Abstract
Purpose
Previously, we successfully developed a pretargeted imaging strategy (atezolizumab-TCO/[99mTc]HYNIC-PEG11-Tz) for evaluating programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression in xenograft mice. However, the surplus unclicked [99mTc]HYNIC-PEG11-Tz is cleared somewhat sluggishly through the intestines, which is not ideal for colorectal cancer (CRC) imaging. To shift the excretion of the Tz-radioligand to the renal system, we developed a novel Tz-radioligand by adding a polypeptide linker between HYNIC and PEG11.
Procedures
Pretargeted molecular probes [99mTc]HYNIC-polypeptide-PEG11-Tz and cetuximab-TCO were synthesized. [99mTc]HYNIC-polypeptide-PEG11-Tz was evaluated for in vitro stability and in vivo blood pharmacokinetics. In vitro ligation reactivity of [99mTc]HYNIC-polypeptide-PEG11-Tz towards cetuximab-TCO was also tested. Biodistribution assay and imaging of [99mTc]HYNIC-polypeptide-PEG11-Tz were performed to observe its excretion pathway. Pretargeted biodistribution was measured at three different accumulation intervals to determine the optimal pretargeted interval time. Pretargeted (cetuximab-TCO 48 h/[99mTc]HYNIC-PEG11-Tz 6 h) and (cetuximab-TCO 48 h/[99mTc]HYNIC-Polypeptide-PEG11-Tz 6 h) imagings were compared to examine the effect of the excretion pathway on tumor imaging.
Results
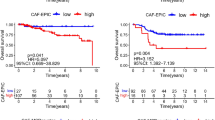
[99mTc]HYNIC-polypeptide-PEG11-Tz showed favorable in vitro stability and rapid blood clearance in mice. SEC-HPLC revealed almost complete reaction between cetuximab-TCO and [99mTc]HYNIC-polypeptide-PEG11-Tz in vitro, with the 8:1 Tz-to-mAb reaction providing a conversion yield of 87.83 ± 3.27 %. Biodistribution and imaging analyses showed that the Tz-radioligand was cleared through the kidneys. After 24, 48, and 72 h of accumulation in HCT116 tumor, the tumor-to-blood ratio of cetuximab-TCO was 0.83 ± 0.13, 1.40 ± 0.31, and 1.15 ± 0.21, respectively. Both pretargeted (cetuximab-TCO 48 h/[99mTc]HYNIC-PEG11-Tz 6 h) and (cetuximab-TCO 48 h/[99mTc]HYNIC-polypeptide-PEG11-Tz 6 h) clearly delineated HCT116 tumor. Pretargeted imaging strategy using cetuximab-TCO/[99mTc]HYNIC-polypeptide-PEG11-Tz could be used for diagnosing CRC, as the surplus unclicked [99mTc]HYNIC-polypeptide-PEG11-Tz was cleared through the urinary system, leading to low abdominal uptake background.
Conclusion
Our novel pretargeted imaging strategy (cetuximab-TCO/[99mTc]HYNIC-polypeptide-PEG11-Tz) was useful for imaging CRC, broadening the application scope of pretargeted imaging strategy. The pretargeted imaging strategy clearly delineated HCT116 tumor, showing that its use could be extended to selection of internalizing antibodies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65(2):87–108
Turker NS, Heidari P, Kucherlapati R, Kucherlapati M, Mahmood U (2014) An EGFR targeted PET imaging probe for the detection of colonic adenocarcinomas in the setting of colitis. Theranostics. 4(9):893–903
Liu J, Zuo X, Li C, Yu T, Gu X, Zhou C, Li Z, Goetz M, Kiesslich R, Li Y (2013) In vivo molecular imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with colorectal neoplasia using confocal laser endomicroscopy. Cancer Lett 330(2):200–207
Winkler AM, Rice PF, Weichsel J, Watson JM, Backer MV, Backer JM et al (2011) In vivo, dual-modality OCT/LIF imaging using a novel VEGF receptor-targeted NIR fluorescent probe in the AOM-treated mouse model. Mol Imaging Biol 13(6):1173–1182
Hsiung PL, Hardy J, Friedland S, Soetikno R, Du CB, Wu AP et al (2008) Detection of colonic dysplasia in vivo using a targeted heptapeptide and confocal microendoscopy. Nat Med 14(4):454–458
Rusckowski M, Gupta S, Liu G, Dou S, Hnatowich DJ (2007) Evidence of specificity of radiolabeled phage display peptides for the TAG-72 antigen. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 22(4):564–572
Yang M, Fan Q, Zhang R, Cheng K, Yan J, Pan D, Ma X, Lu A, Cheng Z (2015) Dragon fruit-like biocage as an iron trapping nanoplatform for high efficiency targeted cancer multimodality imaging. Biomaterials. 69:30–37
Yoon SM, Myung SJ, Kim IW, Do EJ, Ye BD, Ryu JH, Park K, Kim K, Kwon IC, Kim MJ, Moon DH, Yang DH, Kim KJ, Byeon JS, Yang SK, Kim JH (2011) Application of near-infrared fluorescence imaging using a polymeric nanoparticle-based probe for the diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring of colon cancer. Dig Dis Sci 56(10):3005–3013
Sartore-Bianchi A, Martini M, Molinari F, Veronese S, Nichelatti M, Artale S, di Nicolantonio F, Saletti P, de Dosso S, Mazzucchelli L, Frattini M, Siena S, Bardelli A (2009) PIK3CA mutations in colorectal cancer are associated with clinical resistance to EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res 69(5):1851–1857
Aerts HJ, Dubois L, Perk L, Vermaelen P, van Dongen GA, Wouters BG et al (2009) Disparity between in vivo EGFR expression and 89Zr-labeled cetuximab uptake assessed with PET. J Nucl Med 50(1):123–131
Spiegelberg D, Mortensen AC, Selvaraju RK, Eriksson O, Stenerlow B, Nestor M (2016) Molecular imaging of EGFR and CD44v6 for prediction and response monitoring of HSP90 inhibition in an in vivo squamous cell carcinoma model. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43(5):974–982
Shih YH, Peng CL, Lee SY, Chiang PF, Yao CJ, Lin WJ, Luo TY, Shieh MJ (2015) 111In-cetuximab as a diagnostic agent by accessible epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor targeting in human metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6(18):16601–16610
Guo Y, Parry JJ, Laforest R, Rogers BE, Anderson CJ (2013) The role of p53 in combination radioimmunotherapy with 64Cu-DOTA-cetuximab and cisplatin in a mouse model of colorectal cancer. J Nucl Med 54(9):1621–1629
Zeng D, Guo Y, White AG, Cai Z, Modi J, Ferdani R, Anderson CJ (2014) Comparison of conjugation strategies of cross-bridged macrocyclic chelators with cetuximab for copper-64 radiolabeling and PET imaging of EGFR in colorectal tumor-bearing mice. Mol Pharm 11(11):3980–3987
Qiu L, Tan H, Lin Q, Si Z, Mao W, Wang T, Fu Z, Cheng D, Shi H (2020) A pretargeted imaging strategy for immune checkpoint ligand PD-L1 expression in tumor based on bioorthogonal Diels-Alder click chemistry. Mol Imaging Biol 22(4):842–853
Gostring L, Chew MT, Orlova A et al (2010) Quantification of internalization of EGFR-binding affibody molecules: methodological aspects. Int J Oncol 36(4):757–763
Vincenzi B, Schiavon G, Silletta M, Santini D, Tonini G (2008) The biological properties of cetuximab. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 68(2):93–106
Garcia MF, Gallazzi F, Junqueira MS, Fernandez M, Camacho X, Mororo JDS et al (2018) Synthesis of hydrophilic HYNIC-[1,2,4,5].tetrazine conjugates and their use in antibody pretargeting with 99mTc. Org Biomol Chem 16(29):5275–5285
Rossin R, Verkerk PR, van den Bosch SM, Vulders RC, Verel I, Lub J et al (2010) In vivo chemistry for pretargeted tumor imaging in live mice. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49(19):3375–3378
Rossin R, Lappchen T, van den Bosch SM, Laforest R, Robillard MS (2013) Diels-Alder reaction for tumor pretargeting: in vivo chemistry can boost tumor radiation dose compared with directly labeled antibody. J Nucl Med 54(11):1989–1995
Garcia MF, Zhang X, Shah M, Newton-Northup J, Cabral P, Cerecetto H et al (2016) 99mTc-bioorthogonal click chemistry reagent for in vivo pretargeted imaging. Bioorg Med Chem 24(6):1209–1215
Zeglis BM, Sevak KK, Reiner T, Mohindra P, Carlin SD, Zanzonico P, Weissleder R, Lewis JS (2013) A pretargeted PET imaging strategy based on bioorthogonal Diels-Alder click chemistry. J Nucl Med 54(8):1389–1396
Zeglis BM, Brand C, Abdel-Atti D, Carnazza KE, Cook BE, Carlin S, Reiner T, Lewis JS (2015) Optimization of a pretargeted strategy for the PET imaging of colorectal carcinoma via the modulation of radioligand pharmacokinetics. Mol Pharm 12(10):3575–3587
Rossin R, van den Bosch SM, Ten HW, Carvelli M, Versteegen RM, Lub J et al (2013) Highly reactive trans-cyclooctene tags with improved stability for Diels-Alder chemistry in living systems. Bioconjug Chem 24(7):1210–1217
Qiu L, Mao W, Yin H et al (2019) Pretargeted nuclear imaging and radioimmunotherapy based on the inverse electron-demand Diels-Alder reaction and key factors in the pretargeted synthetic design. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2019:9182476
Nichols B, Qin Z, Yang J, Vera DR, Devaraj NK (2014) 68Ga chelating bioorthogonal tetrazine polymers for the multistep labeling of cancer biomarkers. Chem Commun (Camb). 50(40):5215–5217
Devaraj NK, Thurber GM, Keliher EJ, Marinelli B, Weissleder R (2012) Reactive polymer enables efficient in vivo bioorthogonal chemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(13):4762–4767
Garcia GE, Schweinsberg C, Maes V, Brans L, Blauenstein P, Tourwe DA et al (2008) Influence of the molecular charge on the biodistribution of bombesin analogues labeled with the [99mTc(CO)3]-core. Bioconjug Chem 19(12):2409–2416
Tsiapa I, Loudos G, Varvarigou A, Fragogeorgi E, Psimadas D, Tsotakos T, Xanthopoulos S, Mihailidis D, Bouziotis P, Nikiforidis GC, Kagadis GC (2013) Biological evaluation of an ornithine-modified 99mTc-labeled RGD peptide as an angiogenesis imaging agent. Nucl Med Biol 40(2):262–272
Antunes P, Ginj M, Walter MA, Chen J, Reubi JC, Maecke HR (2007) Influence of different spacers on the biological profile of a DOTA-somatostatin analogue. Bioconjug Chem 18(1):84–92
Meyer JP, Kozlowski P, Jackson J, Cunanan KM, Adumeau P, Dilling TR, Zeglis BM, Lewis JS (2017) Exploring structural parameters for pretargeting radioligand optimization. J Med Chem 60(19):8201–8217
Janzer M, Larbig G, Kubelbeck A, Wischnjow A, Haberkorn U, Mier W (2016) Drug conjugation affects pharmacokinetics and specificity of kidney-targeted peptide carriers. Bioconjug Chem 27(10):2441–2449
Flook AM, Yang J, Miao Y (2014) Substitution of the Lys linker with the beta-Ala linker dramatically decreased the renal uptake of 99mTc-labeled Arg-X-Asp-conjugated and X-Ala-Asp-conjugated alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone peptides. J Med Chem 57(21):9010–9018
Meyer JP, Houghton JL, Kozlowski P, Abdel-Atti D, Reiner T, Pillarsetty NVK, Scholz WW, Zeglis BM, Lewis JS (2016) 18F-based pretargeted PET imaging based on bioorthogonal Diels-Alder click chemistry. Bioconjug Chem 27(2):298–301
Houghton JL, Membreno R, Abdel-Atti D, Cunanan KM, Carlin S, Scholz WW, Zanzonico PB, Lewis JS, Zeglis BM (2017) Establishment of the in vivo efficacy of pretargeted radioimmunotherapy utilizing inverse electron demand Diels-Alder click chemistry. Mol Cancer Ther 16(1):124–133
Evans HL, Nguyen QD, Carroll LS, Kaliszczak M, Twyman FJ, Spivey AC, Aboagye EO (2014) A bioorthogonal 68Ga-labelling strategy for rapid in vivo imaging. Chem Commun (Camb) 50(67):9557–9560
Membreno R, Cook BE, Fung K, Lewis JS, Zeglis BM (2018) Click-mediated pretargeted radioimmunotherapy of colorectal carcinoma. Mol Pharm 15(4):1729–1734
Houghton JL, Zeglis BM, Abdel-Atti D, Sawada R, Scholz WW, Lewis JS (2016) Pretargeted immuno-PET of pancreatic cancer: overcoming circulating antigen and internalized antibody to reduce radiation doses. J Nucl Med 57(3):453–459
Keinänen O, Fung K, Pourat J et al (2017) Pretargeting of internalizing trastuzumab and cetuximab with a 18F-tetrazine tracer in xenograft models. EJNMMI Res 7(1):1–12
Shi X, Gao K, Huang H, Gao R (2018) Pretargeted immuno-PET based on bioorthogonal chemistry for imaging EGFR positive colorectal cancer. Bioconjug Chem 29(2):250–254
Acknowledgments
We want to thank for the technical supports Prof. Yingjian Zhang and Dr. Jianping Zhang from Center for Biomedical Imaging, Fudan University and Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Molecular Imaging Probes.
Funding
This study was funded partly by The National Nature Science Foundation of China (11875114, 81671735, 81871407, and 81701730); Open Large Infrastructure Research of Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai Municipal Population and Family Planning Commission (19YF 1408300); and the Training Program for Excellent Young Medical Talents of Zhongshan Hospital of Fudan University (2019ZSYQ28).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable institutional and/or national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 648 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, L., Lin, Q., Si, Z. et al. A Pretargeted Imaging Strategy for EGFR-Positive Colorectal Carcinoma via Modulation of Tz-Radioligand Pharmacokinetics. Mol Imaging Biol 23, 38–51 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-020-01539-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-020-01539-z