Abstract
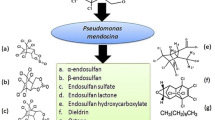
The overapplication of endosulfan on crops has resulted in the widespread contamination of soil. In this study, we examine the potential for bioremediation of the bacteria strain Alcaligenes faecalis JBW4 in degrading endsosulfan in soils. Bacteria were inoculated into sterilized and non-sterilized soils (Argi-Udic Ferrosols and Hapli-Udic Isohumosols) spiked with endosulfan. The results obtained from polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis indicate that JBW4 colonized Argi-Udic Ferrosols and Hapli-Udic Isohumosols successfully. The degradation efficiencies of α and β isomers of endosulfan by JBW4 were higher in Hapli-Udic Isohumosols than in Argi-Udic Ferrosols, and α and β isomers were degraded by 100.0 and 69.8%, respectively. In addition, detected endosulfan metabolites were either endosulfan ether and endosulfan lactone. Results of the single-cell gel electrophoresis assay showed that the toxicity of endosulfan and its metabolites in Hapli-Udic Isohumosols decreased after 77 days when compared to those in Argi-Udic Ferrosols after degradation by JBW4. Strain JBW4 is an excellent bio-remediator through its ability to degrade endosulfan in contaminated Argi-Udic Ferrosols and Hapli-Udic Isohumosols.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenburger, A., Ekelund, F., & Jacobsen, C. S. (2010). Protozoa and their bacterial prey colonize sterile soil fast. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 42, 1636–1639.
Antonious, G. F., & Byers, M. E. (1997). Fate and movement of endosulfan under field conditions. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 16, 644–649.
Beyers, R. A., Woodham, D. W., & Bowman, M. C. G. (1965). Residues on coastal bermuda grass, trash and soil treated with endosulfan. Journal Economic Entomology 58, 160–1.
Castillo, J. M., Casas, J., & Romero, E. (2011). Isolation of an endosulfan-degrading bacterium from a coffee farm soil: persistence and inhibitory effect on its biological functions. Science of the Total Environment, 412–413, 20–27.
Chakrabarty, S., Rajakumar, A., Raghuveer, K., Sridevi, P., Mohanachary, A., Prathibha, Y., Bashyam, L., Dutta-Gupta, A., & Senthilkumaran, B. (2012). Endosulfan and flutamide, alone and in combination, target ovarian growth in juvenile catfish, Clarias batrachus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - Part C, 155, 491–497.
Dorough, H. W., Huhtanen, K., Marshall, T. C., & Bryant, H. E. (1978). Fate of endosulfan in rats and toxicological considerations of apolar metabolites. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 8, 241–252.
Fuentes, M. S., Sáez, J. M., Benimeli, C. S., & Amoroso, M. J. (2011). Lindane biodegradation by defined consortia of indigenous Streptomyces strains. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 222, 217–231.
Giri, K., & Rai, J. P. N. (2012). Biodegradation of endosulfan isomers in broth culture and soil microcosm by Pseudomonas fluorescens isolated from soil. International Journal of Environmental Studies, 69, 729–742.
Girvan, M. S., Bullimore, J., Pretty, J. N., Osborn, A. M., & Ball, A. S. (2003). Soil type is the primary determinant of the composition of the total and active bacterial communities in arable soils. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 1800–1809.
Goswami, S., & Singh, D. K. (2009). Biodegradation of α and β endosulfan in broth medium and soil microcosm by bacterial strain Bordetella sp. B9. Biodegradation, 20, 199–207.
Goswami, S., Vig, K., & Dileep, K. (2009). Biodegradation of α and β endosulfan by Aspergillus sydoni. Chemosphere, 75, 883–888.
Jia, H. L., Li, Y. F., Wang, D. G., Cai, D. J., Yang, M., Ma, J. M., & Hu, J. X. (2009). Endosulfan in China 1—gridded usage inventories. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 16, 295–301.
Jia, H., Liu, L., Sun, B., Wang, D., Su, Y., Kannan, K., & Li, Y. F. (2010). Monitoring and modeling endosulfan in Chinese surface soil. Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 9279–9284.
Kamei, I., Takagi, K., & Kondo, R. (2011). Degradation of endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate by white-rot fungus Trametes hirsute. Journal of Wood Science, 57, 317–322.
Kataoka, R., & Takagi, K. (2013). Biodegradability and biodegradation pathways of endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 3285–3292.
Kong, L. F., Zhu, S. Y., Zhu, L. S., Xie, H., Su, K. C., Yan, T. X., Wang, J., Wang, J. H., Wang, F. H., & Sun, F. X. (2013a). Biodegradation of organochlorine pesticide endosulfan by bacterial strain Alcaligenes faecalis JBW4. Journal of Environmental Science, 25, 2257–2264.
Kong, L. F., Zhu, S. Y., Zhu, L. S., Xie, H., Kai, W., Yan, T. X., Wang, J., Wang, J. H., Wang, F. H., & Sun, F. X. (2013b). Colonization of Alcaligenes faecalis strain JBW4 in natural soils and its detoxification of endosulfan. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98, 1407–1416.
Kullman, S. W., & Matsumura, F. (1996). Metabolic pathways utilized by Phanerochaete chrysosporium for degradation of the cyclodiene pesticide endosulfan. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 593–600.
Kumar, M., & Philip, L. (2006). Adsorption and desorption characteristics of hydrophobic pesticide endosulfan in four Indian soils. Chemosphere, 62, 1064–1077.
Lu, R. K. (2000). Soil agricultural chemistry analytical methods [M]. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press.
Nikolic, V., Velickovic, S., & Popovic, A. (2014). Biodegradation of polystyrene-graft-starch copolymers in three different types of soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 9877–9886.
Øvreas, L., & Torsvik, V. (1998). Microbial diversity and community structure in two different agricultural soil communities. Microbial Ecology, 36, 303–315.
Parkpian, P., Anurakpongsatorn, P., Pakkong, P., & Patrick, W. H. (1998). Adsorption, desorption and degradation of a-endosulfan in tropical soils of Thailand. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part. B, 33(3), 211–233.
Phillips, T. M., Seech, A. G., Lee, H., & Trevors, J. T. (2005). Biodegradation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) by microorganisms. Biodegradation, 16, 363–392.
Poolpak, T., Pokethitiyook, P., Kruatrachue, M., Arjarasirikoon, U., & Thanwaniwat, N. (2008). Residue analysis of organochlorine pesticides in the Mae Klong river of Central Thailand. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 156, 230–239.
Rao, D., Skovhus, T., Tujula, N., Holmström, C., Dahllöf, I., Webb, J. S., & Kjelleberg, S. (2010). Ability of Pseudoalteromonas tunicata to colonize natural biofilms and its effect on microbial community structure. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 73, 450–457.
Romero-Aguilar, M., Tovar-Sánchez, E., Sánchez-Salinas, E., Mussali-Galante, P., Sánchez-Meza, J. C., Castrejón-Godínez, M. L., Dantán-González, E., Trujillo-Vera, M. Á., & Ortiz-Hernández, M. L. (2014). Penicillium sp. as an organism that degrades endosulfan and reduces its genotoxic effects. SpringerPlus, 3, 536.
Singh, N. S., & Singh, D. K. (2011). Biodegradation of endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate by Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain C8B in broth medium. Biodegradation, 22, 845–857.
Singh, V., & Singh, N. (2014). Uptake and accumulation of endosulfan isomers and its metabolite endosulfan sulfate in naturally growing plants of contaminated area. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 104, 189–193.
Sutherland, T. D., Weir, K. M., Lacey, M. J., Horne, I., Russell, R. J., & Oakeshott, J. G. (2002). Enrichment of a microbial culture capable of degrading endosulphate, the toxic metabolite of endosulfan. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 92, 541–548.
Svartz, G. V., Wolkowicz, R. H., & Coll, C. S. P. (2014). Toxicity of endosulfan on embryo-larval development of the South American toad Rhinella arenarum. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 33, 875–881.
Tao, Y. X., Pan, L. Q., Zhang, H., & Tian, S. M. (2013). Assessment of the toxicity of organochlorine pesticide endosulfan in clams Ruditapes philippinarum. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 93, 22–30.
Thangadurai, P., & Suresh, S. (2014). Biodegradation of endosulfan by soil bacterial cultures. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 94, 38–47.
Varon-Lopez, M., Dias, A. C. F., Fasanella, C. C., Durrer, A., Melo, I. S., Kuramae, E. E., & Andreote, F. D. (2014). Sulphur-oxidizing and sulphate-reducing communities in Brazilian mangrove sediments. Environmental Microbiology, 16, 845–855.
Wan, M. T., Kuo, J.-N., Buday, C., Schroeder, G., Aggelen, G. V., & Pasternak, J. (2005). Toxicity of α-, β-, (α + β)-endosulfan and their formulated and degradation products to Daphnia magna, Hyalella azteca, Oncophynchus mykiss, Oncophynchus kisutch, and biological implications in streams. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 1146–1154.
Zhan, F. Q., Hou, M., Yang, R., & Long, X. Q. (2013). Identification and colonization of a tomato blight antagonistic bacteria in the study of pot experiment. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 50, 1277–1287.
Zhang, J., Qin, J., Zhao, C. C., Liu, C., & Xie, H. J. (2015). Response of bacteria and fungi in soil microcosm under the presence of pesticide endosulfan. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226, 109.
Zhao, C. C., Xie, H. J., Mu, Y., Xu, X. L., Zhang, J., Liu, C., Liang, S., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W. S., Xu, J. T., & Wang, Q. (2014). Bioremediation of endosulfan in laboratory-scale constructed wetlands: effect of bioaugmentation and biostimulation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 12827–12835.
Acknowledgments
We thank the professor of soil and water science, University of Florida, and the student of agricultural science, North Carolina State University for reviewing the manuscript. This study was funded by grants from the National Key Research and Development Plan (No. 2016YFD0800202) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21377075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhu, L., Wang, J. et al. Biodegradation of Endosulfan by Bacterial Strain Alcaligenes faecalis JBW4 in Argi-Udic Ferrosols and Hapli-Udic Isohumosols. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 425 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3125-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3125-3