Abstract
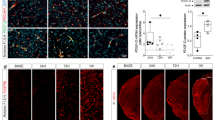
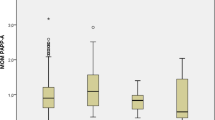
We aim to investigate whether A2A/nitric oxide-mediated regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression is impaired in feto-placental endothelial cells from late-onset pre-eclampsia. Cultures of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and human placental microvascular endothelial cells (hPMECs) from normal and pre-eclamptic pregnancies were used. Assays by using small interference RNA (siRNA) for A2A were performed, and transfected cells were used for estimation of messenger RNA (mRNA) levels of VEGF, as well as for cell proliferation and angiogenesis in vitro. CGS-21680 (A2A agonist, 24 h) increases HUVEC and hPMEC proliferation in a dose response manner. Furthermore, similar to CGS-21680, the nitric oxide donor, S-nitroso-N-acetyl-penicillamine oxide (SNAP), increased cell proliferation in a dose response manner (logEC50 10−9.2 M). In hPMEC, CGS-21680 increased VEGF protein levels in both normal (∼1.5-fold) and pre-eclamptic pregnancies (∼1.2-fold), an effect blocked by the A2A antagonist, ZM-241385 (10−5 M) and the inhibitor of NO synthase, N ω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME). Subsequently, SNAP partially recovered cell proliferation and in vitro angiogenesis capacity of cells from normal pregnancies exposed to siRNA for A2A. CGS-21680 also increased (∼1.5-fold) the level of VEGF mRNA in HUVEC from normal pregnancies, but not in pre-eclampsia. Additionally, transfection with siRNA for A2A decrease (∼30 %) the level of mRNA for VEGF in normal pregnancy compared to untransfected cells, an effect partially reversed by co-incubation with SNAP. The A2A-NO-VEGF pathway is present in endothelium from microcirculation and macrocirculation in both normal and pre-eclamptic pregnancies. However, NO signaling pathway seems to be impaired in HUVEC from pre-eclampsia.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CGS-21680:
-
2-(p-(2-Carbonyl-ethyl)-feniletilamino)-50-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine)
- BrdU:
-
5-Bromo-2-deoxyuridine
- SCH-58261:
-
7-(2-Phenylethyl)-5-amino-2-(2-furyl)-pyrazolo-(4,3-e)-1,2,4-triazolo(1,5-c)pyrimidine
- AR:
-
Adenosine receptors
- HMEC-1:
-
Dermal microvascular endothelial cells
- EOPE:
-
Early onset pre-eclampsia
- hPMEC:
-
Human placental microvascular endothelial cells
- HUVEC:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- LOPE:
-
Late-onset pre-eclampsia
- NECA:
-
N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- L-NAME:
-
N ω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Escudero C, Roberts JM, Myatt L, Feoktistov I (2014) Impaired adenosine-mediated angiogenesis in preeclampsia: potential implications for fetal programming. Front Pharmacol 5:134. doi:10.3389/fphar.2014.00134
Feoktistov I, Goldstein AE, Ryzhov S, Zeng D, Belardinelli L, Voyno-Yasenetskaya T, Biaggioni I (2002) Differential expression of adenosine receptors in human endothelial cells: role of A2B receptors in angiogenic factor regulation. Circ Res 90(5):531–538
Feoktistov I, Ryzhov S, Goldstein AE, Biaggioni I (2003) Mast cell-mediated stimulation of angiogenesis: cooperative interaction between A2B and A3 adenosine receptors. Circ Res 92(5):485–492. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000061572.10929.2D
Feoktistov I, Ryzhov S, Zhong H, Goldstein AE, Matafonov A, Zeng D, Biaggioni I (2004) Hypoxia modulates adenosine receptors in human endothelial and smooth muscle cells toward an A2B angiogenic phenotype. Hypertension 44(5):649–654. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000144800.21037.a5
Grant MB, Davis MI, Caballero S, Feoktistov I, Biaggioni I, Belardinelli L (2001) Proliferation, migration, and ERK activation in human retinal endothelial cells through a(2B) adenosine receptor stimulation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42(9):2068–2073
Grant MB, Tarnuzzer RW, Caballero S, Ozeck MJ, Davis MI, Spoerri PE, Feoktistov I, Biaggioni I, Shryock JC, Belardinelli L (1999) Adenosine receptor activation induces vascular endothelial growth factor in human retinal endothelial cells. Circ Res 85(8):699–706
Feoktistov I, Biaggioni I, Cronstein BN (2009) Adenosine receptors in wound healing, fibrosis and angiogenesis. Handb Exp Pharmacol 193:383–397. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-89615-9_13
Linden J (2005) Adenosine in tissue protection and tissue regeneration. Mol Pharmacol 67(5):1385–1387. doi:10.1124/mol.105.011783
Ryzhov S, McCaleb JL, Goldstein AE, Biaggioni I, Feoktistov I (2007) Role of adenosine receptors in the regulation of angiogenic factors and neovascularization in hypoxia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320(2):565–572. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.114850
Espinoza J, Espinoza AF, Power GG (2011) High fetal plasma adenosine concentration: a role for the fetus in preeclampsia? Am J Obstet Gynecol 205(5):485 . doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2011.06.034e424-487
Yoneyama Y, Sawa R, Suzuki S, Shin S, Power GG, Araki T (1996) The relationship between uterine artery Doppler velocimetry and umbilical venous adenosine levels in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 174(1 Pt 1):267–271
Iriyama T, Sun K, Parchim NF, Li J, Zhao C, Song A, Hart LA, Blackwell SC, Sibai BM, Chan LL, Chan TS, Hicks MJ, Blackburn MR, Kellems RE, Xia Y (2014) Elevated placental adenosine signaling contributes to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Circulation. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013740
Escudero C, Puebla C, Westermeier F, Sobrevia L (2009) Potential cell signalling mechanisms involved in differential placental angiogenesis in mild and severe pre-eclampsia. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 7(4):475–485
Escudero C, Bertoglia P, Hernadez M, Celis C, Gonzalez M, Aguayo C, Acurio J (2013) Impaired A2A adenosine receptor/nitric oxide/VEGF signaling pathway in fetal endothelium during late- and early-onset preeclampsia. Purinergic Signal 9(2):215–226. doi:10.1007/s11302-012-9341-4
Kingdom J, Huppertz B, Seaward G, Kaufmann P (2000) Development of the placental villous tree and its consequences for fetal growth. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 92(1):35–43
Kingdom JC, Kaufmann P (1997) Oxygen and placental villous development: origins of fetal hypoxia. Placenta 18(8):613–621 discussion 623-616
Resta L, Capobianco C, Marzullo A, Piscitelli D, Sanguedolce F, Schena FP, Gesualdo L (2006) Confocal laser scanning microscope study of terminal villi vessels in normal term and pre-eclamptic placentas. Placenta 27(6–7):735–739. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2005.07.006
Escudero C, Celis C, Saez T, San Martin S, Valenzuela FJ, Aguayo C, Bertoglia P, Roberts JM, Acurio J (2014) Increased placental angiogenesis in late and early onset pre-eclampsia is associated with differential activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2. Placenta 35(3):207–215. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2014.01.007
Mayhew TM (2009) A stereological perspective on placental morphology in normal and complicated pregnancies. [review] [97 refs. J Anat 215(1):77–90
Mayhew TM, Manwani R, Ohadike C, Wijesekara J, Baker PN (2007) The placenta in pre-eclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction: studies on exchange surface areas, diffusion distances and villous membrane diffusive conductances. Placenta 28(2–3):233–238. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2006.02.011
Mayhew TM, Ohadike C, Baker PN, Crocker IP, Mitchell C, Ong SS (2003) Stereological investigation of placental morphology in pregnancies complicated by pre-eclampsia with and without intrauterine growth restriction. Placenta 24(2–3):219–226
Egbor M, Ansari T, Morris N, Green CJ, Sibbons PD (2006) Morphometric placental villous and vascular abnormalities in early- and late-onset pre-eclampsia with and without fetal growth restriction. BJOG 113(5):580–589. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2006.00882.x
Gill JS, Salafia CM, Grebenkov D, Vvedensky DD (2011) Modeling oxygen transport in human placental terminal villi. J Theor Biol 291:33–41. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2011.09.008
Ahmad A, Ahmad S, Glover L, Miller SM, Shannon JM, Guo X, Franklin WA, Bridges JP, Schaack JB, Colgan SP, White CW (2009) Adenosine A2 A receptor is a unique angiogenic target of HIF-2alpha in pulmonary endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(26):10684–10689. doi:10.1073/pnas.0901326106
Desai A, Victor-Vega C, Gadangi S, Montesinos MC, Chu CC, Cronstein BN (2005) Adenosine A2 A receptor stimulation increases angiogenesis by down-regulating production of the antiangiogenic matrix protein thrombospondin 1. Mol Pharmacol 67(5):1406–1413. doi:10.1124/mol.104.007807
Dionisotti S, Ongini E, Zocchi C, Kull B, Arslan G, Fredholm BB (1997) Characterization of human A2 A adenosine receptors with the antagonist radioligand [3H]-SCH 58261. Br J Pharmacol 121(3):353–360. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0701119
Rees DD, Palmer RM, Schulz R, Hodson HF, Moncada S (1990) Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 101(3):746–752
Escudero C, Casanello P, Sobrevia L (2008) Human equilibrative nucleoside transporters 1 and 2 may be differentially modulated by A2B adenosine receptors in placenta microvascular endothelial cells from pre-eclampsia. Placenta 29(9):816–825. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2008.06.014
von Dadelszen P, Magee LA, Roberts JM (2003) Subclassification of preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy 22(2):143–148. doi:10.1081/PRG-120021060
Young BC, Levine RJ, Karumanchi SA (2010) Pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Annu Rev Pathol 5:173–192. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathol-121808-102149
Sezer SD, Kucuk M, Doger FK, Yuksel H, Odabasi AR, Turkmen MK, Cakmak BC, Omurlu IK, Kinas MG (2013) VEGF, PIGF and HIF-1alpha in placentas of early- and late-onset pre-eclamptic patients. Gynecol Endocrinol 29(8):797–800. doi:10.3109/09513590.2013.801437
Roberts JM, Escudero C (2012) The placenta in preeclampsia. Hypertension Pregnancy 2(2):72–83
Dye J, Lawrence L, Linge C, Leach L, Firth J, Clark P (2004) Distinct patterns of microvascular endothelial cell morphology are determined by extracellular matrix composition. Endothelium 11(3–4):151–167. doi:10.1080/10623320490512093
Escudero CGM, Acurio J, Valenzuela F, Sobrevia L (2013) The role of placenta in the fetal programming associated to gestational diabetes. Gestational Diabetes - Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment, vol 1. InTeach, Croacia
Escudero C, Sobrevia L (2009) Understanding physiological significance of high extracellular adenosine levels in feto-placental circulation in preeclamptic pregnancies. In: Sobrevia L, Casanello P (eds) Membrane transporters and receptors in disease, vol 1. Research Signpost, Kerala, India, pp. 27–51
Acurio J, Troncoso F, Bertoglia P, Salomon C, Aguayo C, Sobrevia L, Escudero C (2014) Potential role of A2B adenosine receptors on proliferation/migration of fetal endothelium derived from preeclamptic pregnancies. Biomed Res Int 2014:274507. doi:10.1155/2014/274507
Salsoso R, Guzman-Gutierrez E, Saez T, Bugueno K, Ramirez MA, Farias M, Pardo F, Leiva A, Sanhueza C, Mate A, Vazquez C, Sobrevia L (2015) Insulin restores L-arginine transport requiring adenosine receptors activation in umbilical vein endothelium from late-onset preeclampsia. Placenta 36(3):287–296. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2014.12.007
Myatt L (2010) Review: reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and functional adaptation of the placenta. Placenta 31(Suppl):S66–S69. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2009.12.021
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all research staff at the Vascular Physiology Laboratory and the Group of Investigation of Tumor Angiogenesis (GIANT) of the Universidad del Bío-Bío for their technical support. We also give thanks to researchers in the GRIVAS Health group for outstanding discussion regarding ideas presented in this manuscript. We thank Dr. Igor Feoktistov from University of Vanderbilt for active discussion and molecular tools kindly shared with our lab. This study was financed by Fondecyt Regular 1140586, Fondequip EQM140104, DIUBB GI153109/EF, and GI 152920/EF.
Individual contributions
This work was carried out as a full collaboration among all the authors. CE defined the research topic. JA, KH, FT, and CA prepared draft of the manuscript. PB is the clinical responsible for patient inclusion. CE, JA, and CA co-wrote the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Financial disclosure
None.
Conflict of interest
None
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5387 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acurio, J., Herlitz, K., Troncoso, F. et al. Adenosine A2A receptor regulates expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in feto-placental endothelium from normal and late-onset pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Purinergic Signalling 13, 51–60 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-016-9538-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-016-9538-z