Abstract
Purpose
Fibroblast activating protein (FAP) is highly expressed in the synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. The aim of this study was to determine the feasibility of PET imaging with an Al[18F] F-NOTA-labeled FAP inhibitor 04(18F-FAPI-04) for the evaluation of arthritic progression and therapeutic response in experimental arthritis.
Methods
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) were obtained from patients with RA or osteoarthritis (OA), and the relationship between 18F-FAPI-04 uptake and the inflammatory activity of RA FLSs was investigated. Collagen-induce arthritis (CIA) mice models were established and treated with methotrexate (MTX) or etanercept (ETC). Then, PET imaging was performed 24 h following 18F-FAPI-04 injection. The imaging results were compared by assessing macroscopic arthritis scores and histological staining.
Results
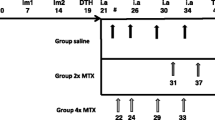
18F-FAPI-04 uptake was obvious in RA FLSs that characterizing FAP activation. The higher the uptake of 18F-FAPI-04, the more severity of the inflammatory phenotype in RA FLS. Furthermore, the uptake of 18F-FAPI-04 in inflamed joints could be found even before the deformity of the parental joints could be observed by histological examination. Both MTX and ETC were effective in inhibiting the progression of arthritis in CIA mice was confirmed by macroscopic, histological, and radiographic pathology scores. Importantly, 18F-FAPI-04 uptake declined accordingly in CIA models following MTX and ETC treatment.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that PET imaging of 18F-FAPI-04 can be used to monitor treatment response in RA, and is more sensitive in disease speculation than macroscopic arthritis scoring.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Mormile I et al (2021) The N-Formyl peptide receptors and rheumatoid arthritis: a dangerous liaison or confusing relationship? Front Immunol 12:685214
Aletaha D, Smolen JS (2018) Diagnosis and Management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review. JAMA 320(13):1360–1372
Scherer HU, Häupl T, Burmester GR (2020) The etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun 110:102400
Zhao J et al (2021) Molecular and cellular heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and clinical implications. Front Immunol 12:790122
Li GF, Qin YH, Du PQ (2015) Andrographolide inhibits the migration, invasion and matrix metalloproteinase expression of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via inhibition of HIF-1α signaling. Life Sci 136:67–72
Maradit-Kremers H et al (2007) Raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate signals heart failure in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66(1):76–80
Hamson EJ et al (2014) Understanding fibroblast activation protein (FAP): substrates, activities, expression and targeting for cancer therapy. Proteomics Clin Appl 8(5–6):454–463
Altmann A, Haberkorn U, Siveke J (2021) The latest developments in imaging of fibroblast activation protein. J Nucl Med 62(2):160–167
Toms J et al (2020) Targeting fibroblast activation protein: radiosynthesis and preclinical evaluation of an (18)F-labeled FAP inhibitor. J Nucl Med 61(12):1806–1813
Ge L et al (2022) Preclinical evaluation and pilot clinical study of [(18)F]AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04 for PET imaging of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 49(12):4025–4036
Kuyumcu S et al (2021) Safety of fibroblast activation protein-targeted radionuclide therapy by a low-dose dosimetric approach using 177Lu-FAPI04. Clin Nucl Med 46(8):641–646
Dorst DN et al (2022) Targeting of fibroblast activation protein in rheumatoid arthritis patients: imaging and ex vivo photodynamic therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford) 61(7):2999–3009
Bauer S et al (2006) Fibroblast activation protein is expressed by rheumatoid myofibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Res Ther 8(6):R171
Dorst DN et al (2021) Targeting of fibroblast activation protein in rheumatoid arthritis patients: imaging and ex vivo photodynamic therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford) 61(7):2999–3009
Song G et al (2019) CD109 regulates the inflammatory response and is required for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 78(12):1632–1641
Ge L et al (2022) ATF6α contributes to rheumatoid arthritis by inducing inflammatory cytokine production and apoptosis resistance. Front Immunol 13:965708
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Ballal S et al (2021) Biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, dosimetry of [(68)Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi, and the head-to-head comparison with [(18)F]F-FDG PET/CT in patients with various cancers. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48(6):1915–1931
Figus FA et al (2021) Rheumatoid arthritis: extra-articular manifestations and comorbidities. Autoimmun Rev 20(4):102776
Radu AF, Bungau SG (2021) Management of rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Cells 10(11):2857
Murray K et al (2021) Long-term remission and biologic persistence rates: 12-year real-world data. Arthritis Res Ther 23(1):25
Adamis D, van Gool WA, Eikelenboom P (2021) Consistent patterns in the inconsistent associations of Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), C-reactive protein (C-RP) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) levels with delirium in surgical populations A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 97:104518
Wakefield RJ et al (2005) Musculoskeletal ultrasound including definitions for ultrasonographic pathology. J Rheumatol 32(12):2485–2487
Wang X, Qian G, Duan H (2020) Diagnostic value of musculoskeletal ultrasound in rheumatoid finger arthritis. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 30(6):617–621
Mona CE et al (2022) Correlation of (68)Ga-FAPi-46 PET Biodistribution with FAP expression by immunohistochemistry in patients with solid cancers: interim analysis of a prospective translational exploratory study. J Nucl Med 63(7):1021–1026
Varasteh Z et al (2019) Molecular imaging of fibroblast activity after myocardial infarction using a (68)Ga-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor, FAPI-04. J Nucl Med 60(12):1743–1749
Röhrich M et al (2022) Fibroblast activation protein-specific PET/CT imaging in fibrotic interstitial lung diseases and lung cancer: a translational exploratory study. J Nucl Med 63(1):127–133
Schmidkonz C et al (2020) Disentangling inflammatory from fibrotic disease activity by fibroblast activation protein imaging. Ann Rheum Dis 79(11):1485–1491
Laverman P et al (2015) Immuno-PET and Immuno-SPECT of rheumatoid arthritis with radiolabeled anti-fibroblast activation protein antibody correlates with severity of arthritis. J Nucl Med 56(5):778–783
Iwamoto N et al (2021) Methotrexate alters the expression of microRNA in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci 22(21):11561
Municio C et al (2018) Methotrexate limits inflammation through an A20-dependent cross-tolerance mechanism. Ann Rheum Dis 77(5):752–759
Zhao S, Mysler E, Moots RJ (2018) Etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunotherapy 10(6):433–445
Funding
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82072850, 81772760, 82101903, 81901666, 82171801, 82271842), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. ZR2020YQ55), Key Research and Development project of Shandong Province (No. 2021ZDSYS27), The Innovation Project of Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences (2021), The Youth Innovation Technology Plan of Shandong University (Grant No. 2019KJK003), and Academic Promotion Programme of Shandong First Medical University (Grant No. 2019LJ001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the writing or revision of the article, and all authors approved the final publication version. In the study, Jinxiang Han had full access to all data and is responsible for the accuracy and integrity. Jinxiang Han and Lin Wang conceptualized and designed the study. Luna Ge and Lin Wang wrote the manuscript. Acquisition of data: Qingyun Zhang, Xuehong Lin, Mengxue Lü, Dandan Shi, Ruojia Zhang, Haojun Shi, Kai Cheng. Yuang Zhang, and Jihong Pan and Guanhua Song analyzed and interpreted data. Luna Ge, Lin Wang, Weiqi Wang, Xiaofan Zhang, and Zhurui Shao revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Lin, X., Wang, W. et al. Evaluation of 18F-FAPI-04 Imaging in Assessing the Therapeutic Response of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol Imaging Biol 25, 630–637 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-023-01817-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-023-01817-6