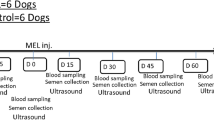
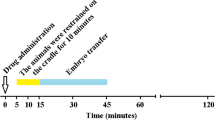
Abstract
Under field conditions, sedation may be required for a full assessment of the reproductive potential of farm animals. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of xylazine sedation on testicular hemodynamics (TBF), echotexture, testicular volume (TV), and circulating hormones in goats. Sixteen male Shiba goats were sedated using the recommended dose of xylazine (0.05 mg/Kg BW). Testicular hemodynamics were evaluated using color-pulsed Doppler ultrasonography before and after sedation. Echotexture of the testicular parenchyma and TV were assessed using computerized image analysis. Concentrations of testosterone, estradiol (E2), inhibin, cortisol, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH) were measured using radioimmunoassay. There were no effects of xylazine sedation in TBF, TV, testicular parenchyma parameters, and concentrations of testosterone, inhibin, FSH, and LH (P ˃ 0.05). However, after sedation, there was significantly (P ˂ 0.05) lower cortisol and E2 concentration (42.88 ± 6.79 ng/ml and 2.47 ± 0.58 pg/ml, respectively) than before sedation (94.89 ± 13.74 ng/ml and 8.65 ± 1.79 pg/ml, respectively). The required time to perform the full scanning of the testis was significantly lower (8.50 ± 0.38 min) after xylazine sedation compared to the non-sedated goats (25.75 ± 1.14 min). In conclusion, xylazine sedation may be practically recommended for the evaluation of TBF in goats because it did not significantly alter velocities parameters and Doppler indices of blood flow within the testicular arteries. Most plasma hormones did not significantly change; however, E2 and cortisol were significantly reduced after xylazine administration.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available by the corresponding author upon a reasonable query.
References
Abril-Sánchez S, Crosignani N, Freitas-de-Melo A, Terrazas A, Damián JP, Beracochea F, Silveira P, Ungerfeld R (2018) Sedation or anaesthesia decrease the stress response to electroejaculation and improve the quality of the collected semen in goat bucks. Animal 12(12):2598–2608. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731118000320
Aghamiri SM, Samimi AS, Hajian M, Samimi AM, Oroumieh A (2022) Effect of xylazine, detomidine, medetomidine and dexmedetomidine during laparoscopic SCNT embryo transfer on pregnancy rate and some physiological variables in goats. BMC Vet Res 18(1):98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-022-03194-8
Ahmadi B, Lau CP, Giffin J, Santos N, Hahnel A, Raeside J, Christie H, Bartlewski P (2012) Suitability of epididymal and testicular ultrasonography and computerized image analysis for assessment of current and future semen quality in the ram. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 237(2):186–193. https://doi.org/10.1258/ebm.2011.011050
Almeida MM, Assis Neto AC, Penno AK, Conde Júnior AM, Menezes DJA, Pereira GR, Azevêdo LM, Carvalho MAM (2008) Testicular arteries systematization based on different levels of scrotal configuration in caprines. Ciência Rural 38:1308–1312
Arai K, Watanabe G, Fujimoto M, Nagata S, Takemura Y, Taya K, Sasamoto S (1995) A sensitive radioimmunoassay for cortisol using 125I-labeled radioligand. J Reprod Dev 41:j15-20
Araki K, Arai KY, Watanabe G, Taya K (2000) Involvement of inhibin in the regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion in the young adult male Shiba goat. J Androl 21(4):558–565
Araujo RR, Ginther OJ (2009) Vascular perfusion of reproductive organs in pony mares and heifers during sedation with detomidine or xylazine. Am J Vet Res 70(1):141–148. https://doi.org/10.2460/ajvr.70.1.141
Barros Adwell CMQ, Brito LFC, Oba E, Wilde RE, Rizzoto G, Thundathil JC, Kastelic JP (2018) Arterial blood flow is the main source of testicular heat in bulls and higher ambient temperatures significantly increase testicular blood flow. Theriogenology 116:12–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.04.022
Baumgartner C, Bollerhey M, Ebner J, Laacke-Singer L, Schuster T, Erhardt W (2010) Effects of ketamine-xylazine intravenous bolus injection on cardiovascular function in rabbits. Can J Vet Res 74(3):200–208
Bergh A, Collin O, Lissbrant E (2001) Effects of acute graded reductions in testicular blood flow on testicular morphology in the adult rat. Biol Reprod 64(1):13–20. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod64.1.13
Bollwein H, Schulze JJ, Miyamoto A, Sieme H (2008) Testicular blood flow and plasma concentrations of testosterone and total estrogen in the stallion after the administration of human chorionic gonadotropin. J Reprod Dev 54(5):335–339. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.20014
Brito LF, Barth AD, Wilde RE, Kastelic JP (2012) Testicular ultrasonogram pixel intensity during sexual development and its relationship with semen quality, sperm production, and quantitative testicular histology in beef bulls. Theriogenology 78(1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2012.01.022
Camela ESC, Nociti RP, Santos VJC, Macente BI, Murawski M, Vicente WRR, Bartlewski PM, Oliveira MEF (2019) Changes in testicular size, echotexture, and arterial blood flow associated with the attainment of puberty in Dorper rams raised in a subtropical climate. Reprod Domest Anim 54(2):131–137. https://doi.org/10.1111/rda.13213
Celestine Okwudili U, Athanasius Chinedu E, Jonas Anayo O (2014) Biochemical Effects of Xylazine, Propofol, and ketamine in west african dwarf goats. J Vet Med 2014:758581. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/758581
Chiba S, Tsukada M (1990) Pharmacological analysis of vasodilator responses to alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists in isolated rat common carotid arteries. Jpn J Pharmacol 53(2):135–143. https://doi.org/10.1254/jjp.53.135
El-Sherbiny HR, El-Shalofy AS, Samir H (2022a) Exogenous L-carnitine administration ameliorates the adverse Effects of Heat stress on testicular hemodynamics, echotexture, and total antioxidant capacity in Rams. Front Vet Sci 9:860771. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2022.860771
El-Sherbiny HR, Fathi M, Samir H, Abdelnaby EA (2022b) Supplemental dietary curcumin improves testicular hemodynamics, testosterone levels, and semen quality in Baladi bucks in the non-breeding season. Theriogenology 188:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.05.020
El-Sherbiny HR, Samir H, El-Shalofy AS, Abdelnaby EA (2022) Exogenous L-arginine administration improves uterine vascular perfusion, uteroplacental thickness, steroid concentrations and nitric oxide levels in pregnant buffaloes under subtropical conditions. Reprod Domest Anim. https://doi.org/10.1111/rda.14225
Ghasemi A, Zahediasl S (2012) Normality tests for statistical analysis: a guide for non-statisticians. Int J Endocrinol Metab 10(2):486–489. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijem.3505
Hamada T, Watanabe G, Kokuho T, Taya K, Sasamoto S, Hasegawa Y, Miyamoto K, Igarashi M (1989) Radioimmunoassay of inhibin in various mammals. J Endocrinol 122(3):697–704. https://doi.org/10.1677/joe.0.1220697
Hsu HS, Chang LS, Chen MT, Wei YH (1994) Decreased blood flow and defective energy metabolism in the varicocele-bearing testicles of rats. Eur Urol 25(1):71–75. https://doi.org/10.1159/000475250
Junior FAB, Junior CK, Fávaro PDC, Pereira GR, Morotti F, Menegassi SRO, Barcellos JOJ, Seneda MM (2018) Effect of breed on testicular blood flow dynamics in bulls. Theriogenology 118:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.05.022
Kastelic JP, Cook RB, Coulter GH (1997) Contribution of the scrotum, testes, and testicular artery to scrotal/testicular thermoregulation in bulls at two ambient temperatures. Anim Reprod Sci 45(4):255–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4320(96)01587-4
Kelly JJ, Mangos G, Williamson PM, Whitworth JA (1998) Cortisol and hypertension. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl 25:S51–S56. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.1998.tb02301.x
Knowlton AA, Lee AR (2012) Estrogen and the cardiovascular system. Pharmacol Ther 135(1):54–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.03.007
Li S, Gupte AA (2017) The role of estrogen in cardiac metabolism and diastolic function. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J 13(1):4–8. https://doi.org/10.14797/mdcj-13-1-4
Machuki JO, Zhang HY, Geng J, Fu L, Adzika GK, Wu L, Shang W, Wu J, Kexue L, Zhao Z, Sun H (2019) Estrogen regulation of cardiac cAMP-L-type Ca2 + channel pathway modulates sex differences in basal contraction and responses to β2AR-mediated stress in left ventricular apical myocytes. Cell Commun Signal 17(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-019-0346-2
Mandour AS, Mahmoud AE, Ali AO, Matsuura K, Samir H, Abdelmageed HA, Ma D, Yoshida T, Hamabe L, Uemura A, Watanabe G, Tanaka R (2021) Expression of cardiac copper chaperone encoding genes and their correlation with cardiac function parameters in goats. Vet Res Commun 45(4):305–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-021-09811-5
Mandour AS, Samir H, Yoshida T, Matsuura K, Abdelmageed HA, Elbadawy M, Al-Rejaie S, El-Husseiny HM, Elfadadny A, Ma D, Takahashi K, Watanabe G, Tanaka R (2020a) Assessment of the cardiac functions using full conventional echocardiography with tissue Doppler imaging before and after xylazine sedation in male Shiba goats. Anim (Basel) 10(12):2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122320
Mandour AS, Samir H, El-Beltagy MA, Abdel-Daim MM, Izumi W, Ma D, Matsuura K, Tanaka R, Watanabe G (2020b) Effect of supra-nutritional selenium-enriched probiotics on hematobiochemical, hormonal, and Doppler hemodynamic changes in male goats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(16):19447–19460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08294-2
Mandour AS, Samir H, Yoshida T, Matsuura K, Hamabe L, Shimada K, Elbadawy M, Uemura A, Abdelmageed H, Takahashi K, Watanabe G, Tanaka R (2022) Novel color-M mode echocardiography for non-invasive assessment of the intraventricular pressure in goats: feasibility, repeatability, and the effect of sedation. Front Vet Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2022.935437
Mishra P, Pandey CM, Singh U, Gupta A, Sahu C, Keshri A (2019) Descriptive statistics and normality tests for statistical data. Ann Card Anaesth 22(1):67–72. https://doi.org/10.4103/aca.ACA_157_18
Mori Y, Kano Y (1984) Changes in plasma concentrations of LH, progesterone and oestradiol in relation to the occurrence of luteolysis, oestrus and time of ovulation in the Shiba goat (Capra hircus). J Reprod Fertil 72(1):223–230. https://doi.org/10.1530/jrf.0.0720223
Moolchand M, Kachiwal A, Soomro S, Bhutto Z (2014) Comparison of sedative and analgesic effects of xylazine, detomidine, and medetomidine in sheep. Egypt J Sheep Goats Sci 9(2):1–6. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejsgs.2014.26737
Morris MC, Hellman N, Abelson JL, Rao U (2016) Cortisol, heart rate, and blood pressure as early markers of PTSD risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev 49:79–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2016.09.001
Naddaf H, Varzi HN, Sabiza S, Falah H (2014) Effects of xylazine-ketamine anesthesia on plasma levels of cortisol and vital signs during laparotomy in dogs. Open Vet J 4(2):85–89
Nomura H, Terayama H, Kiyoshima D, Qu N, Shirose K, Tetsu S, Hayashi S, Sakabe K, Suzuki T (2022) Effects of dexmedetomidine on the localization of α2A-Adrenergic and imidazoline receptors in mouse testis. Appl Sci 12:10409. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010409
Oyama T (1973) Endocrine responses to anaesthetic agents. Br J Anaesth 45(3):276–281. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/45.3.276
Paltiel HJ, Diamond DA, Di Canzio J, Zurakowski D, Borer JG, Atala A (2002) Testicular volume: comparison of orchidometer and US measurements in dogs. Radiology 222(1):114–119. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2221001385
Pozor MA, McDonnell SM (2002) Doppler ultrasound measures of testicular blood flow in stallions. Theriogenology 58(2–4):437–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0093-691X(02)00741-0
Pozor MA (2007) Evaluation of testicular vasculature in stallions. Clin Tech Equine Pract 6:271–277. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ctep.2007.09.007
Pozor MA, McDonnell SM (2004) Color Doppler ultrasound evaluation of testicular blood flow in stallions. Theriogenology 61(5):799–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0093-691x(03)00227-9
Pozor M, Morrissey H, Albanese V, Khouzam N, Deriberprey A, Macpherson ML, Kelleman AA (2017) Relationship between echotextural and histomorphometric characteristics of stallion testes. Theriogenology 99:134–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2017.05.031
Remes J, van Brakel TJ, Bolotin G, Garber C, de Jong MM, van der Veen FH, Maessen JG (2008) Persistent atrial fibrillation in a goat model of chronic left atrial overload. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 136(4):1005–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2008.05.015
Rosenfeld CR, Roy T, Cox BE (2002) Mechanisms modulating estrogen-induced uterine vasodilation. Vascul Pharmacol 38(2):115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-3623(02)00135-0
Samir H, Nyametease P, Elbadawy M, Fathi M, Mandour AS, Radwan F, Nagaoka K, Sasaki K, Watanabe G (2020a) Assessment of correlations and concentrations of salivary and plasma steroids, testicular morphometry, and semen quality in different climatic conditions in goats. Theriogenology 157:238–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.08.002
Samir H, Nyametease P, Elbadawy M, Nagaoka K, Sasaki K, Watanabe G (2020b) Administration of melatonin improves testicular blood flow, circulating hormones, and semen quality in Shiba goats. Theriogenology 146:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.01.053
Samir H, El Sayed MAI, Nagaoka K, Sasaki K, Abo El-Maaty AM, Karen A, Abou-Ahmed MM, Watanabe G (2020c) Passive immunization against inhibin increases testicular blood flow in male goats. Theriogenology 147:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2019.12.022
Samir H, Nagaoka K, Watanabe G (2018a) The stimulatory effect of subluteal progesterone environment on the superovulatory response of passive immunization against inhibin in goats. Theriogenology 121:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.07.031
Samir H, Nyametease P, Nagaoka K, Watanabe G (2018b) Effect of seasonality on testicular blood flow as determined by color Doppler ultrasonography and hormonal profiles in Shiba goats. Anim Reprod Sci 197:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2018.08.027
Samir H, Radwan F, Watanabe G (2021) Advances in applications of color Doppler ultrasonography in the andrological assessment of domestic animals: a review. Theriogenology 161:252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.12.002
Samir H, Sasaki K, Ahmed E, Karen A, Nagaoka K, El Sayed M, Taya K, Watanabe G (2015) Effect of a single injection of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) on testicular blood flow measured by color Doppler ultrasonography in male Shiba goats. J Vet Med Sci 77(5):549–556. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.14-0633
Sanhouri AA, Jones RS, Dobson H (1992) Effects of xylazine on the stress response to transport in male goats. Br Vet J 148(2):119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/0007-1935(92)90103-8
Shahat AM, Rizzoto G, Kastelic JP (2020) Amelioration of heat stress-induced damage to testes and sperm quality. Theriogenology 158:84–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.08.034
Swindle M, Vogler G, Fulton L, Marini R, Popilskis S (2002) Preanesthesia, anesthesia, analgesia, and euthanasia (a book chapter). Elsevier, pp 955–1003
Taya K, Watanabe G, Sasamoto S (1985) Radioimmunoassay for progesterone, testosterone and estradiol 17 b using 125I- iodohistamine radioligands. Jpn J Anim Reprod 31:186–197
Tran QK (2020) Reciprocality between estrogen biology and calcium signaling in the cardiovascular system. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11:568203. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.568203
Tranquilli WJ, Thurmon JC, Grimm KA (2007) Lumb & Jones’ Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia. 4th ed. Blackwell, Oxford
Trautwein LGC, Souza AK, Martins MIM (2019) Can testicular artery Doppler velocimetry values change according to the measured region in dogs? Reprod Domest Anim 54(4):687–695. https://doi.org/10.1111/rda.13410
Väisänen M, Raekallio M, Kuusela E, Huttunen P, Leppäluoto J, Kirves P, Vainio O (2002) Evaluation of the perioperative stress response in dogs administered medetomidine or acepromazine as part of the preanesthetic medication. Am J Vet Res 63(7):969–975. https://doi.org/10.2460/ajvr.2002.63.969
Wagner AE, Muir WW 3rd, Hinchcliff KW (1991) Cardiovascular effects of xylazine and detomidine in horses. Am J Vet Res 52(5):651–657
Whitworth JA, Williamson PM, Mangos G, Kelly JJ (2005) Cardiovascular consequences of cortisol excess. Vasc Health Risk Manag 1(4):291–299. https://doi.org/10.2147/vhrm.2005.1.4.291
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. G.D. Niswender (Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology Laboratory, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO) for providing antisera to estradiol-17β (GDN 244) and testosterone (GDN 250). This study was partially supported by JSPS postdoctoral fellowship for research in Japan (FY19-ID No. P19101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Haney Samir: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Visualization, Curation of Data, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing. Ahmed S. Mandour: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, and Editing the manuscript. Faten Radwan: Methodology, Software, Writing - review & editing. Ayman A. Swelum: Writing - review & editing. Kentaro Nagaoka: Visualization, Validation, Writing - review & editing. Kazuaki Sasaki: Visualization, Validation, Resources. Gen Watanabe: Supervision, Visualization, Validation, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing - review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures in the current study including animal handling were carried out in accordance with the ethical guidelines of the local committee of the Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Japan, for the use of animals (Ethical approval # 30–78).
Consent for publication
All authors gave their consent and accredited this study for research publication.
Concent to participate
All authors approved this version of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 14.8 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Samir, H., Mandour, A.S., Radwan, F. et al. Effect of xylazine sedation on testicular blood flow, testicular echotexture, and circulating hormones in Shiba goats. Vet Res Commun 47, 849–859 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-022-10046-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-022-10046-1