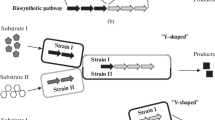
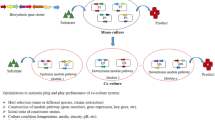
Abstract
Nowadays, microbial synthesis has become a common way for producing valuable chemicals. Traditionally, microbial production of valuable chemicals is accomplished by a single strain. For the purpose of increasing the production titer and yield of a recombinant strain, complicated pathways and regulation layers should be fine-tuned, which also brings a heavy metabolic burden to the host. In addition, utilization of various complex and mixed substrates further interferes with the normal growth of the host strain and increases the complexity of strain engineering. As a result, modular co-culture technology, which aims to divide a target complex pathway into separate modules located at different single strains, poses an alternative solution for microbial production. Recently, modular co-culture strategy has been employed for the synthesis of different natural products. Therefore, in this review, various chemicals produced with application of co-cultivation technology are summarized, including co-culture with same species or different species, and regulation of population composition between the co-culture members. In addition, development prospects and challenges of this promising field are also addressed, and possible solution for these issues were also provided.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akdemir H, Silva A, Zha J, Zagorevski DV, Koffas MAG (2019) Production of pyranoanthocyanins using Escherichia coli co-cultures. Metab Eng 55:290–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.05.008
Asadi F, Barshan-Tashnizi M, Hatamian-Zarmi A, Davoodi-Dehaghani F, Ebrahimi-Hosseinzadeh B (2021) Enhancement of exopolysaccharide production from ganoderma lucidum using a novel submerged volatile co-culture system. Fungal Biol 125(1):25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2020.09.010
Camacho-Zaragoza JM, Hernandez-Chavez G, Moreno-Avitia F, Ramirez-Iniguez R, Martinez A, Bolivar F, Gosset G (2016) Engineering of a microbial coculture of Escherichia coli strains for the biosynthesis of resveratrol. Microb Cell Fact. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0562-z
Chen Y, Kim JK, Hirning AJ, Josic K, Bennett MR (2015) Emergent genetic oscillations in a synthetic microbial consortium. Science 349(6251):986–989. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa3794
Chen Z, Sun X, Li Y, Yan Y, Yuan Q (2017) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for microbial synthesis of monolignols. Metab Eng 39:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.10.021
Chen T, Wang X, Zhuang L, Shao A, Lu Y, Zhang H (2021) Development and optimization of a microbial co-culture system for heterologous indigo biosynthesis. Microb Cell Fact 20(1):154. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01636-w
Davis RM, Muller RY, Haynes KA (2015) Can the natural diversity of quorum-sensing advance synthetic biology? Front Bioeng Biotechnol 3:30. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2015.00099
Dinh CV, Chen XY, Prather KLJ (2020) Development of a Quorum-Sensing based circuit for control o coculture population composition in a naringenin production system. ACS Synth Biol 9:590–597. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00451
Fang Z, Jones JA, Zhou J, Koffas MAG (2018) Engineering Escherichia coli co-cultures for production of curcuminoids from glucose. Biotechnol J 13(5):e1700576. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201700576
Ganesan V, Li Z, Wang X, Zhang H (2017) Heterologous biosynthesis of natural product naringenin by co-culture engineering. Synth Syst Biotechnol 2(3):236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2017.08.003
Hill EA, Chrisler WB, Beliaev AS, Bernstein HC (2017) A flexible microbial co-culture platform for simultaneous utilization of methane and carbon dioxide from gas feedstocks. Bioresour Technol 228:250–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.111
Jagmann N, Philipp B (2018) SpoT-mediated regulation and amino acid prototrophy are essential for pyocyanin production during parasitic growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a co-culture model system with Aeromonas hydrophila. Front Microbiol 9:761. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00761
Jagmann N, Bleicher V, Busche T, Kalinowski J, Philipp B (2016) The guanidinobutyrase gbuA is essential for the alkylquinolone-regulated pyocyanin production during parasitic growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in co-culture with Aeromonas hydrophila. Environ Microbiol 18(10):3550–3564. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13419
Jiang Y et al (2018) Microbial co-culturing systems: butanol production from organic wastes through consolidated bioprocessing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(13):5419–5425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8970-0
Jones JA, Wang X (2018) Use of bacterial co-cultures for the efficient production of chemicals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 53:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2017.11.012
Jones JA et al (2016) Experimental and computational optimization of an Escherichia coli co-culture for the efficient production of flavonoids. Metab Eng 35:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.01.006
Lee CR, Kim C, Song YE, Im H, Oh Y-K, Park S, Kim JR (2018) Co-culture-based biological carbon monoxide conversion by Citrobacter amalonaticus Y19 and Sporomusa ovata via a reducing-equivalent transfer mediator. Bioresour Technol 259:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.02.129
Li H, Schmitz O, Alper HS (2016) Enabling glucose/xylose co-transport in yeast through the directed evolution of a sugar transporter. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(23):10215–10223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7879-8
Li T, Li C-T, Butler K, Hays SG, Guarnieri MT, Oyler GA, Betenbaugh MJ (2017) Mimicking lichens: incorporation of yeast strains together with sucrose-secreting cyanobacteria improves survival, growth, ROS removal, and lipid production in a stable mutualistic co-culture production platform. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0736-x
Li T, Zhou W, Bi H, Zhuang Y, Zhang T, Liu T (2018) Production of caffeoylmalic acid from glucose in engineered Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 40(7):1057–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2580-x
Li Z, Wang X, Zhang H (2019) Balancing the non-linear rosmarinic acid biosynthetic pathway by modular co-culture engineering. Metab Eng 54:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.03.002
Li T, Jiang L, Hu Y, Paul JT, Zuniga C, Zengler K, Betenbaugh MJ (2020) Creating a synthetic lichen: mutualistic co-culture of fungi and extracellular polysaccharide-secreting cyanobacterium Nostoc PCC 7413. Algal Res 45:101755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2019.101755
Li X et al (2022) Design of stable and self-regulated microbial consortia for chemical synthesis. Nat Commun 13(1):1554. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29215-6
Liu F, Wu WH, Tran-Gyamfi MB, Jaryenneh JD, Zhuang X, Davis RW (2017) Bioconversion of distillers’ grains hydrolysates to advanced biofuels by an Escherichia coli co-culture. Microb Cell Fact 16(1):192. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0804-8
Liu X et al (2018a) Convergent engineering of syntrophic Escherichia coli coculture for efficient production of glycosides. Metab Eng 47:243–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.03.016
Liu Y et al (2018b) Engineered monoculture and co-culture of methylotrophic yeast for de novo production of monacolin J and lovastatin from methanol. Metab Eng 45:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.12.009
Liu Y, Xie NZ, Yu B (2022) De novo biosynthesis of D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine by a designed cofactor self-sufficient route and co-culture strategy. ACS Synth Biol 11(3):1361–1372. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.2c00007
Ma Q et al (2020) Enhanced chitin deacetylase production ability of Rhodococcus equi CGMCC14861 by co-culture fermentation with Staphylococcus sp. MC7. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.592477
Miano A, Liao MJ, Hasty J (2020) Inducible cell-to-cell signaling for tunable dynamics in microbial communities. Nat Commun 11(1):1193. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15056-8
Minami H, Kim J-S, Ikezawa N, Takemura T, Katayama T, Kumagai H, Sato F (2008) Microbial production of plant benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(21):7393–7398. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0802981105
Moussa M, Ebrahim W, Kalscheuer R, Liu Z, Proksch P (2020) Co-culture of the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa with the fungus Fusarium tricinctum induces bacterial antifungal and quorum sensing signaling molecules. Phytochem Lett 36:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2020.01.013
Nguyen Huy T, Chaudhary AK, Van Duong C, Nguyen Xuan C (2018a) Engineering co-culture system for production of apigetrin in Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 45(3):175–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-018-2012-x
Nguyen Huy T, Nguyen Thanh T, Nguyen Xuan C, Van Duong C, Van Dong Q, Malla S (2018b) Escherichia coli modular coculture system for resveratrol glucosides production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34(6):75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-018-2458-z
Pang Q, Han H, Qi Q, Wang Q (2022) Application and population control strategy of microbial modular co-culture engineering. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 38(4):1421–1431
Qiu Z, Liu X, Li J, Qiao B, Zhao G-R (2022) Metabolic division in an Escherichia coli coculture system for efficient production of kaempferide. ACS Synth Biol 11(3):1213–1227. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.1c00510
Roell GW, Zha J, Carr RR, Koffas MA, Fong SS, Tang YJ (2019) Engineering microbial consortia by division of labor. Microb Cell Fact 18(1):35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1083-3
Rosero-Chasoy G, Rodriguez-Jasso RM, Aguilar CN, Buitron G, Chairez I, Ruiz HA (2021) Microbial co-culturing strategies for the production high value compounds, a reliable framework towards sustainable biorefinery implementation-an overview. Bioresour Technol 321:124458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124458
Salimi F, Mahadevan R (2013) Characterizing metabolic interactions in a clostridial co-culture for consolidated bioprocessing. BMC Biotechnol 13:95. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-13-95
Sedlak M, Ho NWY (2004) Characterization of the effectiveness of hexose transporters for transporting xylose during glucose and xylose co-fermentation by a recombinant Saccharomyces yeast. Yeast 21(8):671–684. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1060
Stephens K, Pozo M, Tsao C-Y, Hauk P, Bentley WE (2019) Bacterial co-culture with cell signaling translator and growth controller modules for autonomously regulated culture composition. Nat Commun 10(1):4129. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12027-6
Sun J, Raza M, Sun X, Yuan Q (2018) Biosynthesis of adipic acid via microaerobic hydrogenation of cis, cis-muconic acid by oxygen-sensitive enoate reductase. J Biotechnol 280:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.06.304
Tsoi R, Wu F, Zhang C, Bewick S, Karig D, You L (2018) Metabolic division of labor in microbial systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(10):2526–2531. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1716888115
Verhoeven MD, de Valk SC, Daran J-MG, van Maris AJA, Pronk JT (2018) Fermentation of glucose-xylose-arabinose mixtures by a synthetic consortium of single-sugar-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. FEMS Yeast Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/foy075
Wang E-X, Ding M-Z, Ma Q, Dong X-T, Yuan Y-J (2016a) Reorganization of a synthetic microbial consortium for one-step vitamin C fermentation. Microb Cell Fact 15:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0418-6
Wang M, Yu C, Zhao H (2016b) Directed evolution of xylose specific transporters to facilitate glucose-xylose co-utilization. Biotechnol Bioeng 113(3):484–491. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25724
Wang R, Zhao S, Wang Z, Koffas MAG (2020) Recent advances in modular co-culture engineering for synthesis of natural products. Curr Opin Biotechnol 62:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2019.09.004
Weiss TL, Young EJ, Ducat DC (2017) A synthetic, light-driven consortium of cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria enables stable polyhydroxybutyrate production. Metab Eng 44:236–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.10.009
Wender PA, Mucciaro TP (1992) A new and practical approach to the synthesis of taxol and taxol analogs-the pinene path. J Am Chem Soc 114:5878–5879. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00040a070
Zhang H, Stephanopoulos G (2016) Co-culture engineering for microbial biosynthesis of 3-amino-benzoic acid in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol J 11(7):981–987. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201600013
Zhang H, Wang X (2016) Modular co-culture engineering, a new approach for metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 37:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.05.007
Zhang H, Li Z, Pereira B, Stephanopoulos G (2015a) Engineering E-coli-E-coli cocultures for production of muconic acid from glycerol. Microb Cell Fact 14:134. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-015-0319-0
Zhang H, Pereira B, Li Z, Stephanopoulos G (2015b) Engineering Escherichia coli coculture systems for the production of biochemical products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(27):8266–8271. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1506781112
Zhou K, Qiao K, Edgar S, Stephanopoulos G (2015) Distributing a metabolic pathway among a microbial consortium enhances production of natural products. Nat Biotechnol 33(4):377–383. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3095
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31600066, 31870105, 32070111, 32070126, 32270093), Rizhao Science and Technology Innovation Project (2020CXZX1206), the Science and Technology Program of the University of Jinan (XKY2028), and the Higher Educational Science and Technology Program of Jinan City (2021GXRC088).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors were involved in the conception and design of this review. SZ, FL, FY, QM and LL wrote the article; PG, ZH, XF, XL and QL read and corrected the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Li, F., Yang, F. et al. Microbial production of valuable chemicals by modular co-culture strategy. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 6 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03447-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03447-6