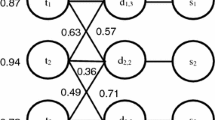
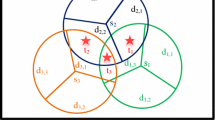
Abstract
Recently, directional sensor networks have received a great deal of attention due to their wide range of applications in different fields. A unique characteristic of directional sensors is their limitation in both sensing angle and battery power, which highlights the significance of covering all the targets and, at the same time, extending the network lifetime. It is known as the target coverage problem that has been proved as an NP-complete problem. In this paper, we propose four learning automata-based algorithms to solve this problem. Additionally, several pruning rules are designed to improve the performance of these algorithms. To evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithms, several experiments were carried out. The theoretical maximum was used as a baseline to which the results of all the proposed algorithms are compared. The obtained results showed that the proposed algorithms could solve efficiently the target coverage problem.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amac Guvensan, M., & Gokhan Yavuz, A. (2011). On coverage issues in directional sensor networks: A survey. Ad Hoc Networks, 9(7), 1238–1255.
Wang, J., Niu, C., & Shen, R. (2009). Priority-based target coverage in directional sensor networks using a genetic algorithm. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 57(11–12), 1915–1922.
Ai, J., & Abouzeid, A. (2006). Coverage by directional sensors in randomly deployed wireless sensor networks. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 11(1), 21–41.
Mohamadi, H., Ismail, A. S., & Salleh, S. (2013). Utilizing distributed learning automata to solve the connected target coverage problem in directional sensor networks. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical. 198(2013), 21–30. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2013.03.03.
Kim, Y.-H., Han, Y.-H., Jeong, Y.-S., & Park, D.-S. (2011). Lifetime maximization considering target coverage and connectivity in directional image/video sensor networks. The Journal of Supercomputing, 1–18. doi:10.1007/s11227-011-0646-9.
Gil, J.-M., & Han, Y.-H. (2011). A target coverage scheduling scheme based on genetic algorithms in directional sensor networks. Sensors, 11(2), 1888–1906.
Cardei, M., & Du, D.-Z. (2005). Improving wireless sensor network lifetime through power aware organization. Wireless Networks, 11(3), 333–340.
Cardei, M., Thai, M. T., Li, Y., & Wu, W. (2005). Energy-efficient target coverage in wireless sensor networks. In Paper presented at the IEEE INFOCOM 2005.
Zorbas, D., Glynos, D., Kotzanikolaou, P., & Douligeris, C. (2010). Solving coverage problems in wireless sensor networks using cover sets. Ad Hoc Networks, 8(4), 400–415.
Ting, C.-K., & Liao, C.-C. (2010). A memetic algorithm for extending wireless sensor network lifetime. Information Sciences, 180(24), 4818–4833.
Mohamadi, H., Ismail, A., Salleh, S., & Nodhei, A. (2013). Learning automata-based algorithms for finding cover sets in wireless sensor networks. The Journal of Supercomputing, 1–20. doi:10.1007/s11227-013-0941-8.
Mostafaei, H., & Meybodi, M. (2012). Maximizing lifetime of target coverage in wireless sensor networks using learning automata. Wireless Personal Communications, 1–17. doi:10.1007/s11277-012-0885-y.
Ma, H., & Liu, Y. (2005). On coverage problems of directional sensor networks. In Lecture notes in computer science: Mobile ad-hoc and sensor networks (pp. 721–31).
Yanli, C., Wei, L., Minglu, L., & Xiang-Yang, L. (2007). Target-Oriented Scheduling in Directional Sensor Networks. In: International Conference on Computer Communications IEEE, p. 1550-58.
Mohamadi, H., Ismail, A., & Salleh, S. (2013). A learning automata-based algorithm for solving coverage problem in directional sensor networks. Computing, 95(1), 1–24. doi:10.1007/s00607-012-0208-x.
Najim, K., & Poznyak, A. S. (1994). Learning automata: theory and applications. New York: Pergamon.
Akbari Torkestani, J., & Meybodi, M. R. (2010). An intelligent backbone formation algorithm for wireless ad hoc networks based on distributed learning automata. Computer Networks. doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2009.10.007.
Thathachar, M. A. L., & Harita, B. R. (1987). Learning automata with changing number of actions. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 17(6), 1095–1100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamadi, H., Ismail, A.S., Salleh, S. et al. Learning Automata-Based Algorithms for Solving the Target Coverage Problem in Directional Sensor Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 73, 1309–1330 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1279-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1279-5