Abstract
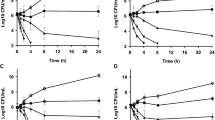
Staphylococcus aureus is an important pathogen for both humans and animals, and it has been an ubiquitous etiological agent of bovine mastitis in dairy farms worldwide. Elimination of S. aureus with classic antibiotics is difficult, and the current study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of ethanolic extracts of propolis (EEP) against S. aureus cultivated in complex media or milk. EEP (0–0.5 mg ml−1) decreased growth of S. aureus in BHI media and 1 mg ml−1 was bactericidal against washed cell suspensions (107 CFU ml−1). Propolis extracts also killed S. aureus cells resuspended in milk, but the bactericidal dose was at least 20-fold greater. Cultures that were transferred for at least 60 generations with sub-lethal doses of propolis did not change much their sensibility to EEP. Atomic force microscopy images revealed changes in morphology and cell size of S. aureus cells exposed to EEP (0.5 mg ml−1). Our results indicate that propolis extracts might be effective against mastitis-causing S. aureus strains in vivo, but milk constituents affect the inhibitory activity of propolis. Considering that propolis-resistance appears to be a phenotype not easily selected, the use of EEP combined or not with other antimicrobial agents might be useful for mastitis control in vivo.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aires-de-Sousa M, Parente C, Vieira-da-Motta O, Bonna I, Silva D, de Lencastre H (2007) Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from buffalo, bovine, ovine, and caprine milk samples collected in Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3845–3849
Ali-Vehmas T, Westphalen P, Myllys V, Sandholm M (1997) Binding of Staphylococcus aureus to milk fat globules increases resistance to penicillin-G. J Dairy Res 64:253–260
Bonvehí J, Coll F, Jordà R (1994) The composition, active components and bacteriostatic activity of propolis in dietetics. J Am Oil Chem Soc 71:529–532
Brito MAVP, Brito JRF (1999) Diagnóstico microbiológico da mastite. Circular Técnica 55, Embrapa Gado de Leite, Juiz de Fora
Capurro A, Aspán A, Ericsson UH, Persson WK, Artursson K (2010) Identification of potential sources of Staphylococcus aureus in herds with mastitis problems. J Dairy Sci 93:180–191
Cushnie T, Lamb A (2005) Detection of galangin-induced cytoplasmic membrane damage in Staphylococcus aureus by measuring potassium loss. J Ethnopharmacol 101:243–248
Denyer SP, Stewart GSAB (1998) Mechanisms of action of disinfectants. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 41:261–268
Eaton P, Fernandes J, Pereira E, Pintado M, Xavier MF (2008) Atomic force microscopy study of the antibacterial effects of chitosans on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Ultramicroscopy 108:1128–1134
Erskine R, Wagner S, DeGraves F (2003) Mastitis therapy and pharmacology. Vet Clin N Am Food Anim Pract 19:109–138
Fernandes Júnior A, Balestrin E, Betoni J, Orsi R, Cunha M, Montelli A (2005) Propolis: anti-Staphylococcus aureus activity and synergism with antimicrobial drugs. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 100:563–566
Fischer G, Paulino N, Marcucci M, Siedler B, Munhoz L, Finger P, Vargas G, Hübner S, Vidor T, Roehe P (2010) Green propolis phenolic compounds act as vaccine adjuvants, improving humoral and cellular responses in mice inoculated with inactivated vaccines. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 105:908–913
Gehring R, Smith G (2006) An overview of factors affecting the disposition of intramammary preparations used to treat bovine mastitis. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 29:237–241
Gould S, Cuschieri P, Rollason J, Hilton A, Easmon S, Fielder M (2010) The need for continued monitoring of antibiotic resistance patterns in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from London and Malta. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 9:20
Gundogan N, Citak S, Yucel N, Devren A (2005) A note on the incidence and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from meat and chicken samples. Meat Sci 69:807–810
Iio A, Ohguchi K, Inoue H, Maruyama H, Araki Y, Nozawa Y, Ito M (2010) Ethanolic extracts of Brazilian red propolis promote adipocyte differentiation through PPARγ activation. Phytomedicine 17:974–979
Juven B, Henis Y, Jacoby B (1972) Studies on the mechanism of the antimicrobial action of oleuropein. J Appl Bacteriol 35:559–567
Kuang Y, Jia H, Miyanaga K, Tanji Y (2009) Effect of milk on antibacterial activity of tetracycline against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:135–142
Lu L, Chen Y, Chou C (2005) Antibacterial activity of propolis against Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Food Microbiol 102:213–220
McDougall S, Parker K, Heuer C, Compton C (2009) A review of prevention and control of heifer mastitis via non-antibiotic strategies. Vet Microbiol 134:177–185
Messerli S, Ahn M, Kunimasa K, Yanagihara M, Tatefuji T, Hashimoto K, Mautner V, Uto Y, Hori H, Kumazawa S (2009) Artepillin C (ARC) in Brazilian green propolis selectively blocks oncogenic PAK1 signaling and suppresses the growth of NF tumors in mice. Phytother Res 23:423–427
Mirzoeva O, Grishanin R, Calder P (1997) Antimicrobial action of propolis and some of its components: the effects on growth, membrane potential and motility of bacteria. Microbiol Res 152:239
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (2003) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility test for bacteria that grow aerobically. Approved standard-sixth edition. Technical report M07-A6, Wayne, PA
Nickerson S (2009) Control of heifer mastitis: antimicrobial treatment-an overview. Vet Microbiol 134:128–135
Owens W, Watts J (1987) Effects of milk on activity of antimicrobics against Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine udders. J Dairy Sci 70:1946–1951
Park Y, Fukuda I, Ashida H, Nishiumi S, Yoshida K, Daugsch A, Sato H, Pastore G (2005) Suppressive effects of ethanolic extracts from propolis and its main botanical origin on dioxin toxicity. J Agric Food Chem 53:10306–10309
Paulino N, Abreu S, Uto Y, Koyama D, Nagasawa H, Hori H, Dirsch V, Vollmar A, Scremin A, Bretz W (2008) Anti-inflammatory effects of a bioavailable compound, Artepillin C, in Brazilian propolis. Eur J Pharmacol 587:296–301
Pinto MS (2008) Atividade de própolis verde e bovicina HC5 sobre bactérias isoladas de mastite bovina. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Viçosa
Raghukumar R, Vali L, Watson D, Fearnley J, Seidel V (2010) Antimethicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) activity of ‘pacific propolis’ and isolated prenylflavanones. Phytother Res 24:1181–1187
Salomao K, Pereira P, Campos L, Borba C, Cabello P, Marcucci M, De Castro S (2008) Brazilian propolis: correlation between chemical composition and antimicrobial activity. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 5:317–324
Sayed S, Abou El-Ella G, Wahba N, El Nisr N, Raddad K, Abd El Rahman M, Abd El Hafeez M, Abd El Fattah Aamer A (2009) Immune defense of rats immunized with fennel honey, propolis, and bee venom against induced Staphylococcal infection. J Med Food 12:569–575
Sears P, McCarthy K (2003) Management and treatment of staphylococcal mastitis. Vet Clin N Am Food Anim Pract 19:171–185
Teixeira E, Negri G, Meira R (2005) Plant origin of green propolis: bee behavior, plant anatomy and chemistry. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2:85–92
Van Eenennaam A, Cullor J, Perani L, Gardner I, Smith W, Dellinger J, Guterbock W, Jensen L (1993) Evaluation of milk antibiotic residue screening tests in cattle with naturally occurring clinical mastitis. J Dairy Sci 76:3041–3053
Varella Coelho M, Santos Nascimento J, Fagundes P, Madureira D, Oliveira S, Vasconcelos de Paiva Brito M, Freire Bastos M (2007) Activity of staphylococcal bacteriocins against Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus agalactiae involved in bovine mastitis. Res Microbiol 158:625–630
Wu J, Hu S, Cao L (2007) Therapeutic effect of nisin Z on subclinical mastitis in lactating cows. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:3131–3135
Zoraghi R, See R, Gong H, Lian T, Swayze R, Finlay B, Brunham R, McMaster W, Reiner N (2010) Functional analysis, overexpression, and kinetic characterization of pyruvate kinase from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry 49:7733–7747
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), Belo Horizonte, Brazil (Grant No. CBB-1318/06) for providing financial support for this research. HFS and AATC received fellowships from the Conselho de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). We thank Dr. Maximiliano Luis Munford, from the Physics Department at the Universidade Federal de Viçosa for technical assistance with the AFM analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santana, H.F., Barbosa, A.A.T., Ferreira, S.O. et al. Bactericidal activity of ethanolic extracts of propolis against Staphylococcus aureus isolated from mastitic cows. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28, 485–491 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0839-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0839-7