Abstract
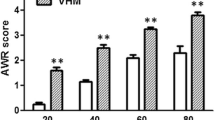
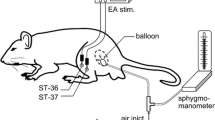
This study explored the role of P2X7 receptors in spinal cord astrocytes in the electroacupuncture-induced inhibition of visceral hypersensitivity (VH) in rats with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Visceral hypersensitivity of IBS was intracolonically induced by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS). Visceromotor responses to colorectal distension (CRD-20,40,60,80 mmHg) and abdominal withdrawal reflex scoring (AWRs) were recorded after electroacupuncture at bilateral Zusanli (ST36) and Sanyinjiao (SP6) acupoints to evaluate the analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on visceral pain in rats with IBS. Fluorocitric acid (FCA), an astrocyte activity inhibitor, was injected intrathecally before electroacupuncture intervention and AWRs were recorded. Western blot and real-time qPCR were used to detect the expression of NMDA and P2X7 receptor to observe the regulation effect of electroacupuncture on NMDA receptor in the spinal cord of rats with visceral hypersensitivity. Intrathecal injection of P2X7 agonist or antagonist was administered before electroacupuncture treatment. To observe the effect of P2X7 receptor in spinal astrocytes on the inhibition of visceral hyperalgesia by electroacupuncture, the changes of AWR score, NMDA receptor in the spinal cord, and GFAP expression in astrocytes were detected. Inflammation of the colon had basically subsided at day 21 post-TNBS; persistent visceral hypersensitivity could be suppressed by electroacupuncture. This analgesic effect could be inhibited by FCA. The analgesic effect, downregulation of NMDA receptor NR1 subunit, and P2X7 protein of electroacupuncture were all reversed by FCA. P2X7 receptor antagonist A740003 can cooperate with EA to carry out analgesic effect in rats with visceral pain and downregulate the expression of NR1, NR2B, and GFAP in spinal dorsal horn. However, the P2X7 receptor agonist BzATP could partially reverse the analgesic effect of EA, inhibiting the downregulatory effect of EA on the expression of NR1, NR2B, and GFAP. These results indicate that EA may downregulate the expression of the NMDA receptor by inhibiting the P2X7 receptor in the spinal cord, thereby inhibiting spinal cord sensitization in IBS rats with visceral pain, in which astrocytes are an important medium.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Aziz I, Törnblom H, Palsson OS, Whitehead WE, Simrén M (2018) How the change in IBS criteria from Rome III to Rome IV impacts on clinical characteristics and key pathophysiological factors. Am J Gastroenterol 113:1017–1025
Chao G-Q, Zhang S (2014) Effectiveness of acupuncture to treat irritable bowel syndrome: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 20:1871–1877
Chen T, Zhang WW, Chu Y-X, Wang Y-Q (2020) Acupuncture for pain management: molecular mechanisms of action. Am J Chin Med 48:793–811
Chen Y, Li G, Huang L-YM (2015) p38 MAPK mediates glial P2X7R-neuronal P2Y1R inhibitory control of P2X3R expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Mol Pain 11:68
Chen Y, Zhang X, Wang C, Li G, Gu Y, Huang L-YM (2008) Activation of P2X7 receptors in glial satellite cells reduces pain through downregulation of P2X3 receptors in nociceptive neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:16773–16778
Chen Y, Zhao Y, Luo D-N, Zheng H, Li Y, Zhou S-Y (2019) Electroacupuncture regulates disorders of gut-brain interaction by decreasing corticotropin-releasing factor in a rat model of IBS. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2019:1759842
Chessell IP, Hatcher JP, Bountra C, Michel AD, Hughes JP, Green P, Egerton J, Murfin M, Richardson J, Peck WL, Grahames CBA, Casula MA, Yiangou Y, Birch R, Anand P, Buell GN (2005) Disruption of the P2X7 purinoceptor gene abolishes chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 114:386–396
Deiteren A, De Man JG, Ruyssers NE, Moreels TG, Pelckmans PA, De Winter BY (2014) Histamine H4 and H1 receptors contribute to postinflammatory visceral hypersensitivity. Gut 63:1873–1882
Drossman DA (2016) Functional gastrointestinal disorders: history, pathophysiology, clinical features, and Rome IV. Gastroenterology 150(6):1262-1279.e2. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.032
Enck P, Aziz Q, Barbara G, Farmer AD, Fukudo S, Mayer EA, Niesler B, Quigley EMM, Rajilić-Stojanović M, Schemann M, Schwille-Kiuntke J, Simren M, Zipfel S, Spiller RC (2016) Irritable bowel syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16014
Fan J, Xiaoyin W, Cao Z, Chen S, Owyang C, Li Y (2009) Up-regulation of anterior cingulate cortex NR2B receptors contributes to visceral pain responses in rats. Gastroenterology 136(5):1732-1740.e3. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2009.01.069
Fan F, Chen Y, Chen Z, Guan L, Ye Z, Tang Y, Chen A, Lin C (2021) Blockade of BK channels attenuates chronic visceral hypersensitivity in an IBS-like rat model. Mol Pain 17:17448069211040364
Fan Y, Ryu Y, Zhao R, Bills KB, Steffensen SC, Yang CH, Kim HY (2020) Enhanced spinal neuronal responses as a mechanism for increased number and size of active acupoints in visceral hyperalgesia. Sci Rep 10:10312
Finnerup NB, Kuner R, Jensen TS (2021) Neuropathic pain: from mechanisms to treatment. Physiol Rev 101(1):259–301
Gao YH, Li CW, Wang JY, Tan LH, Duanmu CL, Jing XH, Chang XR, Liu JL (2017) Effect of electroacupuncture on the cervicospinal P2X7 receptor/fractalkine/CX3CR1 signaling pathway in a rat neck-incision pain model. Purinergic Signal 13:215–225
Grundy L, Erickson A, Brierley SM (2019) Visceral Pain. Annu Rev Physiol 81:261–284
Hao Y, Niu H, An S, Wang M, Wang Z (2018) Downregulation of iNOS, IL-1β, and P2X7 expression in mast cells via activation of PAR4 contributes to the inhibition of visceral hyperalgesia in rats. J Immunol Res 2018:3256908
He JR, Yu SG, Tang Y, Illes P (2020) Purinergic signaling as a basis of acupuncture-induced analgesia. Purinergic Signal 16(3):297–304
Hou T, Xiang H, Yu L, Su W, Shu Y, Li H, Zhu H, Lin L, Hu X, Liang S, Zhang H, Li M (2019) Electroacupuncture inhibits visceral pain via adenosine receptors in mice with inflammatory bowel disease. Purinergic Signal 15:193–204
Illes P, Müller CE, Jacobson KA, Grutter T, Nicke A, Fountain SJ, Kennedy C, Schmalzing G, Jarvis MF, Stojilkovic SS, King BF, Di Virgilio F (2021) Update of P2X receptor properties and their pharmacology: IUPHAR Review 30. Br J Pharmacol 178:489–514
Larsson MB, Tillisch K, Craig AD, Engström M, Labus J, Naliboff B, Lundberg P, Ström M, Mayer EA, Walter SA (2012) Brain responses to visceral stimuli reflect visceral sensitivity thresholds in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 142:463–472
Legendre P, Rosenmund C, Westbrook GL (1993) Inactivation of NMDA channels in cultured hippocampal neurons by intracellular calcium. J Neurosci 13:674–684
Li Y, Yin C, Li X, Liu B, Wang J, Zheng X, Shao X, Liang Y, Junying D, Fang J, Liu B (2019) Electroacupuncture alleviates paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathic pain in rats via suppressing TLR4 signaling and TRPV1 upregulation in sensory neurons. Int J Mol Sci 20(23):5917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235917
Liu H-R, Fang X-Y, Wu H-G, Wu L-Y, Li J, Weng Z-J, Guo X-X, Li Y-G (2015) Effects of electroacupuncture on corticotropin-releasing hormone in rats with chronic visceral hypersensitivity. World J Gastroenterol 21:7181–7190
Liu H, Zhang Y, Qi D, Li W (2017) Downregulation of the spinal NMDA receptor NR2B subunit during electro-acupuncture relief of chronic visceral hyperalgesia. J Physiol Sci 67:197–206
Liu M, Kay JC, Shen S, Qiao L-Y (2015) Endogenous BDNF augments NMDA receptor phosphorylation in the spinal cord via PLCγ, PKC, and PI3K/Akt pathways during colitis. J Neuroinflamm 12:151
Luo X-Q, Cai Q-Y, Chen Y, Guo L-X, Chen A-Q, Wu Z-Q, Lin C (2014) Tyrosine phosphorylation of the NR2B subunit of the NMDA receptor in the spinal cord contributes to chronic visceral pain in rats. Brain Res 1542:167–175
Lv P-R, Su Y-S, He W, Wang X-Y, Shi H, Zhang X-N, Zhu B, Kan Y, Chen L-Z, Wu Q-F, Yu S-G, Jing X-H (2019) Electroacupuncture alleviated referral hindpaw hyperalgesia via suppressing spinal long-term potentiation (LTP) in TNBS-induced colitis rats. Neural Plast 2019:2098083
Lyubashina OA, Sivachenko IB, Panteleev SS (2020) Supraspinal mechanisms of intestinal hypersensitivity. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42:389–417
Manheimer E, Wieland LS, Cheng K, Li SM, Shen X, Berman BM, Lao L (2012) Acupuncture for irritable bowel syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 107:835–47
Ming Q, Zhang J, Xie Y, Cui M, Huang Y, Dou W, Liu Z, Yang Q, Zhao S, Wang X, Wang J (2015) Effects of electro-acupuncture at Zusanli point on the expression of P2X4 receptors as well as neurons and glia cells ultrastructure of Lumbar spinal cord in visceral pain rats induced by colon-rectum distention. Guiding Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology 21:7–10
Petrenko AB, Yamakura T, Baba H, Shimoji K (2003) The role of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in pain: a review. Anesth Analg 97:1108–1116
Qi Q, Chen F, Zhang W, Wang P, Li Y, Zuo X (2017) Colonic N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor contributes to visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 32:828–836
Qiao LY, Tiwari N (2020) Spinal neuron-glia-immune interaction in cross-organ sensitization. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 319:G748–G760
Simrén M, Törnblom H, Palsson OS, van Tilburg MAL, Van Oudenhove L, Tack J, Whitehead WE (2018) Visceral hypersensitivity is associated with GI symptom severity in functional GI disorders: consistent findings from five different patient cohorts. Gut 67:255–262
Tang Yong, Yin Hai-yan, Liu Juan, Rubini Patrizia, Illes Peter (2019) P2X receptors and acupuncture analgesia. Brain Res Bull 151:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.10.015
Tian G-H, Tao S-S, Chen M-T, Li Y-S, Li Y-P, Shang H-C, Tang X-Y, Chen J-X, Tang H-B (2016) Electroacupuncture treatment alleviates central poststroke pain by inhibiting brain neuronal apoptosis and aberrant astrocyte activation. Neural Plast 2016:1437148
Tian S-L, Wang X-Y, Ding G-H (2008) Repeated electro-acupuncture attenuates chronic visceral hypersensitivity and spinal cord NMDA receptor phosphorylation in a rat irritable bowel syndrome model. Life Sci 83:356–363
Traynelis SF, Wollmuth LP, McBain CJ, Menniti FS, Vance KM, Ogden KK, Hansen KB, Yuan H, Myers SJ, Dingledine R (2010) Glutamate receptor ion channels: structure, regulation, and function. Pharmacol Rev 62:405–496
Vermeulen W, De Man JG, Pelckmans PA, De Winter BY (2014) Neuroanatomy of lower gastrointestinal pain disorders. World J Gastroenterol 20:1005–1020
Wang YL, Su YS, He W, Jing XH (2019) Electroacupuncture relieved visceral and referred hindpaw hypersensitivity in colitis rats by inhibiting tyrosine hydroxylase expression in the sixth lumbar dorsal root ganglia. Neuropeptides 77:101957
Weng Z, Wu L, Lu Y, Wang L, Tan L, Dong M, Xin Y (2013) Electroacupuncture diminishes P2X2 and P2X3 purinergic receptor expression in dorsal root ganglia of rats with visceral hypersensitivity. Neural Regen Res 8:802–808
Weng ZJ, Wu LY, Zhou CL, Dou CZ, Shi Y, Liu HR, Wu HG (2015) Effect of electroacupuncture on P2X3 receptor regulation in the peripheral and central nervous systems of rats with visceral pain caused by irritable bowel syndrome. Purinergic Signal 11:321–329
Willert RP, Woolf CJ, Hobson AR, Delaney C, Thompson DG, Aziz Q (2004) The development and maintenance of human visceral pain hypersensitivity is dependent on the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Gastroenterology 126:683–692
Wu Q, Yue J, Lin L, Yu X, Zhou Y, Ying X, Chen X, Tu W, Lou X, Yang G, Zhou K, Jiang S (2021) Electroacupuncture may alleviate neuropathic pain via suppressing P2X7R expression. Mol Pain 17:1744806921997654
Xu GY, Winston JH, Chen JDZ (2009) Electroacupuncture attenuates visceral hyperalgesia and inhibits the enhanced excitability of colon specific sensory neurons in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil 21:1302-e1125
Xu J, Chen X-M, Zheng B-J, Wang X-R (2016) Electroacupuncture relieves nerve injury-induced pain hypersensitivity via the inhibition of spinal P2X7 receptor-positive microglia. Anesth Analg 122:882–892
Yu L, Wang W, Li L, Qin Q, Yu Y, Liu K, Zhao Y, Rong P, Zhu B (2019) Inhibition of electroacupuncture on nociceptive responses of dorsal horn neurons evoked by noxious colorectal distention in an intensity-dependent manner. J Pain Res 12:231–242
Yue N, Li B, Yang L, Han Q-Q, Huang H-J, Wang Y-L, Wang J, Yu R, Wu G-C, Liu Q, Yu J (2018) Electro-acupuncture alleviates chronic unpredictable stress-induced depressive- and anxiety-like behavior and hippocampal neuroinflammation in rat model of depression. Front Mol Neurosci 11:149
Zhang F, Ma Z, Weng Z, Zhao M, Zheng H, Wu L, Lu Y, Bao C, Liu Y, Liu H, Wu H (2020) P2X receptor in primary afferent neurons mediates the relief of visceral hypersensitivity by electroacupuncture in an irritable bowel syndrome rat model. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2020:8186106
Zhao M, Wang Z, Weng Z, Zhang F, Li G, Ma Z, Wu H, Xin Y, Liu H, Zhao J (2020) Electroacupuncture improves IBS visceral hypersensitivity by inhibiting the activation of astrocytes in the medial thalamus and anterior cingulate cortex. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020:2562979
Zhou J, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Wu B, Tan ZY (2019) Up-regulation of P2X7 Receptors Contributes to Spinal Microglial Activation and the Development of Pain Induced by BmK-I. Neurosci Bull 35(4):624–636
Zhu X, Liu Z, Qin Y, Niu W, Wang Q, Li L, Zhou J (2018) Analgesic effects of electroacupuncture at ST25 and CV12 in a rat model of postinflammatory irritable bowel syndrome visceral pain. Acupunct Med 36:240–246
Funding
This study was supported by the Health Industry Clinical Research Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (201940064), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81873367); Three-year Action Plan Project of Shanghai Traditional Chinese Medicine Development, No. ZY(2018–2020)-CCCX-2004–01; National Traditional Chinese Medicine Leading Talents Support Program-Qihuang Scholar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huangan Wu and Huirong Liu designed the research; Zhijun Weng, Min Zhao, Zhiying Zhang, and Yun Zhou performed the experiments; Fang Zhang and Yan Huang collected and analyzed the data; Yuhu Xin performed literature retrieval. Zhijun Weng and Shixiu Hu wrote the manuscript; all authors reviewed the manuscript prior to its submission, and read and approved the final manuscript. Zhijun Weng and Shixiu Hu contributed equally to this study.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All experiments were approved by the Committee for Medical Ethics and the Use of Experimental Animals at Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Informed consent
All authors have informed consent to the publication agreement required by Purinergic Signalling.
Authorship change form
All authors promise no change of author.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, Zj., Hu, Sx., Zhang, F. et al. Spinal cord astrocyte P2X7Rs mediate the inhibitory effect of electroacupuncture on visceral hypersensitivity of rat with irritable bowel syndrome. Purinergic Signalling 19, 43–53 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-021-09830-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-021-09830-6