Abstract
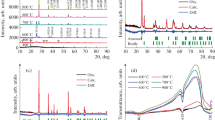
The partial phase transformation of nanometer TiO2 powder from anatase phase to rutile phase was realized by heat-treatment and a new TiO2 photocatalyst which could be excited by visible light was obtained. The heat-treated TiO2 powder at different stage of transition crystal was characterized and monitored by XRD, TEM, FT-IR and UV–vis DRS methods. The test of photocatalytic activity of the heat-treated TiO2 powder was carried out by the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B and acid orange II dyes, respectively, in aqueous solution under visible light irradiation. The results indicate that the nanometer TiO2 photocatalyst heat-treated at 500°C for 60 min shows the highest photocatalytic activity, that is, it can effectively degrade the rhodamine B and acid orange II under visible light irradiation. The remarkable improvement of photocatalytic activity of heat-treated TiO2 powder at 500°C for 60 min was mainly illustrated by the formation of special interphase between rutile and anatase phases, which not only restrains the recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes, but also reduces the adsorbability of nanometer anatase TiO2 powder properly for various dyes. Additionally, the effects of dye-assisting chemicals such as Na2CO3 and NaCl on the photocatalytic degradation were also studied.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, M., Low, G. K. C., & Matthews, R. W. (1990). Effects of common inorganic anions on rates of photocatalytic oxidation of organic carbon over illuminated titanium dioxide. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 94, 6820–6825.
Ahn, Y. U., Kim, E. J., Kim, H. T., & Hahn, S. H. (2003). Variation of structural and optical properties of sol–gel TiO2 thin films with catalyst concentration and calcinations temperature. Materials Letters, 57, 4660–4666.
Al-Assaf, S., Navaratnam, S., Parsons, B. J., & Phillips, G. O. (2006). Chain scission of hyaluronan by carbonate and dichloride radical anions: Potential reactive oxidative species in inflammation. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 40, 2018–2027.
Asahi, R., Morikawa, T., Ohwaki, T., Aoki, K., & Taga, Y. (2001). Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium dioxides. Science, 293, 269–271.
Bezrodnaa, T., Puchkovskaa, G., Shymanovskaa, V., Baranb, J., & Ratajczakb, H. J. (2004). IR-analysis of H-bonded H2O on the pure TiO2 surface. Journal of Molecular Structure, 700, 175–181.
Chen, Y. F., Lee, C. Y., Yang, M. Y., & Chiu, H. T. (2003). The effect of calcination temperature on the crystallinity of TiO2 nanopowders. Journal of Crystal Growth, 247, 363–370.
Diebold, U. (2003). The surface science of titanium dioxide. Surface Science Reports, 48, 53–229.
Epling, G. A., & Lin, C. (2002). Investigation of retardation effects on the titanium dioxide photodegradation system. Chemosphere, 46, 937–944.
Hinda, L., Eric, P., Ammar, H., Mohamed, K., Elimama, E., Chantal, G., et al. (2002). Photocatalytic degradation of various types dyes (Alizarin S, Crocein Orange G, Methyl Red, Congo Red, Methylene Blue) in water by UV-irradiated titania. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 39, 75–90.
Hu, Y., Tsai, H. L., & Huang, C. L. (2003). Phase transformation of precipitated TiO2 nanoparticles. Materials Science and Engineering A, 344, 209–214.
Invanda, M., Musić, S., Popović, S., & Gotić, M. (1999). XRD, Raman and FT-IR spectroscopic observations of nanosized TiO2 synthesized by the sol–gel method based on an esterification reaction. Journal of Molecular Structure, 480–481, 645–649.
Kamat, P. V. (1993). Photochemistry on nonreactive and reactive (semiconductor) surfaces. Chemical Reviews, 93, 267–300.
Kim, E. J., & Hahn, S. H. (2001). Microstructural changes of microemulsion-mediated TiO2 particles during calcination. Materials Letters, 49, 244–249.
Kobayakawa, K., Murakami, Y., & Sato, Y. (2005). Visible-light active N-doped TiO2 prepared by heating of titanium hydroxide and urea. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 170, 177–179.
Kormann, C., Bahnemann, D. W., & Hoffmann, M. R. (1991). Photolysis of chloroform and other organic molecules in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. Environmental Science & Technology, 25, 494–500.
Lei, M., Sakae, T., Shoichi, T., Kenji, K., & Masaki, T. (2004). Heating-sol–gel template process for the growth of TiO2 nanorods with rutile and anatase structure. Applied Surface Science, 238, 175–179.
Li, G. T., Qua, J. H., Zhang, X. W., Liu, H. J., & Liu, H. N. (2006). Electrochemically assisted photocatalytic degradation of Orange II: Influence of initial pH values. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 259, 238–244.
Liu, Y., Chen, X., Li, J., & Burda, C. (2005). Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes by nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanocatalysts. Chemosphere, 61, 11–18.
Madhu, K. P., Badrinarayanan, S., & Sastry, M. (2000). Nanocrystalline TiO2 studied by optical, FTIR and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: Correlation to presence of surface states. Thin Solid Films, 358, 122–130.
Nagaoka, K., Takanabe, K., & Aika, K. (2002). Influence of the phase composition of titania on catalytic behavior of Co/TiO2 for the dry reforming of methane. Chemical Communications, 9, 1006–1007.
Nakaoka, Y., & Nosaka, Y. (1997). ESR investigation into the effects of heat treatment and crystal structure on radicals produced over irradiated TiO2 powder. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 110, 299–305.
Pore, V., Heikkila, M., Ritala, M., Leskela, M., & Areva, S. (2006). Atomic layer deposition of TiO2−xNx thin films for photocatalytic applications. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 177, 68–75.
Shchukin, D. G., & Caruso, R. A. (2003). Inorganic macroporous films from preformed nanoparticles and membrane templates: Synthesis and investigation of photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical properties. Advanced Functional Materials, 13, 789–794.
Tayade, R. J., Kulkarni, R. G., & Jasra, R. V. (2006). Photocatalytic degradation of aqueous nitrobenzene by nanocrystalline TiO2. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 45, 922–927.
Tryba, B., Toyoda, M., Morawski, A. W., & Inagake, M. (2005). Modification of carbon-coated TiO2 by iron to increase adsorptivity and photoactivity for phenol. Chemosphere, 60, 477–484.
Yu, J. C., Wu, L., Lin, J., Li, P., & Li, Q. (2003). Microemulsion-mediated solvothermal synthesis of nanosized CdS-sensitized TiO2 crystalline photocatalyst. Chemical Communications, 13, 1552–1553.
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly acknowledge The National Natural Science Foundation of China for financial support. The authors also thank our colleagues and other students participating in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Li, R., Zhang, Z. et al. Degradation of Hazardous Dyes in Wastewater using Nanometer Mixed Crystal TiO2 Powders under Visible Light Irradiation. Water Air Soil Pollut 189, 225–237 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9570-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9570-2