Abstract
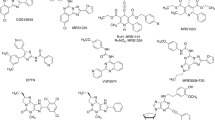
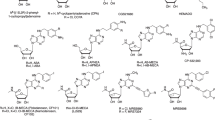
Adenosine receptors (ARs) have emerged as new drug targets. The majority of data on affinity/potency and selectivity of AR ligands described in the literature has been obtained for the human species. However, preclinical studies are mostly performed in mouse or rat, and standard AR agonists and antagonists are frequently used for studies in rodents without knowing their selectivity in the investigated species. In the present study, we selected a set of frequently used standard AR ligands, 8 agonists and 16 antagonists, and investigated them in radioligand binding studies at all four AR subtypes, A1, A2A, A2B, and A3, of three species, human, rat, and mouse. Recommended, selective agonists include CCPA (for A1AR of rat and mouse), CGS-21680 (for A2A AR of rat), and Cl-IB-MECA (for A3AR of all three species). The functionally selective partial A2B agonist BAY60-6583 was found to additionally bind to A1 and A3AR and act as an antagonist at both receptor subtypes. The antagonists PSB-36 (A1), preladenant (A2A), and PSB-603 (A2B) displayed high selectivity in all three investigated species. MRS-1523 acts as a selective A3AR antagonist in human and rat, but is only moderately selective in mouse. The comprehensive data presented herein provide a solid basis for selecting suitable AR ligands for biological studies.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burnstock G (2012) Purinergic signalling: Its unpopular beginning, its acceptance and its exciting future. Bioessays 34:218–225
Burnstock G, Verkhratsky A (2009) Evolutionary origins of the purinergic signaling system. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 195:415–447
Fredholm BB, IJzerman AP, Jacobson KA, Klotz KN, Linden J (2001) International union of pharmacology. XXV. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 53:527–552
Jacobson KA, Balasubramanian R, Deflorian F, Gao ZG (2012) G protein-coupled adenosine (P1) and P2Y receptors: ligand design and receptor interactions. Purinergic Signal 8:419–436
Müller CE, Jacobson KJ (2011) Xanthines as adenosine receptor antagonists. Handb Exp Pharmacol 200:151–199
Müller CE, Jacobson KA (2011) Recent developments in adenosine receptor ligands and their potential as novel drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta 1808:1290–1308
Heisig F, Gollos S, Freudenthal SJ, El-Tayeb A, Iqbal J, Müller CE (2014) Synthesis of BODIPY derivatives substituted with various bioconjugatable linker groups: a construction kit for fluorescent labeling of receptor ligands. J Fluoresc 24:213–230
Stoddart LA, Vernall AJ, Denman JL, Briddon SJ, Kellam B, Hill SJ (2012) Fragment screening at adenosine-A(3) receptors in living cells using a fluorescence-based binding assay. Chem Biol 19:1105–1115
Kozma E, Jayasekara PS, Squarcialupi L, Paoletta S, Moro S, Federico S, Spalluto G, Jacobson KA (2013) Fluorescent ligands for adenosine receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:26–36
Xu F, Wu H, Katritch V, Han GW, Jacobson KA, Gao ZG, Cherezov V, Stevens RC (2011) Structure of an agonist-bound human A2A adenosine receptor. Science 332:322–327
Jaakola VP, Griffith MT, Hanson MA, Cherezov V, Chien EY, Lane JR, Ijzerman AP, Stevens RC (2008) The 2.6 angstrom crystal structure of a human A2A adenosine receptor bound to an antagonist. Science 322:1211–1217
Liu W, Chun E, Thompson AA, Chubukov P, Xu F, Katritch V, Han GW, Roth CB, Heitman LH, IJzerman AP, Cherezov V, Stevens RC (2012) Structural basis for allosteric regulation of GPCRs by sodium ions. Science 337:232–236
Doré AS, Robertson N, Errey JC, Ng I, Hollenstein K, Tehan B, Hurrell E, Bennett K, Congreve M, Magnani F, Tate CG, Weir M, Marshall FH (2011) Structure of the adenosine A(2A) receptor in complex with ZM241385 and the xanthines XAC and caffeine. Structure 19:1283–1293
de Lera RM, Lim YH, Zheng J (2014) Adenosine A2A receptor as a drug discovery target. J Med Chem 57:3623–3650
Chen JF, Eltzschig HK, Fredholm BB (2013) Adenosine receptors as drug targets-what are the challenges? Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:265–286
Albrecht-Küpper BE, Leineweber K, Nell PG (2012) Partial adenosine A1 receptor agonists for cardiovascular therapies. Purinergic Signal 8:91–99
Liao Y, Lin L, Lu D, Fu Y, Bin J, Xu D, Kitakaze M (2011) Activation of adenosine A1 receptor attenuates tumor necrosis factor-α induced hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes. Biomed Pharmacother 65:491–495
Faulhaber-Walter R, Jou W, Mizel D, Li L, Zhang J, Kim SM, Huang Y, Chen M, Briggs JP, Gavrilova O, Schnermann JB (2011) Impaired glucose tolerance in the absence of adenosine A1 receptor signaling. Diabetes 60:2578–2587
Teerlink JR, Iragui VJ, Mohr JP, Carson PE, Hauptman PJ, Lovett DH, Miller AB, Piña IL, Thomson S, Varosy PD, Zile MR, Cleland JG, Givertz MM, Metra M, Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Davison BA, Cotter G, Wolko D, Delucca P, Salerno CM, Mansoor GA, Dittrich H, O’Connor CM, Massie BM (2012) The safety of an adenosine A(1)-receptor antagonist, rolofylline, in patients with acute heart failure and renal impairment: findings from PROTECT. Drug Saf 35:233–244
Nair PK, Marroquin OC, Mulukutla SR, Khandhar S, Gulati V, Schindler JT, Lee JS (2011) Clinical utility of regadenoson for assessing fractional flow reserve. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 4:1085–1092
Cheng AS, Pegg TJ, Karamitsos TD, Searle N, Jerosch-Herold M, Choudhury RP, Banning AP, Neubauer S, Robson MD, Selvanayagam JB (2007) Cardiovascular magnetic resonance perfusion imaging at 3-tesla for the detection of coronary artery disease: a comparison with 1.5-tesla. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:2440–2449
Lappas CM, Rieger JM, Linden J (2005) A2A adenosine receptor induction inhibits IFN-gamma production in murine CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 174:1073–1080
Haskó G, Kuhel DG, Chen JF, Schwarzschild MA, Deitch EA, Mabley JG, Marton A, Szabó C (2000) Adenosine inhibits IL-12 and TNF-[alpha] production via adenosine A2A receptor-dependent and independent mechanisms. FASEB J 14:2065–2074
Flögel U, Burghoff S, van Lent PL, Temme S, Galbarz L, Ding Z, El-Tayeb A, Huels S, Bönner F, Borg N, Jacoby C, Müller CE, van den Berg WB, Schrader J (2012) Selective activation of adenosine A2A receptors on immune cells by a CD73-dependent prodrug suppresses joint inflammation in experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Transl Med 4:146ra108
Armentero MT, Pinna A, Ferré S, Lanciego JL, Müller CE, Franco R (2011) Past, present and future of A(2A) adenosine receptor antagonists in the therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol Ther 132:280–299
Salamone JD, Collins-Praino LE, Pardo M, Podurgiel SJ, Baqi Y, Müller CE, Schwarzschild MA, Correa M (2013) Conditional neural knockout of the adenosine A(2A) receptor and pharmacological A(2A) antagonism reduce pilocarpine-induced tremulous jaw movements: studies with a mouse model of parkinsonian tremor. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 23:972–977
Jerónimo-Santos A, Batalha VL, Müller CE, Baqi Y, Sebastião AM, Lopes LV, Diógenes MJ (2014) Impact of in vivo chronic blockade of adenosine A2A receptors on the BDNF-mediated facilitation of LTP. Neuropharmacology 83:99–106
Jenner P (2005) Istradefylline, a novel adenosine A2A receptor antagonist, for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 14:729–738
Dungo R, Deeks ED (2013) Istradefylline: first global approval. Drugs 73:875–882
Koupenova M, Johnston-Cox H, Vezeridis A, Gavras H, Yang D, Zannis V, Ravid K (2012) A2B adenosine receptor regulates hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Circulation 125:354–363
Michael S, Warstat C, Michel F, Yan L, Müller CE, Nieber K (2010) Adenosine A(2A) agonist and A(2B) antagonist mediate an inhibition of inflammation-induced contractile disturbance of a rat gastrointestinal preparation. Purinergic Signal 6:117–124
Figler RA et al (2011) Links between insulin resistance, adenosine receptors and inflammatory markers in mice and humans. Diabetes 60:669–679
Haskó G, Csóka B, Németh ZH, Vizi ES, Pacher P (2009) A2B adenosine receptors in immunity and inflammation. Trends Immunol 30:263–270
Xiang HJ, Chai FL, Wang DS, Dou KF (2011) Downregulation of the adenosine a2b receptor by RNA interference inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth. ISNR Oncol 2011:875684–875687
Cekic C, Sag D, Li Y, Theodorescu D, Strieter RM, Linden J (2012) Adenosine A2B receptor blockade slows growth of baldder and breast tumors. J Immunol 188:198–205
Silverman MH, Strand V, Markovits D, Nahir M, Reitblat T, Molad Y, RosnerI RM, Mader R, Adawi M, Caspi D, Tishler M, Langevitz P, Rubinow A, Friedman J, Green L, Tanay A, Ochaion A, Cohen S, Kerns WD, Cohn I, Fishman-Furman S, Farbstein M, Yehuda SB, Fishman P (2008) Clinical evidence for the utilization of A3 adenosine receptor as a target to treat rheumatoid arthritis: data from phase II clinical trial. J Rheumatol 35:41–48
Koscsó B, Csóka B, Pacher P, Haskó G (2011) Investigational A3 adenosine receptor targeting agents. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 20:757–768
Wang Z, Do CW, Avila MY, Peterson-Yantorno K, Stone RA, Gao ZG, Joshi B, Besada P, Jeong LS, Jacobson KA, Civan MM (2010) Nucleosine-derived antagonists to A3 adenosine receptors lower mouse intraocular pressure and act across species. Exp Eye Res 90:146–154
Müller CE, Scior T (1993) Adenosine receptors and their modulators. Pharm Acta Helv 68:77–111
Auchampach JA, Kreckler LM, Wan TC, Maas JE, van der Hoeven D, Gizewski E, Narayanan J, Maas GE (2009) Characterization of the A2Badenosinereceptor from mouse, rabbit, and dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329:2–13
Müller CE, Stein B (1996) Adenosine receptor antagonists: Structure and potential therapeutic applications. Curr Pharmaceut Design 2:501–530
X-d J, von Lubitz D, Olah ME, Stiles GL, Jacobson KA (1994) Species differences in ligands affinity at central A3 adenosine receptors. Drug Develop Res 33:51–59
Weyler S, Fülle F, Diekmann M, Schumacher B, Hinz S, Klotz KN, Müller CE (2006) Improving potency, selectivity, and water solubility of adenosine A1 receptor antagonists: xanthines modified at position 3 and related pyrimido[1,2,3-cd] purinediones. Chem Med Chem 1:891–902
Yan L, Bertarelli DC, Hayallah AM, Meyer H, Klotz KN, Müller CE (2006) A new synthesis of sulfonamides by aminolysis of p-nitrophenylsulfonates yielding potent and selective adenosine A2B receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 49:4384–4391
Müller CE, Shi D, Manning M Jr, Daly JW (1993) Synthesis of paraxanthine analogs (1,7-disubstituted xanthines) and other xanthinesunsubstituted at the 3-position: structure-activity relationships at adenosine receptors. J Med Chem 36:3341–3349
Borrmann T, Hinz S, Bertarelli DC, Li W, Florin NC, Scheiff AB, Müller CE (2009) 1-alkyl-8-(piperazine-1-sulfonyl) phenylxanthines: development and characterization of adenosineA2B receptor antagonists and a new radioligand with subnanomolar affinity and subtype specificity. J Med Chem 52:3994–400
Hockemeyer J, Burbiel JC, Müller CE (2004) Multigram-scale syntheses, stability, and photoreactions of A2A adenosine receptor antagonists with 8-styrylxanthine structure: Potential drugs for Parkinson’s disease. J Org Chem 69:3308–3318
Neustadt BR, Hao J, Lindo N, Greenlee WJ, Stamford AW, Tulshian D, Ongini E, Hunter J, Monopoli A, Bertorelli R, Foster C, Arik L, Lachowicz J, Ng K, Feng KI (2007) Potent, selective, and orally active adenosine A2A receptor antagonists: Arylpiperazine derivatives of pyrazolo[4,3-e]-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-c] pyrimidines. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 5:1376–1380
Klotz KN, Hessling J, Hegler J, Owman C, Kull B, Fredholm BB, Lohse MJ (1998) Comparative pharmacology of human adenosine receptor subtypes—Characterization of stably transfected receptors in CHO cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 357:1–9
Klotz KN, Lohse MJ, Schwabe U, Cristalli G, Vittori S, Grifantini M (1989) 2-Chloro-N6-[3H] cyclopentyladenosine ([3H]CCPA)- a high affinity agonist radioligand for A1 adenosine receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 340:679–683
Schumacher B (2002) Identifizierung, Struktur-Wirkungsbeziehungen und Aktivitätsprofile neuer Adenosinrezeptor-Liganden, University of Bonn
Reith U (2001) Native und rekombinante humane Adenosinrezeptoren: Charakterizierung, Interaktion mit pflanzlichen Inhaltsstoffen und Suche nach neuen Leitstrukturen, University of Bonn
Sihver W, Schulze A, Wutz W, Stüsgen S, Olsson RA, Bier D, Holschbach MH (2009) Autoradiographiccomparison of in vitro binding characteristics of various tritiated adenosine A2A receptor ligands in rat, mouse and pig brain and first ex vivo results. Eur J Pharmacol 616:107–114
Daly JW, Padgett WL, Secunda SI, Thompson RD, Olsson RA (1993) Structure-activity relationships for 2-substituted adenosines at A1 and A2 adenosine receptors. Pharmacology 46:91–100
Vittori S, Lorenzen A, Stannek C, Costanzi S, Volpini R, IJzerman AP, Kunzel JK, Cristalli G (2000) N-cycloalkyl derivatives of adenosine and 1-deazaadenosine as agonists and partial agonists of the A(1) adenosine receptor. J Med Chem 43:250–260
Fredholm BB, IJzerman AP, Jacobson KA, Linden J, Müller CE (2011) International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXXI. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors-an update. Pharmacol Rev 63:1–34
Tchilibon S, Joshi BV, Kim SK, Duong HT, Gao ZG, Jacobson KA (2005) (N)-methanocarba 2,N6-disubstituted adenine nucleosides as highly potent and selective A3 adenosine receptor agonists. J Med Chem 6:1745–1758
Müller CE (2001) adenosine receptor ligands-recent developments part I. Agonists. Curr Med Chem 7:1269–1288
Jacobson KA (1998) Adenosine A3 receptors: Novel ligands and paradoxical effects. Trends Pharmacol Sci 5:184–191
Abo-Salem OM, Hayallah AM, Bilkei-Gorzo A, Filipek B, Zimmer A, Müller CE (2004) Antinociceptive effects of novel A2B adenosine receptor antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1:358–366
Kenneth AK, Ijzerman AP, Linden J (1999) 1,3-dialkylxanthine derivatives having high potency as antagonists at human A2B adenosine receptors. Drug Devel Res 47:45–53
Grahner B, Winiwarter S, Lanzner W, Müller CE (1994) Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of deazaxanthines: Analogs of potent A1- and A2-adenosine receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 37:1526–1534
Bulicz J, Bertarelli DC, Baumert D, Fülle F, Müller CE, Heber D (2006) Synthesis and pharmacology of pyrido [2,3-d] pyrimidinediones bearing polar substituents as adenosine receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 14:2837–2849
Massip S, Guillon J, Bertarelli D, Bosc JJ, Léger JM, Lacher S, Bontemps C, Dupont T, Müller CE, Jarry C (2006) Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of new 1- and 3-[1-(2-hydroxy-3-phenoxypropyl)] xanthines from 2-amino-2-oxazolines as potential A1 and A2A adenosine receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 14:2697–2719
Klotz KN, Vogt H, Tawfik-Schlieper H (1991) Comparison of A1 adenosine receptors in brain from different species by radioligand binding and photoaffinity labelling. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 343:196–201
Kieć-Kononowicz K, Drabczyńska A, Pękala E, Michalak B, Müller CE, Schumacher B, Karolak-Wojciechowska J, Duddeck H, Rockitt S, Wartchow R (2001) New developments in A1 and A2A adenosine receptor antagonists. Pure Appl Chem 73:1411–1420
Kim YC, Ji X, Melman N, Linden J, Jacobson KA (2000) Anilide derivatives of an 8-phenylxanthine carboxylic congener are highly potent and selective antagonists at human A(2B) adenosine receptors. J Med Chem 43:1165–1172
Akkari R, Burbiel JC, Hockemeyer J, Müller CE (2006) Recent progress in the development of adenosine receptor ligands as antiinflammartory drugs. Curr Top Med Chem 6:1375–1379
Gao ZG, Blaustein JB, Gross AS, Melman N, Jacobson KA (2003) N6-Substituted adenosine derivatives: selectivity, efficacy, and species differences at A3 adenosine receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 65:1675–1684
Müller CE (2001) A3 adenosine receptor antagonsits. Mini Rev Med Chem 1:417–427
Olson KR, Eglen RM (2007) Beta-galactosidase complementation: a cell-based luminescent assay platform for drug discovery. Assay Drug Dev Technol 5:137–144
Müller CE, Maurinsh J, Sauer R (2000) Binding of [3H]MSX-2 (3-(3-hydroxypropyl)-7-methyl-8-(m-methoxystyryl)-1-propargylxanthine) to rat striatal membranes—a new, selective antagonist radioligand for A(2A) adenosine receptors. Eur J Pharm Sci 10:259–265
Bertarelli DC, Diekmann M, Hayallah AM, Rüsing D, Iqbal J, Preiss B, Verspohl EJ, Müller CE (2006) Characterization of human and rodent native and recombinant adenosine A(2B) receptors by radioligand binding studies. Purinergic Signal 2:559–571
Seibt BF, Schiedel AC, Thimm D, Hinz S, Sherbiny FF, Müller CE (2013) The second extracellular loop of GPCRs determines subtype-selectivity and controls efficacy as evidenced by loop exchange study at A2 adenosine receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 85:1317–1329
Kim SA, Marshall MA, Melman N, Kim HS, Müller CE, Linden J, Jacobson KA (2002) Structure-activity relationships at human and rat A2B adenosine receptors of xanthine derivatives substituted at the 1-, 3-, 7-, and 8-positions. J Med Chem 45:2131–2138
Bruns RF, Lu GH, Pugsley TA (1986) Characterization of the A2 adenosine receptor labeled by [3H]NECA in rat striatal membranes. Mol Pharmacol 29:331–346
Hayallah AM, Sandoval-Ramírez J, Reith U, Schobert U, Preiss B, Schumacher B, Daly JW, Müller CE (2002) 1,8-disubstituted xanthine derivatives: Synthesis of potent A2B-selective adenosine receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 45:1500–1510
Müller CE, Diekmann M, Thorand M, Ozola V (2002) [(3)H]8-Ethyl-4-methyl-2-phenyl-(8R)-4,5,7,8-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo [2,1-i]-purin-5-one ([(3)H]PSB-11), a novel high-affinity antagonist radioligand for human A(3) adenosine receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12:501–503
Salvatore CA, Jacobson MA, Taylor HE, Linden J, Johnson RG (1993) Molecular cloning and characterization of the human A3 adenosine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:10365–10369
van Galen PJ, van Bergen AH, Gallo-Rodriguez C, Melman N, Olah ME, IJzerman AP, Stiles GL, Jacobson KA (1994) A binding site model and structure-activity relationships for the rat A3 adenosine receptor. Mol Pharmacol 45:1101–1111
Rosentreter U, Henning R, Bauser M, Krämer T, Vaupel A, Hübsch W, Dembowsky K, Salcher-Schraufstätter O, Stasch J P, Krahn T, Perzborn E (2006) Substituted 2-thio-3,5-dicyano-4-aryl-6-aminopyridines and the use thereof. 1–273
van der Hoeven D, Wan TC, Gizewski ET, Kreckler LM, Maas JE, Van Orman J, Ravid K, Auchampach JA (2011) A role for the low-affinity A2B adenosine receptor in regulating superoxide generation by murine neutrophils. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338:1004–1012
Hinz S, Lacher SK, Seibt BF, Müller CE (2014) BAY60-6583 acts as a partial agonist at adenosine A2B receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 349:427–436
Jacobson KA (2013) Structure-based approaches to ligands for G-protein-coupled adenosine and P2Y receptors, from small molecules to nanoconjugates. J Med Chem 56:3749–3767
Murphree LJ, Marshall MA, Rieger JM, MacDonald TL, Linden J (2002) Human A(2A) adenosine receptors: High-affinity agonist binding to receptor-G protein complexes containing Gbeta(4). Mol Pharmacol 61:455–462
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 180 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alnouri, M.W., Jepards, S., Casari, A. et al. Selectivity is species-dependent: Characterization of standard agonists and antagonists at human, rat, and mouse adenosine receptors. Purinergic Signalling 11, 389–407 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-015-9460-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-015-9460-9