Abstract
Introduction
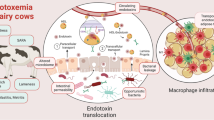
The effects of lipopolysaccharides (i.e., endotoxin; LPS) on metabolism are poorly defined in lactating dairy cattle experiencing hyperlipidemia.
Objectives
Our objective was to explore the effects of acute intravenous LPS administration on metabolism in late-lactation Holstein cows experiencing hyperlipidemia induced by intravenous triglyceride infusion and feed restriction.
Methods
Ten non-pregnant lactating Holstein cows (273 ± 35 d in milk) were administered a single bolus of saline (3 mL of saline; n \(=\) 5) or LPS (0.375 \(\mu\)g of LPS/kg of body weight; n \(=\) 5). Simultaneously, cows were intravenously infused a triglyceride emulsion and feed restricted for 16 h to induce hyperlipidemia in an attempt to model the periparturient period. Blood was sampled at routine intervals. Changes in circulating total fatty acid concentrations and inflammatory parameters were measured. Plasma samples were analyzed using untargeted lipidomics and metabolomics.
Results
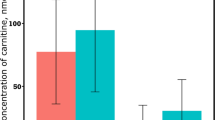
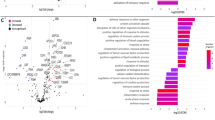
Endotoxin increased circulating serum amyloid A, LPS-binding protein, and cortisol concentrations. Endotoxin administration decreased plasma lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) concentrations and increased select plasma ceramide concentrations. These outcomes suggest modulation of the immune response and insulin action. Lipopolysaccharide decreased the ratio of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanomanine, which potentially indicate a decrease in the hepatic activation of phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase and triglyceride export. Endotoxin administration also increased plasma concentrations of pyruvic and lactic acids, and decreased plasma citric acid concentrations, which implicate the upregulation of glycolysis and downregulation of the citric acid cycle (i.e., the Warburg effect), potentially in leukocytes.
Conclusion
Acute intravenous LPS administration decreased circulating LPC concentrations, modified ceramide and glycerophospholipid concentrations, and influenced intermediary metabolism in dairy cows experiencing hyperlipidemia.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The plasma metabolome and lipidome datasets generated are available on demand in the Cornell Biotechnology Server.
References
Abad, B., Mesonero, J., Salvador, M., et al. (2001). The administration of lipopolysaccharide, in vivo, induces alteration in l-leucine intestinal absorption. Life Sciences, 70(6), 615–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(01)01440-0
Ahmad, M. I., Ijaz, M. U., Hussain, M., et al. (2020). High-fat proteins drive dynamic changes in gut microbiota, hepatic metabolome, and endotoxemia-TLR-4-NF\(\kappa\)b-mediated inflammation in mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 68(42), 11710–11725. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02570.
Arendt, B. M., Ma, D. W., Simons, B., et al. (2013). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with lower hepatic and erythrocyte ratios of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanolamine. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 38(3), 334–340. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2012-0261 pMID: 23537027.
Aspichueta, P., Pérez, S., Ochoa, B., et al. (2005). Endotoxin promotes preferential periportal upregulation of VLDL secretion in the rat liver. Journal of Lipid Research, 46(5), 1017–1026. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.m500003-jlr200
Baumgard, L. H., & Rhoads, R. P. (2013). Effects of heat stress on postabsorptive metabolism and energetics. Annual Review of Animal Biosciences, 1(1), 311–337. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-animal-031412-103644 pMID: 25387022.
Berbee, J. F., Havekes, L. M., & Rensen, P. C. (2005). Apolipoproteins modulate the inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide. Journal of Endotoxin Research, 11(2), 97–103. https://doi.org/10.1177/09680519050110020501 PMID: 15949136.
Bradford, B. J., Mamedova, L. K., Minton, J. E., et al. (2009). Daily injection of tumor necrosis factor-\(\alpha\) increases hepatic triglycerides and alters transcript abundance of metabolic genes in lactating dairy cattle. The Journal of Nutrition, 139(8), 1451–1456. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.109.108233
Bruins, M. J., Soeters, P. B., & Deutz, N. E. P. (2000). Endotoxemia affects organ protein metabolism differently during prolonged feeding in pigs. The Journal of Nutrition, 130(12), 3003–3013. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/130.12.3003
Bruins, M. J., Soeters, P. B., Lamers, W. H., et al. (2002). l-Arginine supplementation in pigs decreases liver protein turnover and increases hindquarter protein turnover both during and after endotoxemia. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 75(6), 1031–1044. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/75.6.1031
Caixeta, L. S., Giesy, S. L., Krumm, C. S., et al. (2017). Effect of circulating glucagon and free fatty acids on hepatic FGF21 production in dairy cows. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 313(5), R526–R534. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00197.2017
Chavez, J., & Summers, S. (2012). A ceramide-centric view of insulin resistance. Cell Metabolism, 15(5), 585–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.002
Cheng, J., Bu, D., Wang, J., et al. (2014). Effects of rumen-protected \(\gamma\)-aminobutyric acid on performance and nutrient digestibility in heat-stressed dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science, 97(9), 5599–5607. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2013-6797
Chong, J., Soufan, O., Li, C., et al. (2018). MetaboAnalyst 4.0: towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 46(W1), W486–W494. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky310
Dai, S., Gao, F., Zhang, W., et al. (2011). Effects of dietary glutamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid on performance, carcass characteristics and serum parameters in broilers under circular heat stress. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 168(1), 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2011.03.005
Davis, A., Myers, W., Chang, C., et al. (2021). Somatotropin increases plasma ceramide in relation to enhanced milk yield in cows. Domestic Animal Endocrinology, 74(106), 480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.domaniend.2020.106480
Davis, A. N., Clegg, J. L., Perry, C. A., et al. (2017). Nutrient restriction increases circulating and hepatic ceramide in dairy cows displaying impaired insulin tolerance. Lipids, 52(9), 771–780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-017-4287-5
Dosogne, H., Meyer, E., Sturk, A., et al. (2002). Effect of enrofloxacin treatment on plasma endotoxin during bovine escherichia coli mastitis. Inflammation Research, 51(4), 201–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00000293
Drobnik, W., Liebisch, G., Audebert, F. X., et al. (2003). Plasma ceramide and lysophosphatidylcholine inversely correlate with mortality in sepsis patients. Journal of Lipid Research, 44(4), 754–761. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.m200401-jlr200
Eckel, E. F., & Ametaj, B. N. (2016). Invited review: Role of bacterial endotoxins in the etiopathogenesis of periparturient diseases of transition dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science, 99(8), 5967–5990. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2015-10727
Gardiner, K. R., Gardiner, R. E., & Barbul, A. (1995). Reduced intestinal absorption of arginine during sepsis. Critical care medicine, 23(7), 1227–1232.
Goetzl, E. J., Graeler, M., Huang, M. C., et al. (2002). Lysophospholipid growth factors and their g protein-coupled receptors in immunity, coronary artery disease, and cancer. The Scientific World JOURNAL, 2, 324–338. https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2002.124
Goldansaz, S. A., Guo, A. C., Sajed, T., et al. (2017). Livestock metabolomics and the livestock metabolome: A systematic review. PLOS ONE, 12(5), e0177675. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0177675.
Gong, X., Guo, C., Huang, S., et al. (2006). Inhaled nitric oxide alleviates hyperoxia suppressed phosphatidylcholine synthesis in endotoxin-induced injury in mature rat lungs. Respiratory Research. https://doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-7-5
Gunn, B. G., Brown, A. R., Lambert, J. J., et al. (2011). Neurosteroids and gabaa receptor interactions: a focus on stress. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 5, 131.
Haji-Michael, P. G., Ladrière, L., Sener, A., et al. (1999). Leukocyte glycolysis and lactate output in animal sepsis and ex vivo human blood. Metabolism, 48(6), 779–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0026-0495(99)90179-8
Hasselgren, P. O., Pedersen, P., Sax, H. C., et al. (1988). Current concepts of protein turnover and amino acid transport in liver and skeletal muscle during sepsis. Archives of Surgery, 123(8), 992–999. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400320078016
Holland, W. L., Bikman, B. T., Wang, L. P., et al. (2011). Lipid-induced insulin resistance mediated by the proinflammatory receptor tlr4 requires saturated fatty acid-induced ceramide biosynthesis in mice. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 121(5), 1858–1870. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI43378
Horst, E., Kvidera, S., Dickson, M., et al. (2019). Effects of continuous and increasing lipopolysaccharide infusion on basal and stimulated metabolism in lactating holstein cows. Journal of Dairy Science, 102(4), 3584–3597. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2018-15627
Horst, E., van den Brink, L., Mayorga, E., et al. (2020). Evaluating acute inflammation’s effects on hepatic triglyceride content in experimentally induced hyperlipidemic dairy cows in late lactation. Journal of Dairy Science, 103(10), 9620–9633. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2020-18686
Jacobsen, S., Andersen, P., Toelboell, T., et al. (2004). Dose dependency and individual variability of the lipopolysaccharide-induced bovine acute phase protein response. Journal of Dairy Science, 87(10), 3330–3339. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(04)73469-4
Jahoor, F., Wykes, L., Del Rosario, M., et al. (1999). Chronic protein undernutrition and an acute inflammatory stimulus elicit different protein kinetic responses in plasma but not in muscle of piglets. The Journal of Nutrition, 129(3), 693–699. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/129.3.693
Ji, Y., Dai, Z., Sun, S., et al. (2018). Hydroxyproline attenuates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice: Involvment of the nf-\(\kappa\)b signaling and oxidative stress. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 62(21), 1800494. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201800494.
Jiang, T., Gao, X., Wu, C. et al. (2016). Apple-derived pectin modulates gut microbiota, improves gut barrier function, and attenuates metabolic endotoxemia in rats with diet-induced obesity. Nutrients 8(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8030126, https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/8/3/126.
Kabarowski, J. H., Xu, Y., & Witte, O. N. (2002). Lysophosphatidylcholine as a ligand for immunoregulation. Biochemical Pharmacology, 64(2), 161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-2952(02)01179-6
Kabarowski, J. H. S., Zhu, K., Le, L. Q., et al. (2001). Lysophosphatidylcholine as a ligand for the immunoregulatory receptor g2a. Science, 293(5530), 702–705. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1061781
Kawakami, M., & Cerami, A. (1981). Studies of endotoxin-induced decrease in lipoprotein lipase activity. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 154(3), 631–639. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.154.3.631
Kenéz, Á., Dänicke, S., Rolle-Kampczyk, U., et al. (2016). A metabolomics approach to characterize phenotypes of metabolic transition from late pregnancy to early lactation in dairy cows. Metabolomics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1112-8
Krawczyk, C. M., Holowka, T., Sun, J., et al. (2010). Toll-like receptor-induced changes in glycolytic metabolism regulate dendritic cell activation. Blood, 115(23), 4742–4749. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-10-249540
Kumar Srivastava, A., Khare, P., Kumar Nagar, H., et al. (2016). Hydroxyproline: a potential biochemical marker and its role in the pathogenesis of different diseases. Current Protein and Peptide Science, 17(6), 596–602.
Kvidera, S., Horst, E., Abuajamieh, M., et al. (2017). Glucose requirements of an activated immune system in lactating holstein cows. Journal of Dairy Science, 100(3), 2360–2374. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2016-12001
Lang, C. H., Obih, J. A., Bagby, G. J., et al. (1991). Endotoxin-induced increases in regional glucose utilization by small intestine: a tnf-independent effect. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 260(4), G548–G555. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.4.G548 pMID: 2018131.
Law, S.H., Chan, M.L., Marathe, G.K. et al. (2019). An updated review of lysophosphatidylcholine metabolism in human diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051149, https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/20/5/1149
Le Floc’h, N., Melchior, D., & Obled, C. (2004). Modifications of protein and amino acid metabolism during inflammation and immune system activation. Livestock Production Science, 87(1), 37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livprodsci.2003.09.005
Lee, E. H., Shin, M. H., Park, J. M., et al. (2020). Diagnosis and mortality prediction of sepsis via lysophosphatidylcholine 16:0 measured by MALDI-TOF MS. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70799-0
Leung, Y.H., Christiane Bäßler, S., Koch, C. et al. (2020). Sphingolipid profiling reveals different extent of ceramide accumulation in bovine retroperitoneal and subcutaneous adipose tissues. Metabolites 10(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10110473, https://www.mdpi.com/2218-1989/10/11/473.
Li, W., Zhang, W., Deng, M., et al. (2018). Stearoyl lysophosphatidylcholine inhibits endotoxin-induced caspase-11 activation. Shock, 50(3), 339–345. https://doi.org/10.1097/shk.0000000000001012
Liew, F. Y., Xu, D., Brint, E. K., et al. (2005). Negative regulation of toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses. Nature Reviews Immunology, 5(6), 446–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1630
Liu, P., Zhu, W., Chen, C., et al. (2020). The mechanisms of lysophosphatidylcholine in the development of diseases. Life Sciences, 247(117), 443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117443
Lozano, J., Berra, E., Municio, M., et al. (1994). Protein kinase c zeta isoform is critical for kappa b-dependent promoter activation by sphingomyelinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269(30), 19200–19202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(17)32152-X.
Lu, J., Fernandes, E. A., Cano, A. E. P., et al. (2013). Changes in milk proteome and metabolome associated with dry period length, energy balance, and lactation stage in postparturient dairy cows. Journal of Proteome Research, 12(7), 3288–3296. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr4001306
Mao, S., Zhang, R., Wang, D., et al. (2013). Impact of subacute ruminal acidosis (sara) adaptation on rumen microbiota in dairy cattle using pyrosequencing. Anaerobe, 24, 12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2013.08.003
Mateus, L., Lopes da Costa, L., Diniz, P., et al. (2003). Relationship between endotoxin and prostaglandin (pge2 and pgfm) concentrations and ovarian function in dairy cows with puerperal endometritis. Animal Reproduction Science, 76(3), 143–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4320(02)00248-8
McFadden, J., & Rico, J. (2019). Invited review: Sphingolipid biology in the dairy cow: The emerging role of ceramide. Journal of Dairy Science, 102(9), 7619–7639. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2018-16095
McFadden, J., Girard, C., Tao, S., et al. (2020). Symposium review: One-carbon metabolism and methyl donor nutrition in the dairy cow. Journal of Dairy Science, 103(6), 5668–5683. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2019-17319
McFadden, J. W. (2020). Review: Lipid biology in the periparturient dairy cow: contemporary perspectives. Animal, 14(S1), s165–s175. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731119003185
McNeil, C. J., Hoskin, S. O., Bremner, D. M., et al. (2016). Whole-body and splanchnic amino acid metabolism in sheep during an acute endotoxin challenge. British Journal of Nutrition, 116(2), 211–222. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114516001860
Murakami, N., Yokomizo, T., Okuno, T., et al. (2004). G2a is a proton-sensing g-protein-coupled receptor antagonized by lysophosphatidylcholine. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(41), 42484–42491. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m406561200.
Myers, W., Rico, J., Davis, A., et al. (2019). Effects of abomasal infusions of fatty acids and one-carbon donors on hepatic ceramide and phosphatidylcholine in lactating holstein dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science, 102(8), 7087–7101. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2018-16200
Newsholme, P., Curi, R., Pithon Curi, T., et al. (1999). Glutamine metabolism by lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils: its importance in health and disease11this review is written to mark the retirement of prof. eric a. newsholme, university of oxford, united kingdom, and to acknowledge his contribution to the field of immune cell metabolism. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 10(6), 316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-2863(99)00022-4
Palsson-McDermott, E. M., & O’Neill, L. A. J. (2013). The warburg effect then and now: From cancer to inflammatory diseases. BioEssays, 35(11), 965–973. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201300084
Pandian, R. P., Kutala, V. K., Liaugminas, A., et al. (2005). Lipopolysaccharide-induced alterations in oxygen consumption and radical generation in endothelial cells. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 278(1–2), 119–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-6936-x
Park, D. W., Kwak, D. S., Park, Y. Y., et al. (2014). Impact of serial measurements of lysophosphatidylcholine on 28-day mortality prediction in patients admitted to the intensive care unit with severe sepsis or septic shock. Journal of Critical Care, 29(5), 882.e5-882.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.05.003
Pires, J., Souza, A., & Grummer, R. (2007). Induction of hyperlipidemia by intravenous infusion of tallow emulsion causes insulin resistance in holstein cows. Journal of Dairy Science, 90(6), 2735–2744. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2006-759
Rico, J., Bandaru, V., Dorskind, J., et al. (2015). Plasma ceramides are elevated in overweight holstein dairy cows experiencing greater lipolysis and insulin resistance during the transition from late pregnancy to early lactation. Journal of Dairy Science, 98(11), 7757–7770. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2015-9519
Rico, J., Myers, W., Laub, D., et al. (2018). Hot topic: Ceramide inhibits insulin sensitivity in primary bovine adipocytes. Journal of Dairy Science, 101(4), 3428–3432. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-13983
Rico, J. E., Giesy, S. L., Haughey, N. J., et al. (2018). Intravenous triacylglycerol infusion promotes ceramide accumulation and hepatic steatosis in dairy cows. The Journal of Nutrition, 148(10), 1529–1535. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxy155
Rico, J. E., Saed Samii, S., Zang, Y., et al. (2021). Characterization of the plasma lipidome in dairy cattle transitioning from gestation to lactation: Identifying novel biomarkers of metabolic impairment. Metabolites. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050290
Sakaguchi, O., & SAKAGUCHI, S. (1979). Alterations of lipid metabolism in mice injected with endotoxin. Microbiology and Immunology, 23(2), 71–85.
Schuster, D. P., Brody, S. L., Zhou, Z., et al. (2007). Regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced increases in neutrophil glucose uptake. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 292(4), L845–L851. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00350.2006 pMID: 17122354.
Shoelson, S. E., Lee, J., & Goldfine, A. B. (2006). Inflammation and insulin resistance. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 116(7), 1793–1801. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI29069
Tian, J., Dang, H., Nguyen, A. V., et al. (2014). Combined therapy With GABA and Proinsulin/Alum acts synergistically to restore long-term normoglycemia by modulating T-cell autoimmunity and promoting \(\beta\)-cell replication in newly diabetic NOD mice. Diabetes, 63(9), 3128–3134. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-1385
Tokumura, A. (2002). Physiological and pathophysiological roles of lysophosphatidic acids produced by secretory lysophospholipase d in body fluids. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 1582(1), 18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-1981(02)00133-6 lysolipid Mediators in Cell Signalling and Disease.
Vakharia, K., & Hinson, J. P. (2005). Lipopolysaccharide directly stimulates cortisol secretion by human adrenal cells by a cyclooxygenase-dependent mechanism. Endocrinology, 146(3), 1398–1402. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2004-0882
van der Veen, J. N., Kennelly, J. P., Wan, S., et al. (2017). The critical role of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes, 1859(9, Part B), 1558–1572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.04.006 membrane Lipid Therapy: Drugs Targeting Biomembranes.
Vats, D., Mukundan, L., Odegaard, J. I., et al. (2006). Oxidative metabolism and pgc-1\(\beta\) attenuate macrophage-mediated inflammation. Cell Metabolism, 4(1), 13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2006.05.011
Wang, Y. Y., Sun, S. P., Zhu, H. S., et al. (2018). Gaba regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of mac-t cells through the lps-induced tlr4 signaling pathway. Research in Veterinary Science, 118, 395–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2018.04.004
Xu, W., Vervoort, J., Saccenti, E., et al. (2018). Milk metabolomics data reveal the energy balance of individual dairy cows in early lactation. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34190-4
Yan, J. J., Jung, J. S., Lee, J. E., et al. (2004). Therapeutic effects of lysophosphatidylcholine in experimental sepsis. Nature Medicine, 10(2), 161–167. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm989
Yang, L., Xie, M., Yang, M., et al. (2014). PKM2 regulates the warburg effect and promotes HMGB1 release in sepsis. Nature Communications. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5436
Funding
This work is supported by Agriculture and Food Research Initiative Grant No. 2018-67015-27548 from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors’ responsibilities were as follows: EAH and LHB developed the experimental design and conducted sampling; MED Rubio performed the mass spectrometry analyses; FW analyzed data. FW, AJ, LW and JWM wrote the manuscript. JWM and LHB conceptualized the idea and were responsible for final content. AJ and FW have equal contributions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Experimental procedures using animals were carried out in compliance with Iowa State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Javaid, A., Wang, F., Horst, E.A. et al. Effects of acute intravenous lipopolysaccharide administration on the plasma lipidome and metabolome in lactating Holstein cows experiencing hyperlipidemia. Metabolomics 18, 75 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-022-01928-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-022-01928-1