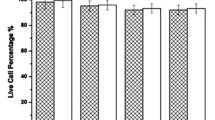
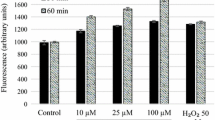
Abstract
We evaluated the leishmanicidal activity of commercially available 5α-cholest-7-en-3β-ol [5α-chol], (+)-4-cholesten-3-one [(+)-4-chol] and the equimolar mixture of the two of them in promastigotes and amastigotes of two different strains of Leishmania mexicana (LCL) and (DCL). The leishmanicidal effectiveness of these sterols was determined by promastigote growth-kinetic experiments and promastigote viability using the propidium iodide staining procedure. The proliferation test was performed using the CFSE (5-Carboxyfluorescein N-succinimidyl ester) staining of parasites at different time points. To determine the leishmanicidal effectiveness of these sterols in amastigotes, we evaluated parasite killing inside of macrophages at different time points. The trypan blue exclusion test was used to determine cytotoxicity of sterols in uninfected macrophages. We included in all experiments a control group of parasites treated with 2% DMSO (Dimethyl Sulfoxide) and another one treated with the reference drug sodium stibogluconate (Sb). Our results showed that the equimolar mixture at 2000 times lower concentration presented similar leishmanicidal activity as Sb. This mixture was similarly effective at 100 times lower concentration than individual sterols tested separately indicating the existence of a synergistic effect against LCL and DCL parasites. The therapeutic index of the equimolar mixture was 10,000—16,000 times higher than the one recorded by Sb and was not cytotoxic to macrophages. Therefore, the equimolar mixture of 5α-Chol and (+)-4-chol may represent a potential alternative for the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Bansal R, Sankar Sen S, Muthuswammi R, Madhubala R (2020) Stigmasterol as a potential biomarker for amphotericin B resistance in Leishmania donovani. J Antimicrob Chemother 75:942–950. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkz515
Bazin MA, Loiseaub PM, Boriesb C, Letourneuxc Y, Raulta S, El Kihel L (2006) Synthesis of oxysterols and nitrogenous sterols with antileishmanial and trypanocidal activities. Eur J Med Chem 41:1109–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2006.03.033
Croft SL, Olliaro R (2011) Leishmaniasis chemotherapy—challenges and opportunities. Clin Microbiol Infect 17:1478–1483. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03630.x
de Menezes JP, Guedes CE, Petersen AL, Fraga DB, Veras PS (2015) Advances in development of new treatment for Leishmaniasis. Biomed Res Int 2015:815023. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/815023
Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative (DNDi) (2021) Cutaneous leishmaniasis. https://dndi.org/diseases/cutaneous-leishmaniasis/. Accessed 2 January 2021
Foglieni C, Meoni C, Davall AM (2001) Fluorescent dyes for cell viability: an application on prefixed conditions. Histochem Cell Biol 115(3):223–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004180100249
Ghorbani M, Farhoudi R (2017) Leishmaniasis in humans: drug or vaccine therapy? Drug Des Devel Ther 12:25–40. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.s146521
Ghosh P, Ghosh A, Mandal A, Sultana SS, Dey S, Pal C (2016) Oxysterols: synthesis and anti-leishmanial activities. Steroids 107:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2015.12.020
Isaac-Márquez AP, Lezama-Dávila CM (2020) Cytokine regulation of female-macrophage resistance to Leishmania mexicana parasites. Role of IL-12p70. Parasite Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1111/pim.12685
Isaac-Márquez AP, Talamás-Rohana P, Galindo-Sevilla N, Gaitan-Puch SE, Díaz-Díaz NA, Hernández-Ballina GA, Lezama-Dávila CM (2018) Decanethiol functionalized silver nanoparticles are new powerful leishmanicidals in vitro. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34:38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-018-2420-0
Leliebre-Lara V, Monzote Fidalgo L, Pferschy-Wenzig EM, Kunert O, Nogueiras Lima C, Bauer R (2016) In vitro antileishmanial activity of sterol from Trametes versicolor (Bres. Rivardens). Molecules 21:1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21081045
Lezama-Dávila CM, Isaac-Márquez AP, Kapadia G, Owens K, Oghumu S, Beverley S, Satoskar AR (2012) Leishmanicidal activity of two naphthoquinones against Leishmania donovani. Biol Pharm Bull 35:1761–1764. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b12-00419
Lezama-Dávila CM, Pan L, Isaac-Márquez AP, Terrazas C, Oghumu S, Isaac-Márquez R, Pech-Dzib MY, Barbi J, Calomeni E, Parinandi N, Kinghorn DA, Satoskar AR (2014) Pentalinon andrieuxii root extract is effective in the topical treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania mexicana. Phytother Res 28:909–916. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5079
Lezama-Dávila CM, McChesney JD, Bastos JK, Miranda MA, Tiossi RF, da Costa JC, Bentley MV, Gaitan-Puch SE, Isaac-Márquez AP (2016) A new antileishmanial preparation of combined solamargine and solasonine heals cutaneous leishmaniasis through different immunochemical pathways. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:2732–2738. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.02804-15
Messaritakis I, Mazeris A, Koutala E, Antoniou M (2010) Leishmania donovani s.l. evaluation of the proliferation potential of promastigotes using CFSE staining and flow cytometry. Exp Parasitol 125:384–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2010.03.006
Ning Y, Frankfater C, Hsu F-F, Soares RP, Cardoso CA, Nogueira PM, Lander NM, Docampo R, Zhang K (2020) Lathosterol oxidase sterol C-5 desaturase deletion confers resistance to amphotericin B and sensitivity to acidic stress in Leishmania major. MSphere 5:e00380-20
Oficial Mexicana NOM-062-ZOO-1999 Especificaciones técnicas para la producción, cuidado y uso de los animales de laboratorio. DOF: 12/12/2001
Okwor I, Uzonna J (2016) Social and Economic Burden of Human Leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 94:489–493. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.15-0408
PAHO Pan American Health Organization (2020) Leishmaniasis: Epidemiological Report in the Americas. https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/51742. Accessed 30 December 2021
Pan L, Lezama-Dávila CM, Isaac-Márquez AP, Calomeni EP, Fuchs JR, Satoskar AR, Kinghorn AD (2012) Sterols with antileishmanial activity isolated from the roots of Pentalinon andrieuxii. Phytochemistry 82:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.06.012
Ponte-Sucre A, Gamarro F, Dujardin J-C, Barrett MP, López Vélez R, García-Hernández R, Pountain AW, Mwenechanya R, Papadopoulou B (2017) Drug resistance and treatment failure in leishmaniasis: a 21st century challenge. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 11:e0006052. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0006052
Purkait B, Kumar A, Nandi N, Hasan Sardar A, Das S, Kumar S, Pandey K, Ravidas V, Kumar M, De T, Singh D, Das P (2012) Mechanism of amphotericin resistance in clinical isolates of Leishmania donovani. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:1031–1041. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00030-11
Secretaría de Agricultura, Ganadería, Desarrollo Rural, Pesca y Alimentación (SAGARPA) (2001) Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-062-ZOO-1999 Especificaciones técnicas para la producción, cuidado y uso de los animales de laboratorio. DOF: 12/12/2001. https://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5405210&fecha=26/08/2015
Sartonelli P, Andrade SP, Melhem MSC, Prado FO, Tempone AG (2007) Isolation of antileishmanial sterol from the fruits of Cassia fistula using bioguided fractionation. Phytother Res 21:644–647. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.2131
Silva AAS, Morais SM, Falcao MJC, Vieira IGP, Ribeiro LM, Viana SM, Teixeira MJ, Barreto FS, Carvalho CA, Cardoso RPA, Andrade-Junior HF (2014) Activity of cycloartane-type triterpenes and sterols isolated from Musa paradisiaca fruit peel against Leishmania infantum chagasi. Phytomedicine 21:1419–1423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2014.05.005
Torres-Santos EC, Sampaio-Santos MI, Buckner FS, Yokoyama K, Gelb M, Urbina JA, Rossi-Bergmann B (2009) Altered sterol profile induced in Leishmania amazonensis by a natural dihydroxymethoxylated chalcone. J Antimicrob Chemother 63:469–472. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkn546
WHO (2021) Leishmaniasis. https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis Accessed 1 January 2021
Yao C, Wilson ME (2016) Dynamics of sterol synthesis during development of Leishmania spp. Parasites to their virulent form. Parasit Vectors. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1470-0
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Universidad Autónoma de Campeche (003/UAC/2016). Authors appreciate Mr Rene Gonzales and Eleazar Velasco´s assistance. We are also in debt to Prof Norma Galindo and Prof Patricia Talamás who provided DCL parasites and J774A.1 cells, respectively.
Funding
This research was supported by Universidad Autónoma de Campeche (003/UAC/2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
APIM: designed, performed experiments, and wrote manuscript. CMLD: designed, performed experiments, and revised manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The manuscript has been read and approved by all authors for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isaac-Márquez, A.P., Lezama-Dávila, C.M. In vitro leishmanicidal activity of two cholesterol derivatives. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 66 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03248-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03248-x