Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the potential of PEGylated dimeric GX1 peptide as a radiotracer for imaging of colorectal cancer vasculature in a LoVo tumor xenografted mouse model.
Procedures
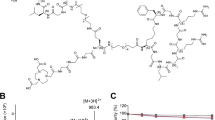
The [99mTc]PEG-(GX1)2 peptide was synthesized and identified. Confocal immunofluorescence analysis, receptor binding assay, and competitive inhibition assay were performed to evaluate the binding specificity and the receptor binding affinity of PEG-(GX1)2 to Co-human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Single photon emission computed tomography imaging and biodistribution were performed to evaluate the targeting ability of PEG-(GX1)2 to colorectal cancer.
Results
The studies in vitro suggested that PEG-(GX1)2 co-localized with Factor VIII in the perinuclear cytoplasm of Co-HUVECs and bound specifically to Co-HUVECs with a high affinity. The studies in vivo demonstrated that the targeting efficacy of PEG-(GX1)2 was superior to GX1.
Conclusions
PEGylation improved the affinity and the targeting ability of the GX1 peptide. PEG-(GX1)2 is a more promising probe for imaging of colorectal vasculature than GX1.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Komizu Y, Ueoka H, Goto K, Ueoka R (2011) Remarkable inhibitory effects of hybrid liposomes on growth of human colon cancer cells through induction of cell cycle arrest along with apoptosis. Int J Nanomedicine 6:1913–1920
Danaei G, Vander HS, Lopez AD et al (2005) Causes of cancer in the world: comparative risk assessment of nine behavioural and environmental risk factors. Lancet 366:1784–1793
Center MM, Jemal A, Ward E (2009) International trends in colorectal cancer incidence rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 18:1688–1694
Jia Y, Liu M, Huang W et al (2012) Recombinant human endostatin endostar inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in a mouse xenograft model of colon cancer. Pathol Oncol Res 18:315–323
Zhi M, Wu KC, Dong L et al (2004) Characterization of a specific phage-displayed peptide binding to vasculature of human gastric cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 3:1232–1235
Chen K, Sun X, Niu G et al (2012) Evaluation of 64Cu labeled GX1: a phage display peptide probe for PET imaging of tumor vasculature. Mol Imaging Biol 14:96–105
Chen K, Yap LP, Park R et al (2012) A Cy5.5-labeled phage-displayed peptide probe for near-infrared fluorescence imaging of tumor vasculature in living mice. Amino Acids 42:1329–1337
Cao S, Liu Y, Li X et al (2009) Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant protein GX1-rmhTNFalpha. Mol Biotechnol 43:1–7
Chen B, Cao S, Zhang Y et al (2009) A novel peptide (GX1) homing to gastric cancer vasculature inhibits angiogenesis and cooperates with TNF alpha in anti-tumor therapy. BMC Cell Biol 10:63
Hui X, Han Y, Liang S et al (2008) Specific targeting of the vasculature of gastric cancer by a new tumor-homing peptide CGNSNPKSC. J Control Release 131:86–93
Li W, Lang L, Niu G et al (2012) N-Succinimidyl 4-[(18)F]-fluoromethylbenzoate-labeled dimeric RGD peptide for imaging tumor integrin expression. Amino Acids 43:1349–1357
Guo N, Lang L, Gao H et al (2012) Quantitative analysis and parametric imaging of 18 F-labeled monomeric and dimeric RGD peptides using compartment model. Mol Imaging Biol 14:743–752
Liu Z, Shi J, Jia B et al (2011) Two (9)(0)Y-labeled multimeric RGD peptides RGD4 and 3PRGD2 for integrin targeted radionuclide therapy. Mol Pharm 8:591–599
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG, Minick CR (1973) Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest 52:2745–2756
Liang S, Lin T, Ding J et al (2006) Screening and identification of vascular-endothelial-cell-specific binding peptide in gastric cancer. J Mol Med (Berl) 84:764–773
Strippoli R, Benedicto I, Foronda M et al (2010) p38 maintains E-cadherin expression by modulating TAK1-NF-kappa B during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Sci 123:4321–4331
Hussain T, Nguyen QT (2014) Molecular imaging for cancer diagnosis and surgery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 66:90–100
Chen K, Chen X (2010) Design and development of molecular imaging probes. Curr Top Med Chem 10:1227–1236
Cai W, Gambhir SS, Chen X (2008) Chapter 7. Molecular imaging of tumor vasculature. Methods Enzymol 445:141–176
Chen K, Chen X (2011) Positron emission tomography imaging of cancer biology: current status and future prospects. Semin Oncol 38:70–86
Palomero J, Vegliante MC, Rodriguez ML, et al (2014) SOX11 promotes tumor angiogenesis through transcriptional regulation of PDGFA in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood
Shao Y, Liang W, Kang F et al (2014) A direct comparison of tumor angiogenesis with (68)Ga-labeled NGR and RGD peptides in HT-1080 tumor xenografts using microPET imaging. Amino Acids 46:2355–2364
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Folkman J (2002) Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol 29:15–18
Hollenbach M, Stoll SJ, Jorgens K et al (2013) Different regulation of physiological and tumor angiogenesis in zebrafish by protein kinase D1 (PKD1). PLoS One 8:e68033
Bergers G, Benjamin LE (2003) Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer 3:401–410
Seneviratne D, Ma J, Tan X, et al (2014) Genomic instability causes HGF gene activation in colon cancer cells, promoting their resistance to necroptosis. Gastroenterology
Vernin C, Thenoz M, Pinatel C et al (2014) HTLV-1 bZIP factor HBZ promotes cell proliferation and genetic instability by activating oncomiRs. Cancer Res 74:6082–6093
Folkman J (2003) Angiogenesis and apoptosis. Semin Cancer Biol 13:159–167
Neri D, Bicknell R (2005) Tumour vascular targeting. Nat Rev Cancer 5:436–446
Deutscher SL (2010) Phage display in molecular imaging and diagnosis of cancer. Chem Rev 110:3196–3211
Ueberberg S, Schneider S (2010) Phage library-screening: a powerful approach for generation of targeting-agents specific for normal pancreatic islet-cells and islet-cell carcinoma in vivo. Regul Pept 160:1–8
Dezsi L, Fulop T, Meszaros T et al (2014) Features of complement activation-related pseudoallergy to liposomes with different surface charge and PEGylation: comparison of the porcine and rat responses. J Control Release 195:2–10
Holm LS, Mcumber A, Rasmussen JE et al (2014) The effect of protein PEGylation on physical stability in liquid formulation. J Pharm Sci 103:3043–3054
Vine KL, Lobov S, Chandran VI, et al (2014) Improved pharmacokinetic and biodistribution properties of the selective urokinase inhibitor PAI-2 (SerpinB2) by site-specific PEGylation: implications for drug delivery. Pharm Res DOI 1-.1007/s11096-014-1517-x
Liu J, Wang Z, He J et al (2014) Effect of site-specific PEGylation on the fibrinolytic activity, immunogenicity, and pharmacokinetics of staphylokinase. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 46:782–791
Dijkgraaf I, Yim CB, Franssen GM et al (2011) PET imaging of alphavbeta(3) integrin expression in tumours with (6)(8)Ga-labelled mono-, di- and tetrameric RGD peptides. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38:128–137
Liu S, Hsieh WY, Jiang Y et al (2007) Evaluation of a (99 m)Tc-labeled cyclic RGD tetramer for noninvasive imaging integrin alpha(v)beta3-positive breast cancer. Bioconjug Chem 18:438–446
Henriques ST, Costa J, Castanho MA (2005) Translocation of beta-galactosidase mediated by the cell-penetrating peptide pep-1 into lipid vesicles and human HeLa cells is driven by membrane electrostatic potential. Biochemistry-Us 44:10189–10198
Deshayes S, Heitz A, Morris MC et al (2004) Insight into the mechanism of internalization of the cell-penetrating carrier peptide Pep-1 through conformational analysis. Biochemistry-Us 43:1449–1457
Li YJ, Li XH, Wang LF et al (2014) Therapeutic efficacy of a novel non-peptide alphavbeta3 integrin antagonist for pathological retinal angiogenesis in mice. Exp Eye Res 129:119–126
Lai KC, Hsu SC, Yang JS et al (2014) Diallyltrisulfide inhibits migration, invasion and angiogenesis of human colon cancer HT-29 cells and umbilical vein endothelial cells, and suppresses murine xenograft tumour growth. J Cell Mol Med. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12486
Segaliny AI, Mohamadi A, Dizier B et al (2014) Interleukin-34 promotes tumor progression and metastatic process in osteosarcoma through induction of angiogenesis and macrophage recruitment. Int J Cancer. doi:10.1002/ijc.29376
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81090270, No. 81090273, No. 81471717 and No. 81371615), the National Key and Basic Research Development Program of China (No. 2010CB529302), and Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2013 K12-05-11). We thank Dr. Zhe Wang and Wenhui Ma for their help in SPECT imaging.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jipeng Yin, Xiaoli Hui and Liping Yao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, J., Hui, X., Yao, L. et al. Evaluation of Tc-99 m Labeled Dimeric GX1 Peptides for Imaging of Colorectal Cancer Vasculature. Mol Imaging Biol 17, 661–670 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-015-0838-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-015-0838-4