Abstract
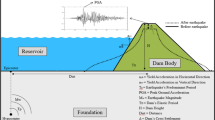
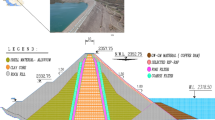
With systems engineering and artificial intelligent methods, an early-warning system of dam health (EWSDH) is developed. This system consists of integration control module, intelligent inference engine (IIE), support base cluster, information management and input/output modules. As a central processing unit of EWSDH, IIE is a decision support system for monitoring the operation characteristics and diagnosing unexpected behaviour of dam health. With the time-frequency domain localization properties and self-learning ability of wavelet networks based on wavelet frames, IIE builds some new monitoring models of dam health. The models are used to approximate and forecast the operation characteristics of dam. The methods of attributions reduction in rough sets theory are presented to diagnose adaptively the unexpected behaviour. The proposed system has been used to monitor dam health successfully.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aussen A, Murtagh F (1997) Combining neural network forecast on wavelet-transformed time series. Connection Science 9:113–121
Barbagallo S, Consoli S, Pappalardo N, Greco S, Zimbone SM (2006) Discovering reservoir operating rules by a rough set approach. Water Resour Manag 20(1):19–36
Benedetto J, Heinig H (2003) Weighted Fourier inequalities: new proof and generalization. J Fourier Anal Appl 9:1–37
Crepon O (1999) An analytical approach to monitoring. Int Water Power Dam Constr 6:52–54
Enns R, Si J (2002) Apache helicopter stabilization using neural dynamic programming. J Guid Control Dyn 25(1):19–25
Fournier A (2003) Atmospheric energetics in the wavelet domain II: time-averaged observed atmospheric blocking. J Atmos Sci 60(15):319–338
Gaziev EG (2000) Safety provision and an expert system for diagnosing and predicting dam behavior. Hydrotech Constr 34(4):285–289
Lei P, Gu CS (2005) Prediction model for dam safety monitoring based on rough set reasoning. J Hohai Univ (Nat Sci) 33(4):391–394
Lian CJ (2000) An overview of rough set semantics for modal and quantifier logics. Int J Uncertainty Fuzziness Knowledge Based Syst 8(1):93–118
Liu ZG, Wang XR, Qian QQ (2003) A review of wavelet networks and their applications. Autom Electr Power Syst 27(4):73–79
Luo JX, Shao HH (2003) A neurofuzzy system based on rough set theory. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ 37(5):1702–1705
Marengo H (2000) Considerations on dam safety and the history of overtopping events. Dam Eng XI(1):29–59
Peyras L, Royet P, Boissier D (2006) Dam ageing diagnosis and risk analysis: development of methods to support expert judgment. Can Geotech J 43(1):169–186
Razavi S, Araghinejad S (2009) Reservoir inflow modeling using temporal neural networks with forgetting factor approach. Water Resour Manag 23(1):39–55
Su HZ, Wen ZP, Dai HC (2003) A method of mining adaptively the pattern between disease and pathogeny of dam. In: 2003 international conference on machine learning and cybernetics, China, pp 3050–3055
Swiniarski RW, Hargis L (2001) Rough sets as a front end of neural-networks texture classifiers. Eurocomputing 36:85–102
Wu ZR, Su HZ (2005) Dam health diagnosis and evaluation. Smart Mater Struct 14(2):S130–S136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Wen, Z. & Wu, Z. Study on an Intelligent Inference Engine in Early-Warning System of Dam Health. Water Resour Manage 25, 1545–1563 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9760-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9760-3