Abstract
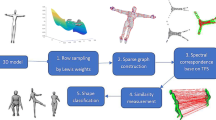
This paper presents a matching method for 3D shapes, which comprises a new technique for surface sampling and two algorithms for matching 3D shapes based on point-based statistical shape descriptors. Our sampling technique is based on critical points of the eigenfunctions related to the smaller eigenvalues of the Laplace-Beltrami operator. These critical points are invariant to isometries and are used as anchor points of a sampling technique, which extends the farthest point sampling by using statistical criteria for controlling the density and number of reference points. Once a set of reference points has been computed, for each of them we construct a point-based statistical descriptor (PSSD, for short) of the input surface. This descriptor incorporates an approximation of the geodesic shape distribution and other geometric information describing the surface at that point. Then, the dissimilarity between two surfaces is computed by comparing the corresponding sets of PSSDs with bipartite graph matching or measuring the L 1-distance between the reordered feature vectors of a proximity graph. Here, the reordering is given by the Fiedler vector of a Laplacian matrix associated to the proximity graph. Our tests have shown that both approaches are suitable for online retrieval of deformed objects and our sampling strategy improves the retrieval performances of isometry-invariant matching methods. Finally, the approach based on the Fiedler vector is faster than using the bipartite graph matching and it has a similar retrieval effectiveness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baloch, S., Krim, H., Kogan, I., & Zenkov, D. (2005). Rotation invariant topology coding of 2D and 3D objects using Morse theory. In Proc. of the IEEE international conference on image processing 2005 (pp. 796–799).
Banchoff, T. (1967). Critical points and curvature for embedded polyhedra. Journal of Differential Geometry, 1, 245–256.
Biasotti, S., Marini, S., Spagnuolo, M., & Falcidieno, B. (2006). Sub-part correspondence by structural descriptors of 3D shapes. Computer-Aided Design, 38(9), 1002–1019.
Biasotti, S., Giorgi, D., Patané, G., Reuter, M., & Spagnuolo, M. (2008). Discrete Laplace-Beltrami operators for shape analysis (IMATI-CNR Technical Report N. 8/2008).
Bremer, P.-T., Edelsbrunner, H., Hamann, B., & Pascucci, V. (2004). A topological hierarchy for functions on triangulated surfaces. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 10(4), 385–396.
Bronstein, A. M., Bronstein, M. M., & Kimmel, R. (2006). Efficient computation of isometry-invariant distances between surfaces. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 28(5), 1812–1836.
Bronstein, A. M., Bronstein, M. M., Carmon, Y., & Kimmel, R. (2009). Partial similarity of shapes using a statistical significance measure. Computer Vision and Application, 1, 105–114.
Brunelli, R., & Mich, O. (2001). Histograms analysis for image retrieval. Pattern Recognition, 34(8), 1625–1637.
Brusco, M. J., & Stahl, S. (Eds.) (2005). Branch-and-bound applications in combinatorial data analysis. Berlin: Springer.
Bustos, B., Keim, D. A., Saupe, D., Schreck, T., & Vranić, D. V. (2005). Feature-based similarity search in 3D object databases. ACM Computing Surveys, 37(4), 345–387.
Castellani, U., Cristani, M., Fantoni, S., & Murino, V. (2008). Sparse points matching by combining 3D mesh saliency with statistical descriptors. Computer Graphics Forum, 27(2), 643–652.
Chung, F. R. K. (1997). Spectral graph theory. Providence: American Mathematical Society.
Cook, W., & Rohe, A. (1999). Computing minimum-weight perfect matchings. Journal on Computing, 11(2), 138–148.
Darom, T., Ruggeri, M., Saupe, D., & Kiryati, N. (2006). Compression of textured surfaces represented as surfel sets. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 21(9), 770–786.
Elad, A., & Kimmel, R. (2003). On bending invariant signatures for surfaces. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 25(10), 1285–1295.
Elad, M., Tal, A., & Ar, S. (2002). Content based retrieval of vrml objects: an iterative and interactive approach. In Proc. of the Eurographics workshop on multimedia (pp. 107–118).
Eldar, I., Lindenbaum, M., Porat, M., & Zeevi, I. I. (1997). The farthest point strategy for progressive image sampling. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 6(9), 1305–1315.
Fiedler, M. (1975). A property of eigenvectors of nonnegative symmetric matrices and its application to graph theory. Czechoslovak Mathematical Journal, 25, 619–633.
Fomenko, A., & Kunii, T. L. (1997). Topological modelling for visualization. Berlin: Springer.
Funkhouser, T., & Shilane, P. (2006). Partial matching of 3D shapes with priority-driven search. In Proc. of the symposium on geometry processing (pp. 131–142).
Gal, R., & Cohen-Or, D. (2006). Salient geometric features for partial shape matching and similarity. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 25(1), 130–150.
Gal, R., Shamir, A., & Cohen-Or, D. (2007). Pose-oblivious shape signature. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 13(2), 261–271.
Gelfand, N., Mitra, N. J., Guibas, L. J., & Pottmann, H. (2005). Robust global registration. In Proc. of symposium on geometry processing (p. 197).
Hamza, A. B., & Krim, H. (2003). Geodesic object representation and recognition. In International conference on discrete geometry for computer imagery (pp. 378–387).
Hilaga, M., Shinagawa, Y., Kohmura, T., & Kunii, T. L. (2001). Topology matching for fully automatic similarity estimation of 3D shapes. In ACM siggraph (pp. 203–212).
Isenburg, M., & Lindstrom, P. (2005) Streaming meshes. In Proc. of visualization (pp. 231–238).
Itti, L., Koch, C., & Niebur, E. (1998). A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 20(11), 1254–1259.
Jain, V., & Zhang, H. (2007). A spectral approach to shape-based retrieval of articulated 3D models. Computer Aided Design, 39, 398–407.
Katz, S., & Tal, A. (2003). Hierarchical mesh decomposition using fuzzy clustering and cuts. In ACM siggraph (pp. 954–961).
Kimmel, R., & Sethian, J. A. (1998). Computing geodesics on manifolds. In Proc. of national academy of sciences (Vol. 95, pp. 8431–8435).
Koren, Y., Carmel, L., & Harel, D. (2002). Ace: a fast multiscale eigenvectors computation for drawing huge graphs. In Proc. of the IEEE symposium on information visualization (p. 137).
Korte, B., & Vygen, J. (Eds.) (2000). Combinatorial optimization, theory and algorithms. Berlin: Springer.
Lee, C. H., Varshney, A., & Jacobs, D. W. (2005). Mesh saliency. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 24(3), 659–666.
Li, X., & Guskov, I. (2005). Multi-scale features for approximate alignment of point-based surfaces. In Proc. of the symposium on geometry processing (pp. 217–226).
Ling, H., & Okada, K. (2006). Diffusion distance for histogram comparison. In IEEE conference on computer visualization and pattern recognition (pp. 246–253).
Liu, Y.-S., Liu, M., Kihara, D., & Ramani, K. (2007). Salient critical points for meshes. In Proc. of symposium on solid and physical modeling (pp. 277–282).
Mateus, D., Cuzzolin, F., Horaud, R., & Boyer, E. (2007). Articulated shape matching using locally linear embedding and orthogonal alignment. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 1–8).
Mémoli, F. (2007). On the use of Gromov-Hausdorff distances for shape comparison. In Proc. of the symposium on point-based graphics (pp. 81–90).
Mémoli, F., & Sapiro, G. (2005). Distance functions and geodesics on submanifolds of R d and point clouds. SIAM Journal of Applied Mathematics, 65(4), 1227–1260.
Mémoli, F., & Sapiro, G. (2005). A theoretical and computational framework for isometry invariant recognition of point cloud data. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 5(3), 313–347.
Milnor, J. (1963). Annals of mathematics studies: Vol. 51. Morse theory. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Moenning, C., & Dodgson, N. A. (2003). Fast marching farthest point sampling. In Computer graphics forum.
Mortara, M., & Patanè, G. (2002). Shape-covering for skeleton extraction. International Journal of Shape Modelling, 8(2), 245–252.
Mortara, M., Patanè, G., Spagnuolo, M., Falcidieno, B., & Rossignac, J. (2004). Blowing bubbles for multi-scale analysis and decomposition of triangle meshes. Algorithmica, 38(1), 227–248.
Nehab, D., & Shilane, P. (2004). Stratified point sampling of 3D models. In Proc. of the symposium on point-based graphics (pp. 49–56).
Ni, X., Garland, M., & Hart, J. C. (2004). Fair Morse functions for extracting the topological structure of a surface mesh. In ACM siggraph (pp. 613–622).
Ohbuchi, R., Osada, K., Furuya, T., & Banno, T. (2008). Salient local visual features for shape-based 3D model retrieval. In Proc. of shape modeling international 2004 (pp. 93–102).
Osada, R., Funkhouser, T., Chazelle, B., & Dobkin, D. (2002). Shape distributions. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 21(4), 807–832.
Ovsjanikov, M., Sun, J., & Guibas, J. (2008). Global intrinsic symmetries of shapes. In Eurographics symposium on geometry processing (SGP).
Patanè, G., Spagnuolo, M., & Falcidieno, B. (2009, to appear). A minimal contouring approach to the computation of the Reeb graph. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics.
Pauly, M., Gross, M., & Kobbelt, L. P. (2002). Efficient simplification of point-sampled surfaces. In Proc. of visualization (pp. 163–170).
Pauly, M., Keiser, R., Kobbelt, L. P., & Gross, M. (2003). Shape modeling with point-sampled geometry. In ACM siggraph (pp. 641–650).
Press, W. H., Vetterling, W. T., Teukolsky, S. A., & Flannery, B. P. (2007). Numerical recipes in C++: the art of scientific computing (3rd edn.) Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Qiu, H., & Hancock, E. R. (2003). Graph partition for matching. In Graph based representations in pattern recognition (Vol. 2726, pp. 178–189).
Raviv, D., Bronstein, A. M., Bronstein, M. M., & Kimmel, R. (2007). Symmetries of non-rigid shapes. In IEEE workshop on non-rigid registration and tracking through learning.
Reuter, M., Wolter, F.-E., & Peinecke, N. (2006). Laplace-Beltrami spectra as Shape-DNA of surfaces and solids. Computer-Aided Design, 38(4), 342–366.
Reuter, M., Biasotti, S., Giorgi, D., Patanè, G., & Spagnuolo, M. (2009, to appear). Discrete Laplace-Beltrami operators for shape analysis and segmentation. Computer & Graphics.
Rubner, Y., Tomasi, C., & Guibas, L. J. (2000). The earth mover’s distance as a metric for image retrieval. International Journal of Computer Vision, 40(2), 99–121.
Ruggeri, M. R., & Saupe, D. (2008). Isometry-invariant matching of point set surfaces. In Proc. of the Eurographics workshop on 3D object retrieval.
Ruggeri, M. R., Darom, T., Saupe, D., & Kiryati, N. (2006). Approximating geodesics on point set surfaces. In Proc. of the symposium on point-based graphics (pp. 85–93).
Rustamov, R. M. (2007). Laplace-Beltrami eigenfunctions for deformation invariant shape representation. In Proc. of the symposium on geometry processing (pp. 225–233).
Schwartz, J., Steger, A., & Weißl, A. (2005). Fast algorithms for weighted bipartite matching. In Experimental and efficient algorithms (Vol. 3503, pp. 476–487).
Sumner, R. W., & Popović, J. (2004). Deformation transfer for triangle meshes. In ACM siggraph (pp. 399–405).
Surazhsky, V., Surazhsky, T., Kirsanov, D., Gortler, S. J., & Hoppe, H. (2005). Fast exact and approximate geodesics on meshes. ACM siggraph, 24(3), 553–560.
Tangelder, J. W. H., & Veltkamp, R. C. (2004). A survey of content based 3D shape retrieval methods. In Proc. of shape modeling international 2004 (pp. 145–156).
Turk, M., & Pentland, A. (1991). Face recognition using eigenfaces. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 586–591).
Vallet, B., & Levy, B. (2008). Spectral geometry processing with manifold harmonics. Computer Graphics Forum, 27(2), 251–260.
Zhang, Z. (1994). Iterative point matching for registration of free-form curves and surfaces. International Journal of Computer Vision, 13(2), 119–152.
Zhang, H., & Liu, R. (2005). Mesh segmentation via recursive and visually salient spectral cuts. In Proc. of vision, modeling, and visualization (pp. 429–436).
Zhang, H., van Kaick, O., & Dyer, R. (2007). Spectral methods for mesh processing and analysis. In Proc. of Eurographics state-of-the-art report (pp. 1–22).
Zhang, H., Sheffer, A., Cohen-Or, D., Zhou, Q., van Kaick, O., & Tagliasacchi, A. (2008). Deformation-drive shape correspondence. Symposium on Geometry Processing, 27(5), 431–1439.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruggeri, M.R., Patanè, G., Spagnuolo, M. et al. Spectral-Driven Isometry-Invariant Matching of 3D Shapes. Int J Comput Vis 89, 248–265 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-009-0250-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-009-0250-0