Summary
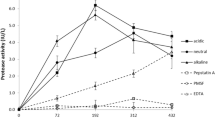
Extracellular laccase in cultures of Grifola frondosa grown in liquid culture on a defined medium was first detectable in the early/middle stages of primary growth, and enzyme activity continued to increase even after fungal biomass production had peaked. Laccase production was significantly increased by supplementing cultures with 100–500 (M Cu over the basal level (1.6 mM Cu) and peak levels observed at 300 mM Cu were ∼ ∼7-fold higher than in unsupplemented controls. Decreased laccase activity similar to levels detected in unsupplemented controls, as well as an adverse effect on fungal growth, occurred with further supplementation up to and including 0.9 mM Cu, but higher enzyme titres (2- to 16-fold compared with controls) were induced in cultures supplemented with 1–2 mM Cu2+. SDS-PAGE combined with activity staining revealed the presence of a single protein band (M r ∼ ∼70 kDa) exhibiting laccase activity in control culture fluids, whereas an additional distinct second laccase protein band (M r␣∼ ∼45 kDa) was observed in cultures supplemented with 1–2 mM Cu. Increased levels of extracellular laccase activity, and both laccase isozymes, were also detected in cultures of G. frondosa supplemented with ferulic, vanillic, veratric and 4-hydroxybenzoic acids, and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde. The optimal temperature and pH values for laccase activity were 65 °C and pH 2.2 (using 2,2′-azinobis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonate) {ABTS} as substrate), respectively, and the enzyme was relatively heat stable. In solid-state cultures of G. frondosa grown under conditions adopted for industrial-scale mushroom production, extracellular laccase levels increased during the substrate colonization phase, peaked when the substrate was fully colonized, and then decreased sharply during fruit body development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archibald F., Roy B., 1992 Production of manganic chelates by laccase from the lignin degrading fungus Trametes (Coriolus) versicolor Applied and Environmental Microbiology 58:1496–1499
Ardon O., Kerem Z., Hadar Y., 1988 Enhancement of lignin degradation and laccase activity in Pleurotus ostreatus by cotton stalk extract Canadian Journal of Microbiology 44:676–680
Baldrian P., Gabriel J., 2002 Copper and cadmium increase laccase activity in Pleurotus ostreatus FEMS Microbiology Letters 206:69–74
Bollag J.-M., Leonowicz A., 1984 Comparative studies of extracellular fungal laccases Applied and Environmental Microbiology 48:849–854
Bollag J.-M., Shuttleworth K.L., Anderson D.H., 1988 Laccase-mediated detoxification of phenolic compounds Applied and Environmental Microbiology 54:3086–3091
Bourbonnais R., Paice M.G., 1988 Veratryl alcohol oxidases from the lignin-degrading basidiomycete Pleurotus sajor-caju Biochemical Journal 255:445–450
Buswell J.A., Cai Y.J., Chang S.T., Peberdy J.F., Fu S.Y., Yu H.-S., 1996 Lignocellulolytic enzyme profiles of edible mushroom fungi World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 12:537–542
Cai Y.J., Chapman S.J., Buswell J.A., Chang S.T., 1999 Production and distribution of endoglucanase, cellobiohydrolase, and β-glucosidase components of the cellulolytic system of Volvariella volvacea, the edible straw mushroom Applied and Environmental Microbiology 65:553–559
Chang S.T. 2005 Witnessing the development of the mushroom industry in China. In Tan, Q., Zhang, J.S., Chen, M.J., Cao, H. & Buswell, J.A., (eds). Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Mushroom Biology and Mushroom Products, Shanghai, 8–12 April 2005, Acta Edulis Fungi, Shanghai, China, pp. 3–19
Chen S.C., Ma D., Ge W., Buswell J.A., 2003 Induction of laccase activity in the edible straw mushroom, Volvariella volvacea FEMS Microbiology Letters 218:143–148
Chen S.C., Ge W., Buswell J.A., 2004a Biochemical and molecular characterization of a laccase from the edible straw mushroom, Volvariella volvacea European Journal of Biochemistry 271:318–328
Chen S.C., Ge W., Buswell J.A., 2004b Molecular cloning of a new laccase from the edible straw mushroom Volvariella volvacea: possible involvement in fruit body development FEMS Microbiology Letters 230:171–176
Cherney J.H., Anliker K.S., Albrecht K.A., Wood K.V., 1989 Soluble phenolic monomers in forage crops Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 37:345–350
Collins P.J., Dobson A.D.W., 1997 Regulation of laccase gene transcription in Trametes versicolor Applied and Environmental Microbiology 63:3444–3450
Das N., Sengupta S., Mukherjee M., 1997 Importance of laccase in vegetative growth of Pleurotus florida Applied and Environmental Microbiology 63:4120–4122
De Vries O.M.H., Koolstra W.H.C.F., Wessels. G.H., 1986 Formation of an extracellular laccase by Schizophyllum commune dikaryon Journal of General Microbiology 132:2817–2826
Eggert C., Temp U., Eriksson K.-E., 1996 The ligninolytic system of the white rot fungus Pycnoporus cinnabarinus: purification and characterization of the laccase Applied and Environmental Microbiology 62:1151–1158
Eggert C., Temp U., Eriksson K.-E., 1997 Laccase is essential for lignin degradation by the white rot fungus Pycnoporus cinnabarinus FEBS Letters 407:89–92
Fåhraeus G., Reinhammar B., 1967 Large scale production and purification of laccase from culture of the fungus Polyporus versicolor and some properties of laccase A Acta Chemica Scandinavica 21:2367–2378
Fu S.Y., Yu H.-S., Buswell J.A., 1997 Effect of nutrient nitrogen and manganese on manganese peroxide and laccase production by Pleurotus sajor-caju FEMS Microbiology Letters 147:133–137
Fukushima M., Ohashi T., Fujiwara Y., Sonoyama K., Nakano M., 2001 Cholesterol-lowering effects of maitake (Grifola frondosa) fiber, shiitake (Lentinus edodes) fiber, and enokitake (Flammulina velutipes) fiber in rats Experimental Biology and Medicine 226:758–765
Galhaup C., Goller S., Peterbauer C.K., Strauss J., Haltrich D., 2002 Characterization of the major laccase isozyme from Trametes pubescens and regulation of its synthesis by metal ions Microbiology 148:2159–2169
Galliano H., Gas G., Seris J.L., Boudet A.M., 1991 Lignin degradation by Rigidoporus lignosus involves synergistic action of two enzymes: Mn peroxidase and laccase Enzyme and Microbial Technology 13:478–482
Horio H., Ohtsuru M., (2001) Maitake (Grifola frondosa) improve glucose tolerance of experimental diabetic rats Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology 47:57–63
Kodama N., Komuta K., Nanba H., 2003 Effect of Maitake (Grifola frondosa) D-fraction on the activation of NK cells in cancer patients Journal of Medicinal Food 6:371–377
Kofujita H., Ohta T., Asada Y., Kuwuhara M., 1991 Purification and characterisation of laccase from Lentinus edodes Mokuzai Gakkaishi 37:562–569
Kubo K., Aoki H., Nanba H., (1994) Anti-diabetic activity present in the fruit body of Grifola frondosa (Maitake) Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 17:1106–1110
Kubo K., Nanba H., (1997) Anti-hyperliposis effect of maitake fruit body (Grifola frondosa) Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 20:781–785
Leatham G.F., Stahmann M.A., 1981 Studies on the laccase of Lentinus edodes: specificity, localization and association with the development of fruiting bodies Journal of General Microbiology 125:147–157
Lo S.C., Ho Y.S., Buswell J.A., 2001 Effect of phenolic monomers on the production of laccases by the edible mushroom Pleurotus sajor-caju, and partial characterization of a major laccase component Mycologia 93:413–421
Messerschmidt A., Huber R., 1990 The blue oxidases, ascorbate oxidase, laccase and ceruloplasmin. Modelling and structural relationships European Journal of Biochemistry 187:341–352
Ohga S., 1992 Comparison of extracellular enzyme activities among different strains of Lentinus edodes grown on sawdust-based cultures in relation to their fruiting bodies Mokuzai Gakkaishi 38:310–316
Ohga S., Royse D.J., 2001 Transcriptional regulation of laccase and cellulase genes during growth and fruiting of Lentinula edodes on supplemented sawdust FEMS Microbiology Letters 201:111–115
Ohga S., Smith M., Thurston C.F., Wood D.A., 1999 Transcriptional regulation of laccase and cellulase genes in the mycelium of Agaricus bisporus during fruit body development on a solid substrate Mycological Research 103:1557–1560
Ohno N., Adachi Y., Suzuki I., Oikawa S., Sato K., Ohsawa M., Yadomae T., 1986 Antitumor activitiy of a beta-1,3-glucan obtained from liquid cultured mycelium of Grifola frondosa Journal of Pharmacobiodynamics 9:861–864
Palmieri G., Giardina P., Bianco C., Fontanella B., Sannia G., 2000 Copper induction of laccase isoenzymes in the ligninolytic fungus Pleurotus ostreatus Applied and Environmental Microbiology 66:920–924
Palmieri G., Bianco C., Cennamo G., Giardina P., Marino G., Monti M., Sannia G., 2001 Purification, characterization and functional role of a novel extracellular protease from Pleurotus ostreatus Applied and Environmental Microbiology 67:2574–2579
Périé F.H., Reddy G.V.B., Blackburn N.J., Gold M.H., 1998 Purification and characterization of laccases from the white-rot basidiomycete Dichomitus squalens Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 353:349–355
Sannia G., Giardina P., Luna M., Rossi M., Buonocore V., 1986 Laccases from Pleurotus ostreatus Biotechnology Letters 8:797–800
Soden D.M., Dobson A.D.W., 2001 Differential regulation of laccase gene expression in Pleurotus sajor-caju Microbiology 147:1755–1763
Srinivasan C., D’Souza T.M., Boominathan K., Reddy C.A., 1995 Demonstration of laccase in the white rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium BKM-F1767 Applied and Environmental Microbiology 61:4274–4277
Takayama C., Ohga S., Sakai K., 1993 Sawdust-based cultivation and changes of the culture mature degree of the edible mushroom, Pleurotus abalonus Journal of Faculty Agriculture, Kyushu University 38:19–33
Thurston C.F., 1994. The structure and function of fungal laccases Microbiology 140:19–26
Wood D.A., 1980 Inactivation of extracellular laccase during fruiting of Agaricus bisporus Journal of General Microbiology 117:339–345
Wood D.A., Goodenough P., 1977 Fruiting of Agaricus bisporus: changes in extracellular enzyme activities during growth and fruiting Archives of Microbiology 114:161–165
Yaver D.S., Xu F., Golightly E.J., Brown K.M., Brown S.H., Rey M.W., Schneider P., Halkier T., Mondorf K., Dalboge H., 1996 Purification, characterization, molecular cloning, and expression of two laccase genes from the white rot basidiomycete Trametes villosa Applied and Environmental Microbiology 62:834–841
Zhang Y., Mills G.L., Nair M.G. (2002) Cyclooxygenase inhibitory and antioxidant compounds from the mycelia of the edible mushroom Grifola frondosa Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 50:7581–7585
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr Yaosong Wang for technical assistance, and John Buswell for linguistic revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, Z., Cheng, J., Tan, Q. et al. Effect of nutritional parameters on laccase production by the culinary and medicinal mushroom, Grifola frondosa . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22, 799–806 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-005-9106-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-005-9106-0