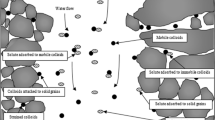
Abstract
There are several classes of subsurface colloids, abiotic and biotic. Basically, small particles of inorganic, organic and pathogenic biocolloids variety exist in natural subsurface system. Transport of these pathogenic biocolloidal contaminants (Viruses, bacteria and protozoa) pose a great risk in water resources and have caused large outbreaks of waterborne diseases. Biocolloid transport processes through saturated and unsaturated porous media is of significant interest, from the perspective of protection of groundwater supplies from contamination, assessment of risk from pathogens in groundwater and for the design of better water treatment systems to remove biocolloids from drinking water supplies This paper has reviewed the large volume of work that has already been done and the progress that has been made towards understanding the various basic multi-processes to predicting the biocolloid transport in saturated and unsaturated porous media. There are several basic processes such as physical, chemical and biological processes which are important in biocolloid transport. The physical processes such as advection, dispersion, diffusion, straining and physical filtration, adsorption and biological processes such as growth/decay processes and include active adhesion/detachment, survival and chemotaxis are strongly affected on biocolloid transport in saturated and unsaturated porous media. The unsaturated zone may play an important role in protecting aquifers from biocolloidal contamination by retaining them in the solid phase during their transport through the zone. Finally, author here highlighted the future research direction based on his critical review on biocolloid transport in saturated and unsaturated porous media.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C :
-
Total biocolloidal mass particle concentration (kg/m3)
- D :
-
Hydrodynamic dispersion coefficient of colloids (m2/s)
- d p :
-
Particle diameter (m)
- d m :
-
Diameter of medium/collector (m)
- d 50 :
-
Median grain size
- dh/dl :
-
Hydraulic gradient (Pa/m)
- K :
-
Permeability of porous medium (m2)
- K d :
-
Dissociation constant
- S :
-
Total retained biocolloid concentration (kg/kg)
- t :
-
Duration of time (s)
- v :
-
Pore water velocity (m/s)
- v c :
-
Chemotactic velocity (m/s)
- x :
-
Distance travelled (m)
- X (C F ) :
-
Chemotactic sensitivity coefficient
- θ :
-
Effective porosity
- ρ bulk :
-
Bulk density of porous medium, kg/m3
- ADS:
-
Advection–dispersion–sorption
- AWI:
-
Air–water interface
- DLVO:
-
Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek
- DO:
-
Dissolved oxygen
- E. coli :
-
Escherichia coli
- SWI:
-
Solid–water interface
References
Abdel-Fattah, A. I., & EL-Genk, M. S. (1998). On colloidal particle sorption onto a stagnant air-water interface. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 78, 237–266.
Adamczyk, Z., Jaszczolt, K., & Siwelk, B. (2005). Irreversible adsorption of colloid particles on heterogeneous surfaces. Applied Surface Science, 252, 723–729.
Adler, J. (1966). Chemotaxis in bacteria. Science, 153(3737), 708–716.
Arturo, A. K., & Auset, M. (2007). A review of visualization technique of biocolloid transport processes at the pore scale under saturated and unsaturated conditions. Advances in Water Resources, 30, 1392–1407.
Auset, M., & Keller, A. A. (2004). Pore-scale processes that control dispersion of colloids in saturated porous media. Water Resources Research, 40, W03503. doi:10.1029/2003WR002800.
Ausland, G., Stevik, T. K., Hanssen, J. F., Kohler, J. C., & Jenssen, P. D. (2002). Intermittent filtration of wastewater—removal of fecal coliforms and fecal streptococci. Water Research, 36, 3507–3516.
Azerdo, J., Visser, J., & Oliveira, R. (1999). Exopolymers in bacterial adhesion: interpretation in terms of DLVO and XDLVO theories. Colloids and Surfaces B, 14, 141–148.
Bales, R. C., Gerba, C. P., Grondrn, G. H., & Jensen, S. L. (1989). Bacteriophase transport in sandy soil and fractured tuff. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 55, 2061–2067.
Bales, R. C., Hinkle, S. R., & Kroeger, T. W. (1991). Bacterophase adsorption during transport through porous media: chemical perturbations and reversibility. Environmental Science & Technology, 25, 2088–2095.
Bales, R. C., Li, S., Maguire, K. M., Yahya, M. T., & Gerba, C. P. (1993). Ms-2 and poliovirus transport in porous media: hydrophobic effects and chemical perturbations. Water Resources Research, 29, 957–963.
Baygents, J. D., Glynn, J. R., Albinger, O., Biesemeyer, B. K., Ogden, K. L., & Arnold, R. G. (1998). Variation of surface charge density in monoclonal bacterial populations: implications for transport through porous media. Environmental Science & Technology, 32(11), 1596–1603.
Benenson, A. S. (1995). Control of communicable diseases manual (16th ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Bergendahl, J., & Grasso, D. (1999). Prediction of colloidal detachment in a model porous media: thermodynamics. AIChE Journal, 45, 475–484.
Bhattacharjee, S., Ryan, J. N., & Elimelech, M. (2002). Virus transport in physically and geochemically heterogeneous subsurface porous media. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 57, 161–187.
Bitton, G., & Gerba, C. P. (1984). Groundwater pollution microbiology: the emerging issue. New York: Wiley.
Bradford, S. A., Simunek, M., Bellahar, M. T., Van, G., & Yates, S. R. (2003). Modelling colloid attachment, straining and exclusion in saturated porous media. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 2242–2250.
Bradford, S. A., Simunek, T., Bettahar, M., Tadassa, Y. F., van Genuchten, M. T., & Yates, S. R. (2005). Straining of colloids at textural interface. Water Resources Research, 41(W10404), 1–17. doi:10.1029/2004WR003675.
Bradford, S. A., Simunik, J., & Walker, S. L. (2006). Transport and straining of E. coli O157:H7 in saturated porous media. Water Resources Research, 42(W12S12), 1–12. doi:10.1029/2005WR004805.
Bradford, S. A., Torkzaban, S., & Walker, S. L. (2007). Coupling of physical and chemical mechanisms of colloid straining in saturated porous media. Water Research, 41, 3012–3024.
Bradford, S. A., Yates, S. R., Bettahar, M., & Simunek, J. (2002). Physical factors affecting the transport and fate of colloids in saturated porous media. Water Resources Research, 38, 1327.
Bruens, M. R., Kapil, S., & Oehme, F. W. (2000). Pseudomonas picleettic: a common soil and groundwater aerobic bacteria with pathogenic and biodegradation properties. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 47(2), 105–111.
Camesano, T. A., & Logan, B. E. (2000). Probing bacterial electrostatic interactions using atomic force microscopy. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(16), 3354–3362.
Canter, L., & Knox, R. (1984). Evaluation of septic tank system effects on groundwater quality. EPA project Summary, EPA-600/S2-84-107. Washington: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Chen, L., Sabatini, D. A., & Kibbey, T. C. G. (2008). Role of the air-water interface in the retention of TiO2 nanoparticles in porous media during primary drainage. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 1916–1921.
Cherrey, K. D., Flury, M., & Harsh, J. B. (2003). Nitrate and colloid transport through coarse Hanford sediments under steady state variably saturated flow. Water Resources Research, 39, 1165. doi:10.1029/2002WR001944.
Chet, I., & Mitchell, R. (1976). Ecological aspects of microbial chemotacic behaviour. Annual Review of Microbiology, 30, 221–239.
Chin, G., & Flurry, M. (2005). Retention of mineral colloids in unsaturated porous media as related to their surface properties. Colloids and Surfaces A, 256, 207–216.
Chrysikopoulos, C. V., & Sim, Y. (1996). One-dimentional virus transport in homogeneous porous media with time-dependent distribution coefficient. Journal of Hydrology, 185, 199–219.
Chu, Y., Jin, Y., Flurry, M., & Yates, M. V. (2001). Mechanisms of virus removal during transport in unsaturated porous media. Water Resources Research, 37, 253–263.
Chu, Y., Jin, Y., & Yates, M. V. (2000). Virus transport through saturated sand columns as affected by different buffer solutions. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29, 1103–1110.
Corapcioglu, M. Y., & Haridas, A. (1984). Transport and fate of microorganisms in porous media: a theoretical investigation. Journal of Hydrology, 72, 149–169.
Corapcioglu, M. Y., & Haridas, A. (1985). Microbial transport in soils and groundwater: a numerical model. Advances in Water Resources, 8, 188–200.
Crist, J. T., McCarthy, J. F., Zevi, Y., Baveye, P., Throop, J. A., & Steenhuis, T. S. (2004). Pore-scale visualization of colloid transport and retention in partially saturated porous media. Vadose Zone Journal, 3, 444–450.
Crist, J. T., Zevi, Y., McCarthy, J. F., Throop, J. A., & Steenhuis, T. S. (2005). Transport and retention mechanisms of colloid in partially saturated porous media. Vadose Zone Journal, 4, 184–195.
Daniels, S. L. (1980). Mechanisms involved in sorption of microorganisms to solid surface. In G. Bitton & K. C. Marshall (Eds.), Adsorption of microorganisms to surfaces. New York: Wiley.
Dawson, M. P., Humphrey, B. A., & Marshall, K. C. (1981). Adhesion: a tactic in the survival strategy of a marine vibrio during starvation. Current Microbiology, 6, 195–199.
de Marsily, G. (1986). Quantitative hydrogeology. San Diego (CA): Academic.
Demenico, P. A., & Schwartz, F. W. (1990). Physical and chemical hydrology. New York: Wiley.
Duboise, S. M., Moore, B. E., & Sagik, B. P. (1976). Poliovirus survival and movement in a sandy forest soil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 31(4), 536–543.
Ducker, W. A., Xu, Z., & Israelachvili, J. N. (1994). Measurement of hydrophobic and DLVO forces in bubble-surface interactions in aqueous solutions. Langmuir, 10, 3279–3289.
Elimelech, M., & Ryan, J. N. (2002). The role of mineral colloids in the facilitated transport of contaminants in saturated porous media. In interactions between soil particles and microorganisms: impact on the terrestrial ecosystem. IUPAC Series on Analytical and Physical Chemistry of Environmental Systems (pp. 495–548). Chichester: Wiley.
Fattom, A., & Shilo, M. (1984). Phormidium J-1 bioflocculant: production and activity. Archives of Microbiology, 139, 421–426.
Fetter, C. W. (1999). Contaminant hydrology (2nd ed.). New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Fontes, D. E., Mills, A. L., Hornberger, G. M., & Herman, J. S. (1991). Physical and chemical factors influencing transport of microorganisms through porous media. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 57, 2473–2481.
Ford, R.-M., & Lauffenburger, D. A. (1991). Analysis of chemotactic bacterial distribution in population migration assays using a mathematical model applicable to steep or shallow attractant gradients. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 53, 721–749.
Ford, R. M., Phillips, B. R., Quinn, J. A., & Douglas, A. L. (1991). Measurement of bacterial random motility and chemotaxis coefficients: 1. Stopped-flow diffusion chamber assay. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 37, 647–660.
Freeze, R. A., & Cherry, J. A. (1979). Groundwater. New York: Prentice-Hall.
Gamerdinger, A. P., & Kaplan, D. I. (2001). Physical and chemical determinants of colloid transport and deposition in water-unsaturated sand and Yucca mountain tuff material. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 2497–2504.
Gannen, J. T., Manital, V. B., & Alexander, M. (1991). Relationship between cell surface properties and transport of bacteria through soil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 57, 190–193.
Gao, B., Saiers, J. E., & Ryan, J. N. (2006). Pore-scale mechanisms of colloid deposition and mobilization during steady and transient flow through unsaturated granular media. Water Resources Research, 42, W01410. doi:10.1029/2005WR004233.
Gao, B., Steenhuis, T. S., Zevi, Y., Morales, V. L., et al. (2008). Capillary retention of colloids in unsaturated porous media. Water Resources Research, 44, W04504. doi:10.1029/2006WR005332.
Gerba, C. P., & Bitton, G. (1984). Microbial pollutants: their survival and transport pattern to groundwater. In G. Bitton & C. P. Gerba (Eds.), Groundwater Pollution Microbiology. New York: Wiley Interscience.
Gerba, C. P., & Goyal, S. M. (1985). Pathogen removal from wastewater during groundwater recharges artificial recharge of groundwater. Boston: Butterworth Publishers.
Ghiorse, W. C., & Wilson, J. T. (1988). Microbial ecology of the terrestrial subsurface. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 33, 107–172.
Gibert, O., Ferguson, A. S., Kalin, R. M., Doherty, R., Dickson, K. W., McGeough, K. L., et al. (2007). Performance of a sequential reactive barrier for bioremediation of coal tar contaminated groundwater. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 6795–6801.
Gilbert, P., & Brown, M. R. W. (1995). Phenotypic plasticity and mechanisms of protection of bacterial biofilms from Antimicrobial agents. In H. E. Lappin Scott & J. W. Costerton (Eds.), Microbial biofilms (pp. 118–132). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Gilbert, P., Evans, D. J., Evans, E., Duguid, I. G., & Brown, M. R. W. (1991). Surface characteristics and adhesion of Escherichia coli. Journal of Applied Biotechnology, 71, 72–77.
Ginn, T. R., Wood, B. D., Nelson, K. E., Scheibe, T. D., Murphy, E. M., & Clement, T. P. (2002). Processes in microbial transport in the natural subsurface. Advances in Water Resources, 25(8–12), 1017–1042.
Goyal, S. M., Amundson, D. A., Robinson, R. A., & Gerba, C. P. (1989). Viruses and drug resistant bacteria in groundwater of southestern Minnesota. Journal of the Minnesota Academy of Science, 55(1), 58–62.
Grabinski, K. J. (2007). Pathogen transport and capture in a porous media biofilm reactor. Master of Science Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University.
Gross, M., Cramton, S., Gotz, F., & Peschel, A. (2001). Key role of teichoic acid net charge in staphlococces aureus colonization of artificial surfaces. Infection and Immunity, 69, 3423–3426.
Gschwend, P. M., & Reynolds, M. D. (1987). Monodisperse ferrous phosphate colloids in an anoxic groundwater plume. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 1, 309–327.
Guan, H., Makuch, D. S., Schaffer, S., & Pillai, S. D. (2003). The effect of critical pH on virus fate and treatment in saturated porous media. Groundwater, 41, 701–708.
Harvey, R. W. (1997). Microorganisms as tracers in groundwater injection and recovery experiments: a review. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 20, 461–472.
Herb Ward, C (2005). Transport and survival of viruses in the subsurface-processes, experiments and simulation models, Remediation Summer (pp. 23–48). Wiley Interscience. doi:10.1002/rem.20048.
Hornberger, G. M., Mills, A. L., & Herman, J. S. (1992). Bacterial transport in porous media: evaluation of a model using laboratory observations. Water Resources Research, 28, 915–938.
Huysman, F., & Verstraete, W. (1993). Effect of cell-surface characteristics on the adhesion of bacteria to soil particles. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 16, 21–26.
Jamieson, R. C., Gordon, R. J., Sharples, K. E., Stratton, G. W., & Madani, A. (2002). Movement and persistence of fecal bacteria in agricultural soils and subsurface drainage water: a review. Canadian Biosystems Engineering, 44, 1.1–1.9.
Jeremy, A. R., Sharon, W. L., & Elimelech, M. (2004). Bacterial adhesion and transport in porous media: role of the secondary energy minimum. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 1777–1785.
Jewett, D. G., Logan, B. E., Arnold, R. G., & Bales, R. C. (1999). Transport od pseudomonous fluorescens strain P17 through quartz sand columns as a function of water content. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 36, 73–89.
Jin, Y., Yates, M. V., Thompson, S. S., & Jury, W. A. (1997). Sorption of viruses during flow through saturated sand columns. Environmental Science & Technology, 31, 548–555.
John, D. E., & Rose, J. B. (2005). Review of factors affecting microbial survival in groundwater. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 7345–7356.
Keller, A. A., & Auset, M. (2007). A review of visualization techniques of biocolloid transport processes at the pore scale under saturated and unsaturated conditions. Advances in Water Resources, 30, 1392–1407.
Kim, M.-K., Kim, S.-B., & Park, S.-J. (2008). Bacteria transport in an unsaturated porous media: incorporation of air-water interface area model into transport modelling. Hydrological Processes, 22, 2370–2376.
Kinoshita, T., Bales, R. C., Yahya, M. T., & Gerba, C. P. (1993). Bacteria transport in a porous medium: retention of bacillus and pseudomonas on silica surface. Water Research, 27, 1295–1301.
Kjelleberg, S., & Hermansson, M. (1984). Starvation induced effects on bacterial surface characterization. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 48, 497–503.
Kramer, M. H., Herwaldt, B. L., Craun, G. P., Calderon, R. L., & Juranek, D. D. (1996). Surveillance for waterborne-disease outbreaks—United states, 1993–1994. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 45(SS-1), 1–33.
Krekeler, C., Ziehr, H., & Klein, J. (1991). Influence of physicochemical bacterial surface properties on adsorption to inorganic porous supports. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 35(4), 484–490.
Lance, J. C., & Gerba, C. P. (1984). Virus movement in soil during saturated and unsaturated flow. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 47(2), 335–337.
Lawrence, J. R., & Hendry, M. J. (1996). Transport of bacteria through geologic media. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 42, 410–422.
Lazouskaya, V., & Jin, Y. (2006). Interfacial interactions and colloid retention under steady flows in a capillary channel. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 303, 171–184.
Lazouskaya, V., & Jin, Y. (2008). Colloid retention at air-water interface in a capillary channel. Colloids and Surfaces A, 325, 141–151.
Logan, D. (2001). Transport modelling in hydrogeochemical systems. New York: Springer.
Macler, B. A., & Merkle, J. C. (2000). Current knowledge on groundwater microbial pathogens and their control. Hydrogeology Journal, 8(1), 29–40.
Martinez-Martinez, L., Pascual, A., & Perea, E. J. (1991). Kinetics of adherence of mucoid and non mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa to plastic catheters. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 34, 7–12.
McCarthy, J. F., & McKay, L. D. (2004). Colloid transport in the subsurface: past, present and future challenges. Vadose Zone Journal, 3, 326–337.
McCarthy, J., & Zachara, J. (1989). Subsurface transport of contaminants. Environmental Science & Technology, 23, 496–502.
McDowell-Boyer, L. M., Hunt, J. R., & Sitar, N. (1986). Particle transport through porous media. Water Resources Research, 22, 1901–1921.
McEldowney, S., & Fletcher, M. (1986). Adhesion of bacteria from mixed cell suspension to solid surfaces. Archives of Microbiology, 148(1), 57–62.
McKay, L. D., Cherry, J. A., Bales, R. C., Moyasar, Y. T., & Gerba, C. P. (1993). Field example of bacteriophase as tracers of fracture flow. Environmental Science & Technology, 27, 1075–1079.
Mercer, J. R., Ford, R. M., Stitz, J. L., & Bradbeer, C. (1993). Growth rate effects on fundamental transport properties of bacterial populations. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 42, 1277–1286.
Mesibov, R., Ordal, G. W., & Adler, J. (1973). The range of attractant concentrations for bacterial chemotaxis and the threshold and size of response over the range. The Journal of General Physiology, 62, 203–223.
Meyer, E. E., Rosenberg, K. J., & Israelachvile, J. (2006). Recent progress in understanding hydrophobic interactions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(43), 15739–15746.
Molozhavaya, E. I., & Chugunikhina, N. V. (1979). Forecasting groundwater microbial self-purification. Gigiena i Sanitariâ, 8, 23–27.
Morales, V. L., Gao, B., & Steenhuis, T. (2009). Grain surface-roughness effects on colloidal retention in the vadose zone. Vadose Zone Journal, 8, 11–20.
Morris, B. L., & Foster, S. S. D. (2000). Cryptos’ poridium contamination hazard assessment and risk management for british groundwater sources. Water Science and Technology, 41(7), 67–77.
Mozes, N., Marchal, F., Hermesse, M. P., Van Haecht, J. L., Peuliaux, L., & Leonard, A. J. (1987). Immobilization of microorganisms by adhesion interplay of electrostatic and nonelectrostatic interactions. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 30, 439–450.
Murphy, E. M., & Ginn, T. R. (2000). Modeling microbial processes in porous media. Hydrogeology Journal, 8, 142–158.
Murrey, J. P., & Parks, G. A. (1980). Polivirus adsorption on oxide surface. In M. C. Kavanaugh & J. O. Lockie (Eds.), Particulates in water. Characterization, fate effects and removal (pp. 97–133). Washington DC: American Chemical Society.
Nalaskowski, J., Nguyen, A., Hupka, J., & Miller, J. (2002). Study of particle-bubble interaction using atomic force microscopy-current possibilities and challenges. Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing, 36, 253–272.
Nevecherya, I. K., Shestakov, V. M., Mazaev, V. T., & Shlepnina, T. G. (2005). Survival rate of pathogenic bacteria and viruses in groundwater. Water Resources, 32(2), 209–214.
Nola, M., Njine, T., Sikati, V. F., & Djuikom, E. (2001). Distribution of pseudomonas aeruginosa and aeromonas hydrophila in groundwater in equatorial zone in Camerun and relationship with some environmental chemical factors. Rev Sci Eau/J Water Sci, 14(1), 35–53.
Nyham, J. W., Brennon, B. J., Abeele, M. L., Wheeler, W. D., et al. (1985). Distribution of plutonium and americium beneath a 33 year old liquid waste disposal site. Journal of Environmental Quality, 14, 501–509.
Oettel, M., & Dietrich, S. (2008). Colloidal interactions at fluid interfaces. Langmuir, 24, 1425–1441.
Olsson, T., & Westergren, G. (1982). Hydrophobic properties of oral streptococci. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 15, 319–323.
Pang, L., Close, M., Goltz, M., Sinton, L., & Davies, H. (2003). Estimation of septic tank setback distances based on transport of E. coli and F-RNA phases. Environment International, 29, 907–921.
Pang, L., Close, M., Noonan, M., Flintoft, M., & denBrink, P. V. (2002). DIAS report. Plant production no, 80, 209–214.
Pekdeger, A., Mathess, G. & Schroter, J. 1985. Hydrogeology in the service of man, memoires of the 18th congress of the international association of hydrogeologists, Cambridge
Penrod, S. L., Olsen, T. M., & Grant, S. B. (1996). Deposition kinetics of two viruses in packed bed of quartz granular media. Langmuir, 12, 5576–5587.
Peterson, T., & Ward, R. C. (1989). Development of a bacterial transport model for coarse soils. Water Resour Bulletin, 25, 349–357.
Poortinga, A. T., Bos, R., Norde W., & Busscher, H. J. (2002). Electric double layer interactions in bacterial adhesion to surfaces. Surface Science Reports, 47, 3–32.
Poortinga, A. T., Smit, J., vander Mei, H. C., & Busscher, H. J. (2001). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 76(4), 395–399.
Powelson, D. K., & Gerba, C. P. (1994). Viral removal from sewage effluents during saturated and unsaturated flow through soil columns. Water Research, 28, 2175–2181.
Powelson, D. K., & Mills, A. L. (1996). Bacterial enrichment at the gas-water interface of a laboratory apparatus. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 2593–2597.
Powelson, D. K., & Mills, A. L. (2001). Transport of Escherichia coli in sand columns with constant and changing water contents. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 238–245.
Powelson, D. K., Simpson, J. R., & Gerba, C. P. (1990). Virus transport and survival in saturated and unsaturated flow through soil columns. Journal of Environmental Quality, 19, 396–401.
Quyang, Y., Shinde, D., Mansell, R. S., & Harris, W. (1996). Colloid enhanced transport of chemicals in subsurface environments: a review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 26, 189–204.
Reddy, K. R., Khaleel, R., & Overcash, M. R. (1981). Behavior and transport of microbial pathogen and indicator organisms in soils treated with organic wastes. Journal of Environmental Quality, 10, 255–266.
Redman, J. A., Grant, S. B., Olson, T. M., & Estes, M. K. (2001). Pathogen filtration, heterogeneity and potable reuse of wastewater. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(9), 1798–1805.
Redman, J. A., Walker, S. L., & Elimelech, M. (2004). Bacterial adhesion and transport in porous media: Role of the secondary energy minimum. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 1777–1785.
Reynolds, P. J., Sharma, P., Jenneman, G. E., & McInerney, M. J. (1989). Mechanisms of microbial movement in subsurface materials. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 55(9), 2280–2286.
Rose, J. B., Vasconcelos, G. J., Harris, S. I., Klonicki, P. T., Sturbaum, G. D., & Moulton-Hancock, C. (2000). Giardea and cryptosporidium occurrence in groundwater. Journal of the American Water Works Association, 92(9), 117–123.
Rosers, B., & Logan, B. E. (2000). Bacterial transport in NAPL-contaminated porous media. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 126(7), 657–666.
Ryan, J. N., & Elimelech, M. (1996). Colloidal mobilization and transport in groundwater. Colloid Surf A, 107, 1–56.
Ryan, J. N., Elimelech, M., Arid, R. A., Harvey, R. W., & Johnson, P. R. (1999). Bacteriophase PRD1 and silica colloid transport and recovery in an iron oxide coated sand aquifer. Environmental Science & Technology, 33, 63–73.
Ryan, J. N., & Gschwend, P. M. (1990). Colloid mobilization in two Atlantic coastal plain aquifers: Field studies. Water Resources Research, 26, 307–322.
Saiers, J. E., & Lenhart, J. J. (2003). Colloid mobilization and transport within unsaturated porous media under transient flow conditions. Water Resources Research, 39, 1019. doi:10.1029/2002WR001370.
Santoro, T., & Stotzky, G. (1968). Sorption between microorganisms and clay minerals as determined by electrical sensing zone particle analyser. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 14(4), 299–307.
Scandura, J. E., & Sobsey, M. D. (1997). Viral and bacterial contamination of groundwater from on-site sewage pre-treatment systems. Water Science and Technology, 38(12), 141–146.
Schafer, A., Harman, H., & Zehnder, A. J. B. (1998). Bacterial accumulation at the air-water interface. Environmental Science & Technology, 32, 3704–3712.
Scheibe, T. D., & Wood, B. D. (2003). A particle-based model of size or anion exclusion with application to microbial transport in porous media. Water Resources Research, 39(4), 1080. doi:10.1029/2001WR.
Schijven, J. F., & Hassanizadeh, S. M. (2001). Virus removal by soil passage at field scale and groundwater protection of sandy aquifers. Second world water congress: environmental monitoring, contaminants and pathogens. Water Science and Technology, 46(3), 123–129.
Sen, T. K., Das, D., Khilar, K. C., & Suraishkumar, G. K. (2005). Bacterial transport in porous media: new aspects of the mathematical model. Colloids Surf A, 260, 53–62.
Sen, T. K., & Khilar, K. C. (2006). Review on subsurface colloids and colloid-associated contaminant transport in saturated porous media. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 119, 71–96.
Sen, T. K., & Khilar, K. C. (2009). Mobile subsurface colloids and colloid-mediated transport of contaminants in subsurface soil. In K. S. Birdi (Ed.), Handbook of surface and colloid chemistry (3rd ed., pp. 107–130). CRC Press: London.pp.
Sen, T. K., Mahajan, S. P., & Khilar, K. C. (2002). Colloid-associated contaminant transport in porous media: Experimental study. AIChE Journal, 48(10), 2366–2375.
Sen, T. K., Shanbag, S., & Khilar, K. C. (2004). Subsurface colloids in groundwater contamination: a mathematical model. Colloid Surf A, 232, 29–38.
Shang, J., Flury, M., Chin, G., & Zhuang, J. (2008). Impact of flow rate, water content and capillary forces on insitu colloid mobilization during infiltration in unsaturated sediments. Water Resources Research, 44(W06411), 137–148. doi:10.1029/2007WR006516.
Shang, J., Flury, M., & Deng, Y. (2009). Force measurements between particles and the air-water interface: implications for particle mobilization in unsaturated porous media. Water Resources Research, 45(W06420), 1–14. doi:10.1029/2008WR007384.
Sharma, M. M., Chamoun, H., Sita Rama Sarma, D. S. H., & Schechter, R. S. (1992). Factors controlling the hydrodynamic detachment of particles from surfaces. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 149, 121–134.
Sharma, P., Flury, M., & Zhou, J. (2008). Detachment of colloid from a solid surface by a moving air-water interface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 326, 143–150.
Sharma, P. K., & McInerney, M. J. (1994). Effect of grain size on bacterial penetration and reproduction and metabolic activity in porous glass bead chambers. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60, 1481–1486.
Shaw, D. J. (1998). Colloid and Surface Chemistry (4th ed.). Oxford: Butterworth Heinemann.
Sing, R., & Olson, M. S. (2008). Application of bacterial swimming and chemotaxis for enhanced bioremediation. Emerging Environmental Technologies (pp. 149–172). Netherlands: Springer.
Sirivithayapakorn, S., & Keller, A. (2003). Transport of colloids in unsaturated porous media: a pore-scale observation of processes during the dissolution of air-water interface. Water Resources Research, 39, 1346. doi:10.1029/2003WR002487.
Smith, M. S., Thomas, G. W., White, R. E., & Ritonga, D. (1985). Transport of E. coli through intact and disturbed columns. Journal of Environmental Quality, 14, 87–91.
Stenstrom, T. A. (1989). Bacterial hydrophobicity, overall parameters for the measurement of adhesion potential to soil particles. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 55, 142–147.
Stevik, T. K., Aa, K., Ausland, G., & Hanssen, J. F. (2004). Retention and removal of pathogenic bacteria in wastewater percolating through porous media: a review. Water Research, 38, 1355–1367.
Surampalli, R. Y., Lin, K. L., Banerji, S. K., & Sievers, D. M. (1997). Impact of long term land application of biosolids on groundwater quality and surface soils. Journal of Environmental Systems, 26(3), 305–324.
Tate, R. L. (1978). Cultural and environmental factors affecting the longevity of Escherichia coli in histosols. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 35, 925–929.
Taylor, R., Cronin, A., Pedley, S., Barker, J., & Atkinson, T. (2004). The implications of groundwater velocity variations on microbial transport and wellhead protection-review of field evidence. FEMS Microbialogy Ecology, 49(1), 17–26.
Taylor, S. W., Milly, P. C., & Jaffe, P. R. (1990). Biofilm growth and related changes in the physical properties of a porous medium. Water Resources Research, 26, 2161–2170.
Thompson, S. S., Flury, M., Yates, M. V., & Jury, W. A. (1998). Role of the air-water-solid interface in bacteriophage sorption experiments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64, 304–309.
Tindall, M., Maini, P., Porter, J., & Armitage, J. P. (2008). Overview of mathematical approaches used to model bacterial chemotaxis II: bacterial populations. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 70, 1570–1607.
Torkzaban, S., Bradford, S. A., van Genuchten, M. T., & Walker, S. L. (2008). Colloid transport in unsaturated porous media: The role of water content and ionic strength on particle straining. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 96, 113–127.
Torkzaban, S., Hassanizadeh, S. M., Schijven, J. F., & de Roda Husman, A. M. (2006). Virus transport in saturated and unsaturated sand columns. Vadose Zone Journal, 5, 877–885.
Truesdail, S. E., Lukasik, J., Farrah, S. R., Shah, D. O., & Dickinson, R. B. (1998). Analyses of bacterial deposition on metal oxide-coated sand filter media. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 203, 369–378.
Tutenkji, N. (2007). Modeling microbial transport in porous media: Traditional approaches and recent developments. Advances in Water Resources, 30, 1455–1469.
Van Loosdrecht, M. C. M., Lyklema, J., Norde, W., & Zehnder, A. J. B. (1989). Bacterial adhesion: a physicochemical approach. Microbial Ecology, 17, 1–15.
van Oss, C. J. (1994). Interfacial forces in aqueous media. New York: Marcel Dekker.
van Oss, C. J. (2006). Interfacial forces in aqueous media (2nd ed.). Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis.
Vigeant, M. A. S., Ford, R. M., Wagner, M., & Tamm, L. K. (2002). Reversible and irreversible adhesion of motile Escherich coli cells analysed by total internal reflection aqueous fluorescence microscopy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 2794–2801.
Wan, J., & Tokunaga, T. K. (1997). Film straining of colloids in unsaturated porous media: conceptual model and experimental testing. Environmental Science & Technology, 31, 2413–2420.
Wan, J. M., & Tokunaga, T. K. (2002). Partitioning of clay colloids at air-water interfaces. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 247, 54–61.
Wan, J., & Wilson, J. L. (1994). Colloid transport in unsaturated porous media. Water Resources Research, 30, 857–864.
Wang, M., & Ford, R. (2009). Transverse Bacterial migration induced by chemotaxis in a packed column with structured physical heterogeneity. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 5921–5927.
Williams, D. F., & Berg, J. C. (1992). The aggregation of colloidal particles at the air-water interface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 152, 218–229.
Yao, K. M., Habibian, M. T., & O’Melea, C. R. (1971). Water and waste water filtration. Concepts and applications Environ Sci Technol, 5, 1105–1112.
Yates, M. V., & Gerba, C. P. (1985). Factors controlling the survival of viruses in groundwater. Water Science and Technology, 17, 681–687.
Yates, M. V., Stetzenbach, L. D., Gerba, C. P., & Sinclair, N. A. (1990). The effect of indigenous bacteria on virus survival in groundwater. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A: Environmental Science, 25, 81–100.
Yates, M. V., & Yates, S. R. (1988). Modelling microbial fate in the subsurface environment. Critical Reviews in Environmental Control, 17, 307–344.
Yoon, R. H., & Mao, L. (1996). Application of extended DLVO theory. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 181, 613–626.
Zevi, Y., Dathe, A., McCarthy, J. F., Richards, B. K., & Steenhuis, T. S. (2005). Distribution of colloidal particles onto interface in partially saturated sand. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 7055–7064.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, T.K. Processes in Pathogenic Biocolloidal Contaminants Transport in Saturated and Unsaturated Porous Media: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut 216, 239–256 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0531-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0531-9