea, hypertension, and their interaction on arterial stiffness and heart remodeling. Chest 131(5):1379–1386. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.06-2703
White LH, Bradley TD, Logan AG (2014) Relationship of circadian pattern of urine sodium excretion to hypertension and obstructive sleep apnoea. J Hypertens 32(11):2253–2260; discussion 2260. https://doi.org/10.1097/hjh.0000000000000327
Walia HK, Li H, Rueschman M, Bhatt DL, Patel SR, Quan SF, Gottlieb DJ, Punjabi NM, Redline S, Mehra R (2014) Association of severe obstructive sleep apnea and elevated blood pressure despite antihypertensive medication use. J Clin Sleep Med 10(8):835–843. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.3946
Kasiakogias A, Tsioufis C, Thomopoulos C, Andrikou I, Aragiannis D, Dimitriadis K, Tsiachris D, Bilo G, Sideris S, Filis K, Parati G, Stefanadis C (2015) Evening versus morning dosing of antihypertensive drugs in hypertensive patients with sleep apnoea: a cross-over study. J Hypertens 33(2):393–400. https://doi.org/10.1097/hjh.0000000000000371
Serinel Y, Yee BJ, Grunstein RR, Wong KH, Cistulli PA, Arima H, Phillips CL (2017) Chronotherapy for hypertension in obstructive sleep apnoea (CHOSA): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. Thorax 72(6):550–558. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-209504
Quintana-Gallego E, Carmona-Bernal C, Capote F, Sanchez-Armengol A, Botebol-Benhamou G, Polo-Padillo J, Castillo-Gomez J (2004) Gender differences in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: a clinical study of 1166 patients. Respir Med 98(10):984–989
Mohsenin V, Yaggi HK, Shah N, Dziura J (2009) The effect of gender on the prevalence of hypertension in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med 10(7):759–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2008.09.005
Nieto FJ, Young TB, Lind BK, Shahar E, Samet JM, Redline S, D'Agostino RB, Newman AB, Lebowitz MD, Pickering TG (2000) Association of sleep-disordered breathing, sleep apnea, and hypertension in a large community-based study. Sleep Heart Health Study. Jama 283(14):1829–1836
Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Skatrud J (2000) Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med 342(19):1378–1384. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200005113421901
Hu W, Jin X, Chen C, Zhang P, Li D, Su Q, Yin G, Hang Y (2017) Diastolic blood pressure rises with the exacerbation of obstructive sleep apnea in males. Obesity (Silver Spring) 25(11):1980–1987. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.21960
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Bohm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Galderisi M, Grobbee DE, Jaarsma T, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, Ruilope LM, Schmieder RE, Sirnes PA, Sleight P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Zannad F, Burnier M, Ambrosioni E, Caufield M, Coca A, Olsen MH, Tsioufis C, van de Borne P, Zamorano JL, Achenbach S, Baumgartner H, Bax JJ, Bueno H, Dean V, Deaton C, Erol C, Ferrari R, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Knuuti J, Kolh P, Lancellotti P, Linhart A, Nihoyannopoulos P, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Tamargo JL, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Wijns W, Windecker S, Clement DL, Gillebert TC, Rosei EA, Anker SD, Bauersachs J, Hitij JB, Caulfield M, De Buyzere M, De Geest S, Derumeaux GA, Erdine S, Farsang C, Funck-Brentano C, Gerc V, Germano G, Gielen S, Haller H, Jordan J, Kahan T, Komajda M, Lovic D, Mahrholdt H, Ostergren J, Parati G, Perk J, Polonia J, Popescu BA, Reiner Z, Ryden L, Sirenko Y, Stanton A, Struijker-Boudier H, Vlachopoulos C, Volpe M, Wood DA (2013) 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 34(28):2159–2219. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/eht151
Armstrong C (2014) JNC8 guidelines for the management of hypertension in adults. Am Fam Physician 90(7):503–504
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ (2003) Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension 42(6):1206–1252. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000107251.49515.c2
Weber SA, Santos VJ, Semenzati Gde O, Martin LC (2012) Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in children with obstructive sleep apnea and primary snoring. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76(6):787–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2012.02.041
Schulz H (2007) Phasic or transient? Comment on the terminology of the AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events. J Clin Sleep Med 3(7):752
Dean DA, Wang R, Jacobs DR, Duprez D, Punjabi NM, Zee PC, Shea S, Watson K, Redline S (2015) A systematic assessment of the association of polysomnographic indices with blood pressure: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Sleep 38(4):587–596. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.4576
Jin ZN, Wei YX (2016) Meta-analysis of effects of obstructive sleep apnea on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. J Geriatr Cardiol 13(4):333–343. https://doi.org/10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2016.03.020
Kario K, Saito I, Kushiro T, Teramukai S, Tomono Y, Okuda Y, Shimada K (2016) Morning home blood pressure is a strong predictor of coronary artery disease: The HONEST Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 67(13):1519–1527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2016.01.037
Stradling JR, Partlett J, Davies RJ, Siegwart D, Tarassenko L (1996) Effect of short term graded withdrawal of nasal continuous positive airway pressure on systemic blood pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Blood Press 5(4):234–240
Haskell WL, Lee IM, Pate RR, Powell KE, Blair SN, Franklin BA, Macera CA, Heath GW, Thompson PD, Bauman A (2007) Physical activity and public health: updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation 116(9):1081–1093. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.107.185649
Hinojosa-Laborde C, Mifflin SW (2005) Sex differences in blood pressure response to intermittent hypoxia in rats. Hypertension 46(4):1016–1021. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000175477.33816.f3
Stupfel M, Pesce VH, Gourlet V, Bouley G, Elabed A, Lemercerre C (1984) Sex-related factors in acute hypoxia survival in one strain of mice. Aviat Space Environ Med 55(2):136–140
Milnor WR (1990) Cardiovascular physiology. Oxford University Press
Beevers G, Lip GY, O'Brien E (2001) ABC of hypertension: the pathophysiology of hypertension. BMJ 322(7291):912–916
Oparil S, Zaman MA, Calhoun DA (2003) Pathogenesis of hypertension. Ann Intern Med 139(9):761–776
Cho JS, Ihm SH, Kim CJ, Park MW, Her SH, Park GM, Kim TS (2015) Obstructive sleep apnea using watch-PAT 200 is independently associated with an increase in morning blood pressure surge in never-treated hypertensive patients. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 17(9):675–681. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.12581
Wu Y, Huang R, Zhong X, Xiao Y (2017) Cardiovascular consequences of repetitive arousals over the entire sleep duration. Biomed Res Int 2017:4213861. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4213861
Mokhlesi B, Finn LA, Hagen EW, Young T, Hla KM, Van Cauter E, Peppard PE (2014) Obstructive sleep apnea during REM sleep and hypertension. Results of the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 190(10):1158–1167. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201406-1136OC
Koo BB, Dostal J, Ioachimescu O, Budur K (2008) The effects of gender and age on REM-related sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Breath 12(3):259–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-007-0161-7
(2017) Recommended standards for assessing blood pressure in human research where blood pressure or hypertension is a major focus. Kidney Int Rep 2 (4):733–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2017.02.009
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, DePalma SM, Gidding S, Jamerson KA, Jones DW, MacLaughlin EJ, Muntner P, Ovbiagele B, Smith SC Jr, Spencer CC, Stafford RS, Taler SJ, Thomas RJ, Williams KA Sr, Williamson JD, Wright JT Jr (2018) 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 138(17):e426–e483. https://doi.org/10.1161/cir.0000000000000597
Mbanya VN, Mbanya JC, Kufe C, Kengne AP (2016) Effects of single and multiple blood pressure measurement strategies on the prediction of prevalent screen-detected diabetes mellitus: a population-based survey. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 18(9):864–870. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.12774
Fagan TC, Conrad KA, Mayshar PV, Mackie MJ, Hagaman RM (1988) Single versus triplicate measurements of blood pressure and heart rate. Hypertension 11(3):282–284
Acknowledgments
This report was supported by the Asan Medical Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 169 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, SH., Kim, H.J. & Lee, SA. The effect of high evening blood pressure on obstructive sleep apnea–related morning blood pressure elevation: does sex modify this interaction effect?. Sleep Breath 23, 1255–1263 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-019-01869-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-019-01869-5