Abstract
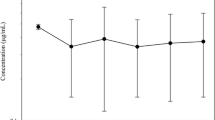
The pharmacokinetics of erythromycin was studied in five lactating dairy cows following single intramammary infusion of 300 mg erythromycin in each of two quarters per cow with specific mastitis. Levels of erythromycin in plasma and quarter milk samples were measured by agar plate diffusion assay using Micrococcus luteus (ATCC 9341) as the test organism. Erythromycin level in plasma reached a peak concentration value (C max) of 0.07 ± 0.01 μg/ml at 30 min; thereafter, levels declined gradually to reach 0.05 ± 0.00 μg/ml 12 h post drug administration. The pharmacokinetic profile of the drug revealed mean absorption half life (t 1/2ka) as 0.26 ± 0.05 h. The drug was eliminated slowly with elimination half-life (t 1/2β) of 13.75 ± 0.35 h and elimination rate constant (k el) of 0.04 ± 0.00 h−1. The volume of distribution based on the zero-time plasma concentration intercept of the least-squares regression line of the elimination phase (V d(B)) was 0.032 L/kg. The drug crossed to untreated quarters also; mean drug levels of 0.20 ± 0.07, 0.23 ± 0.07, 0.17 ± 0.04, and 0.17 ± 0.04 μg/ml were found at 3, 6, 8 and 12 h, respectively. The mean drug concentration for treated quarters was measured as 22.97 ± 2.31 μg/ml milk at first milking (12 h) following drug infusion. No apparent adverse reaction was seen in cows administered erythromycin. It is concluded that following intramammary infusion erythromycin diffuses readily and extensively in various body fluids and tissues and adequate concentration is maintained in udder tissues for at least 12 h post intramammary administration. Thus, erythromycin may be recommended for local therapy of acute mastitis caused by Gram-positive bacteria in lactating dairy cows.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATCC:
-
American Type Culture Collection
- AUC0−∞ :
-
area under the curve from zero to infinity by the trapezoidal integral
- AUMC0−∞ :
-
area under the moment curve
- β:
-
elimination rate constant
- C 0 :
-
zero-time plasma drug concentration intercept of the least-squares regression line of elimination phase
- C max :
-
peak plasma drug concentration value
- IDF:
-
International Dairy Federation
- k a :
-
absorption rate constant
- k el :
-
overall elimination rate constant
- MIC:
-
minimum inhibitory concentration
- MRT:
-
mean residual time
- t 1/2ka :
-
absorption half life
- t 1/2β :
-
elimination half-life
- V d(B) :
-
volume of distribution based on zero time plasma drug concentration intercept of the least-squares regression line of elimination phase
References
Arret, B., Johnson, D.P. and Kirshbaum, A., 1971. Outline of details of microbiological assay of antibiotics: Second revision. Journal of Pharmacological Science, 60, 1689–1694
Bajwa, N.S., Bansal, B.K., Dua, K. and Mawi, P.S., 2005. Effect of erythromycin in specific mastitis and quality of milk in cows. Indian Veterinary Journal, 82, 728–730
Ballarini, I.G., 2001. Drug therapy of bovine mastitis and pharmacokinetics. Obiettive Documenti Veterinari, 22, 27–31
Bansal, B.K., Hamann, J., Classens, I., Kroemker, V. and Singh, K.B., 2003. Distribution of oxacillin in serum and milk of treated and untreated quarters in cows following intramammary infusion. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica. Supplementum, 98, 231
Brown, R.W., Barnum, D.A., Jasper, D.E., McDonald, J.S. and Schultze, W. D., 1981. Microbiological Procedures for Use in the Diagnosis of Bovine Mastitis, (National Mastitis Council, Inc., Arlington, VA)
Burrows, G.E., Griffin, D.D., Pippin, A. and Harris, K., 1989. A comparision of the various routes of administration of erythromycin in the cattle. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 12, 289–295
Carli, S., Sonzogni, O., Invernizzi, A., Granata, G. and Pignattelli, P., 1983. Blood concentrations and milk excretion of cefacetrile given by the intramammary route to cows. Atti-della Societa Italiana-delle-Scienze Veterinarie, 37, 250–252
Cattell, M.B., Dinsmore, R.P., Belschner, A.P., Carmen, J. and Goodell, G., 2001. Environmental gram-positive mastitis treatment: in vitro sensitivity and bacteriologic cure. Journal of Dairy Science, 84, 2036–2043
Hardman, J.G., Limbird, L.E. and Gilman, A.G., 2001. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, (McGraw-Hill, New York)
International Dairy Federation, 1987. Definitions and Guidelines for Diagnosis of Bovine Mastitis, (IDF Bulletin), 258
Malinowski, E., Klossowska, A., Kuzma, K. and Krukowski, H., 1992. Antibiotic sensitivity of bacteria isolated from bovine mastitis. Medycyna Weterynaryjna, 48, 366–367
McKeller Q.A., 1991. Intramammary treatment of mastitis in cows. In Practice, (November) , 244–249
Owens, W.E, Watts, J.L., Greene, B.B. and Ray, C.H., 1990. Minimum inhibitory concentrations and disk diffusion zone diameter for selected antibiotics against streptococci isolated from bovine intramammary infections. Journal of Dairy Science, 73, 1225–1231
Owens, W.E., Ray, C.H., Watts, J.L. and Yancey, R.J., 1997. Comparison of success of antibiotic therapy during lactation and results of antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bovine mastitis. Journal of Dairy Science, 80, 313–317
Radostits, O.M., Gay, C.C., Blood, D.C. and Hinchcliff, K.W., 2000. Veterinary Medicine, (W.B. Saunders, London)
Salmon, S.A., Watts, J.L., Aarestrup, F.M., Pankey, J.W. and Yancey, R. J. Jr., 1998. Minimum inhibitory concentration for selected antimicrobials agents against organisms isolated from the mammary glands of dairy heifers in New Zealand and Denmark. Journal of Dairy Science, 81, 570–578
Seymour, E.H., Jones, G.M. and McGilliard, M.L., 1988. Persistence of residues in milk following antibiotic treatment of dairy cattle. Journal of Dairy Science, 71, 2292–2296
Shephard, R.W., Malmo, J. and Pfeiffer D.U., 2000. A clinical trial to evaluate the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment of lactating cows with high somatic cell counts in their milk. Australian Veterinary Journal, 78, 763–768
Smith, G.W., Gehring, R, Riviere, J.L., Yeatts, J.L. and Baynes, R.E., 2004. Elimination kinetics of ceftiofur hydrochloride after intramammary administration in lactating dairy cows. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, 224, 1827–1830
Snedecor, G.W. and Cocharan W.G., 1989. Statistical Methods, (Iowa State University Press, Ames, IA)
Watts, J.L. and Salmon, S.A., 1997. Activity of selected antimicrobial agents against strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine intramammary infections that produce β-lactamase. Journal of Dairy Science, 80, 313–317
Wuschko, S., Kunter, U., Schwabe, K.H. and Kalvelage, H., 1998. Erythromycin in the udder-results of a pharmacokinetic study on bioavailability. Praktische Tierarzt, 79, 1157–1159
Ziv, G. and Sulman, F.G., 1974. Absorption of antibiotics by the bovine udder. Journal of Dairy Science, 58, 1637–1644
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bajwa, N.S., Bansal, B.K., Srivastava, A.K. et al. Pharmacokinetic Profile of Erythromycin after Intramammary Administration in Lactating Dairy Cows with Specific Mastitis. Vet Res Commun 31, 603–610 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-007-3505-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-007-3505-7