Abstract
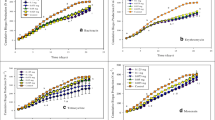
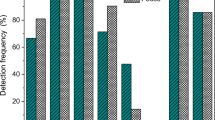
Colistin is a peptide antibiotic widely used as a food additive in animal farming, specially swine and poultry, and also has recently been applied in human medicine to treat infections caused by multiresistant gram-negative bacteria strains. When orally administered, colistin is eliminated in feces virtually unaltered; thus, it may reach water bodies and wastewater treatment facilities in its active form. Apart from the risks associated with development of antimicrobial resistance and environmental toxicity issues, the presence of antimicrobials in wastewater can, additionally, interfere in biological processes commonly used to treat them. Nitrifying bacteria are among the most sensitive microorganisms to inhibitory compounds, including pharmaceuticals, and are useful as biosensors to access contaminant toxicity information in wastewater treatment plants. Therefore, in order to assess the colistin acute toxicity to the microorganisms involved in the nitrification processes, the nitritation and nitratation kinetics were monitored under different colistin concentrations. The results showed that only ammonia-oxidizing bacteria are sensitive to the antibiotic, presenting an IC50 of 10.8 mg L−1 of colistin when used as a commercial formulation and 67.0 mg L−1 when used as raw colistin sulfate. For nitrite-oxidizing bacteria, even the highest colistin concentration used in the assays (316 mg L−1) was not sufficient to inhibit the process. According to these results, the colistin concentrations expected in animal farming wastewater, when its dosage is used as a growth promoter, would not be enough to keep nitrification from taking place. Nevertheless, when used in higher concentrations, such as for therapeutic purposes, it could endanger the maintenance of the process.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alighardashi, A., Pandolfi, D., Potier, O., & Pons, M. N. (2009). Acute sensitivity of activated sludge bacteria to erythromycin. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(2–3), 685–692. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.051.
APHA, AWWA, & WEF. (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Azap, O. K., Timurkaynak, F., Arslan, H., Basaran, O., & Haberal, M. (2008). Colistin: an old drug for difficult-to-treat burn infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 12, S40–S40.
Batt, A. L., Kim, S., & Aga, D. S. (2006). Enhanced biodegradation of iopromide and trimethoprim in nitrifying activated sludge. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(23), 7367–7373. doi:10.1021/Es060835v.
Bernet, N., & Spérandio, M. (2009). Principles of nitrifying processes. In F. J. Cervantes (Ed.), Environmental technologies to treat nitrogen pollution (pp. 23–39). London: IWA Publishing.
Blum, D. J. W., & Speece, R. E. (1991). A database of chemical toxicity to environmental bacteria and its use in interspecies comparisons and correlations. Research Journal of the Water Pollution Control Federation, 63(3), 198–207.
Callens, B., Persoons, D., Maes, D., Laanen, M., Postma, M., Boyen, F., et al. (2012). Prophylactic and metaphylactic antimicrobial use in Belgian fattening pig herds. Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 106(1), 53–62. doi:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2012.03.001.
Campos, J. L., Garrido, J. M., Mendez, R., & Lema, J. M. (2001). Effect of two broad-spectrum antibiotics on activity and stability of continuous nitrifying system. Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 95(1), 1–10.
Carucci, A., Cappai, G., & Piredda, M. (2006). Biodegradability and toxicity of pharmaceuticals in biological wastewater treatment plants. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part a-Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 41(9), 1831–1842.
Casal, J., Mateu, E., Mejia, W., & Martin, M. (2007). Factors associated with routine mass antimicrobial usage in fattening pig units in a high pig-density area. Veterinary Research, 38(3), 481–492. doi:10.1051/vetres:2007010.
Cataldo, D. A., Haroon, M., Schrader, L. E., & Youngs, V. L. (1975). Rapid colorimetric determination of nitrate in plant tissue by nitration of salicylic acid. Comum Soil Sci. Plant Anal., 6, 71–80.
Dokianakis, S. N., Kornaros, M. E., & Lyberatos, G. (2004). On the effect of pharmaceuticals on bacterial nitrite oxidation. Water Sci Technol, 50(5), 341–346.
EMEA (2002). Colistin—summary report (EMEA/MRL/016/95-Final), 6.
Ghosh, G. C., Okuda, T., Yamashita, N., Tanaka, H. (2008). Antibiotics biodegradation during nitrification: a novel approach to reduce antibiotics load to water environment from nitrogen enriched wastewater. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, WEFTEC: Session 101 through session 115, 7494–7507.
Gomez, J., Mendez, R., & Lema, J. M. (1996). The effect of antibiotics on nitrification processes. Batch assays. Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 57–58, 869–876.
Grunditz, C., & Dalhammar, G. (2001). Development of nitrification inhibition assays using pure cultures of Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter. Water Research, 35(2), 433–440.
Kim, S., Weber, A. S., Batt, A., & Aga, D. S. (2008). Removal of pharmaceuticals in biological wastewater treatment plants. In D. S. Aga (Ed.), Fate of Pharmaceuticals in the environment and in water treatment systems (pp. 349–361). New York: CRC Press.
Kümmerer, K. (2009). Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—a review—part I. Chemosphere, 75(4), 417–434.
Kunz, A., Miele, M., & Steinmetz, R. L. R. (2009). Advanced swine manure treatment and utilization in Brazil. Bioresource Technology, 100(22), 5485–5489.
Louvet, J. N., Giammarino, C., Potier, O., & Pons, M. N. (2010). Adverse effects of erythromycin on the structure and chemistry of activated sludge. Environmental Pollution, 158(3), 688–693.
Massone, A., Gernaey, K., Rozzi, A., & Verstraete, W. (1998). Measurement of ammonium concentration and nitrification rate by a new titrimetric biosensor. Water Environment Research, 70(3), 343–350. doi:10.2175/106143098x124975.
Moore, J. E., & Elborn, J. S. (2012). Implications for colistin use in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF): letter in response to “Prophylactic and metaphylactic antimicrobial use in Belgian fattening pig herds” by Callens [Prev. Vet. Med. 106 (2012) 53–62]. Preventive Veterinary Medicine. doi:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2012.09.006.
Nasnas, R., Saliba, G., & Hallak, P. (2009). The revival of colistin: an old antibiotic for the 21st century. Pathologie Biologie, 57(3), 229–235.
Nation, R. L., & Li, J. (2009). Colistin in the 21st century. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases, 22(6), 535–543.
Ren, S. J. (2004). Assessing wastewater toxicity to activated sludge: recent research and developments. Environment International, 30(8), 1151–1164. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2004.06.003.
Sarkar, S., DeSantis, E. R. H., & Kuper, J. (2007). Resurgence of colistin use. American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy, 64(23), 2462–2466.
Tanaka, H., Uzman, S., & Dunn, J. (1981). Kinetics of nitrification using a fluidized sand bed reactor with attached growth. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 23, 1683–1702.
Tang, C. J., Zheng, P., Chen, T. T., Zhang, J. Q., Mahmood, Q., Ding, S. A., et al. (2011). Enhanced nitrogen removal from pharmaceutical wastewater using SBA-ANAMMOX process. Water Research, 45(1), 201–210. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.036.
Tomlinson, T. G., Boon, A. G., & Trotman, C. N. A. (1966). Inhibition of nitrification in the activated sludge process of sewage disposal. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 29(2), 266–291.
Toth, J. D., Feng, Y. C., & Dou, Z. X. (2011). Veterinary antibiotics at environmentally relevant concentrations inhibit soil iron reduction and nitrification. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 43(12), 2470–2472. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.09.004.
Vanotti, M. B., & Hunt, P. G. (2000). Nitrification treatment of swine wastewater with acclimated nitrifying sludge immobilized in polymer pellets. Transactions of the Asae, 43(2), 405–413.
Vogel, A. I. (1981). Análise Inorgânica Quantitativa (4ath ed.). Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara.
Wang, S. Y., & Gunsch, C. K. (2011). Effects of selected pharmaceutically active compounds on the ammonia oxidizing bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea. Chemosphere, 82(4), 565–572. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.007.
Zdradek, C. P. (2005). Seleção de linhagens oxidadoras de amônio e remoção de nitrogênio via nitrito em reator descontínuo alimentado (SBR), sob condições de limitação de oxigênio. UFSC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bressan, C.R., Kunz, A., Schmidell, W. et al. Toxicity of the Colistin Sulfate Antibiotic Used in Animal Farming to Mixed Cultures of Nitrifying Organisms. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1441 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1441-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1441-4