Abstract
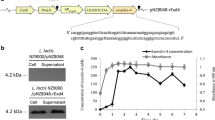
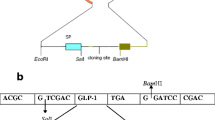
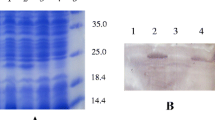
Glucagon-like peptide-1(GLP-1) is an incretin hormone secreted primarily from the intestinal L-cells in response to meals. GLP-1 is a key regulator of energy metabolism and food intake. It has been proven that P9 protein from A. muciniphila could increase GLP-1 release and improve glucose homeostasis in HFD-induced mice. To obtain an engineered Lactococcus lactis which produced P9 protein, mature polypeptide chain of P9 was codon-optimized, fused with N-terminal signal peptide Usp45, and expressed in L. lactis NZ9000. Heterologous secretion of P9 by recombinant L. lactis NZP9 were successfully detected by SDS-PAGE and western blotting. Notably, the supernatant of L. lactis NZP9 stimulated GLP-1 production of NCI-H716 cells. The relative expression level of GLP-1 biosynthesis gene GCG and PCSK1 were upregulated by 1.63 and 1.53 folds, respectively. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the secretory expression of carboxyl-terminal processing protease P9 from A. muciniphila in L. lactis. Our results suggest that genetically engineered L. lactis which expressed P9 may have therapeutic potential for the treatment of diabetes, obesity and other metabolic disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- PCSK1 :
-
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 gene
- GCG :
-
Proglucagon gene
- SCFAs:
-
Short-chain fatty acids
- GPCR:
-
G-protein-coupled receptors
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
References
Alexiadou K, Tan TM-M (2020) Gastrointestinal peptides as therapeutic targets to mitigate obesity and metabolic syndrome. Curr Diabetes Rep 20:26
Anandhakrishnan A, Korbonits M (2016) Glucagon-like peptide 1 in the pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy of clinical obesity. World J Diabetes 7:572–598
Andersen A, Lund A, Knop FK, Vilsboll T (2018) Glucagon-like peptide 1 in health and disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol 14:390–403
Ang SY, Evans BA, Poole DP et al (2018) INSL5 activates multiple signalling pathways and regulates GLP-1 secretion in NCI-H716 cells. J Mol Endocrinol 60:213–224
Bala V, Rajagopal S, Kumar DP et al (2014) Release of GLP-1 and PYY in response to the activation of G protein-coupled bile acid receptor TGR5 is mediated by Epac/PLC-ε pathway and modulated by endogenous H2S. Front Physiol 5:420
Cani PD, Knauf C (2021) A newly identified protein from Akkermansia muciniphila stimulates GLP-1 secretion. Cell Metab 33:1073–1075
Chimerel C, Emery E, Summers DK et al (2014) Bacterial metabolite indole modulates incretin secretion from intestinal enteroendocrine L cells. Cell Rep 9:1202–1208
Covasa M, Stephens RW, Toderean R, Cobuz C (2019) Intestinal sensing by gut microbiota: targeting gut peptides. Front Endocrinol 10:82
de Ruyter PG, Kuipers OP, de Vos WM (1996) Controlled gene expression systems for Lactococcus lactis with the food-grade inducer nisin. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3662–3667
Derrien M, Vaughan EE, Plugge CM, de Vos WM (2004) Akkermansia muciniphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a human intestinal mucin-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1469–1476
Jin T (2008) Mechanisms underlying proglucagon gene expression. J Endocrinol 198:17–28
Lyck R, Enzmann G (2015) The physiological roles of ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 in neutrophil migration into tissues. Curr Opin Hematol 22:53–59
Mierau I, Kleerebezem M (2005) 10 years of the nisin-controlled gene expression system (NICE) in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:705–717
Pathak P, Xie C, Nichols RG et al (2018) Intestine farnesoid X receptor agonist and the gut microbiota activate G-protein bile acid receptor-1 signaling to improve metabolism. Hepatology 68:1574–1588
Quevrain E, Maubert MA, Michon C et al (2016) Identification of an anti-inflammatory protein from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, a commensal bacterium deficient in Crohn’s disease. Gut 65:415–425
Reimer RA, Darimont C, Gremlich S et al (2001) A human cellular model for studying the regulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion. Endocrinology 142:4522–4528
Sandoval DA, D’Alessio DA (2015) Physiology of proglucagon peptides: role of glucagon and Glp-1 in health and disease. Physiol Rev 95:513–548
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Tolhurst G, Heffron H, Lam YS et al (2012) Short-chain fatty acids stimulate Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 secretion via the G-Protein–coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes 61:364–371
van Tilburg AY, Cao H, van der Meulen SB et al (2019) Metabolic engineering and synthetic biology employing Lactococcus lactis and Bacillus subtilis cell factories. Curr Opin Biotechnol 59:1–7
Wang G, Li J, Xie S et al (2020) The N-terminal domain of rhamnosyltransferase EpsF influences exopolysaccharide chain length determination in Streptococcus thermophilus. PeerJ 8:05–34
Wu J, Tian X, Xu X et al (2022) Engineered Probiotic Lactococcus lactis for Lycopene production against ROS stress in intestinal epithelial cells. ACS Synth Biol 11:1568–1576
Xiong Y, Zhai Z, Lei Y et al (2020) A Novel Major Pilin subunit protein FimM is involved in adhesion of Bifidobacterium longum BBMN68 to intestinal epithelial cells. Front Microbiol 11:590435
Yin J, Li G, Ren X, Herrler G (2007) Select what you need: a comparative evaluation of the advantages and limitations of frequently used expression systems for foreign genes. J Biotechnol 127:335–347
Yoon HS, Cho CH, Yun MS et al (2021) Akkermansia muciniphila secretes a glucagon-like peptide-1-inducing protein that improves glucose homeostasis and ameliorates metabolic disease in mice. Nat Microbiol 6:563–573
Yu Z, Jin T (2010) New insights into the role of cAMP in the production and function of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). Cell Signal 22:1–8
Yu Y, Liu L, Wang X et al (2010) Modulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 release by berberine: in vivo and in vitro studies. Biochem Pharmacol 79:1000–1006
Yu Y, Hao G, Zhang Q et al (2015) Berberine induces GLP-1 secretion through activation of bitter taste receptor pathways. Biochem Pharmacol 97:173–177
Yu Y, Raka F, Adeli K (2019) The role of the gut microbiota in lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. J Clin Med 8:2227
Zhai Q, Feng S, Arjan N, Chen W (2019) A next generation probiotic, Akkermansia muciniphila. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59:3227–3236
Zhang F-L, Yang Y-L, Zhang Z et al (2021) Surface-displayed Amuc_1100 from Akkermansia muciniphila on Lactococcus lactis ZHY1 improves hepatic steatosis and Intestinal Health in High-Fat-Fed zebrafish. Front Nutr 8:726108
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2022YFF1100102) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31972055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.D. (First Author): Investigation, Formal Analysis, Writing - Original Draft Y.Z.: Data Curation, Writing - Original Draft X.Z.: Visualization, Investigation L.H.: Formal Analysis L.Z.: Review & Editing Y.H.: Review & Editing Z.Z.(Corresponding Author): Conceptualization, Funding Acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Di, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, X. et al. Heterologous expression of P9 from Akkermansia muciniphila increases the GLP-1 secretion of intestinal L cells. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 199 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-04012-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-04012-z