Abstract
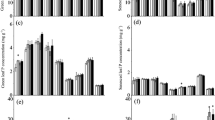
We measured aboveground biomass allocation and resorption of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in the fronds of a winter-deciduous fern Athyrium distentifolium in ambient and N-enhanced treatments. Studies were done in the Moravian-Silesian Beskydy Mts. (Czech Republic) during 2007 and 2008. Athyrium distentifolium formed taller fronds and petioles and allocated more biomass to supporting tissue relative to photosynthetically active leaf tissue in response to N addition. Resorption of P from green fronds was more efficient than N resorption (on average 50% P, 21% N from supporting and 44% P, 24% N from photosynthetic tissues were withdrawn during senescence). The N/P-ratios were higher in photosynthetic tissue (10.8 in 2007 and 13.0 in 2008) in comparison with supporting tissue (5.5 and 7.7, respectively). In N-enhanced treatment, a positive relationship was found between the amount of supporting tissue relative to photosynthetic tissue and resorption of nutrients from photosynthetic tissue. However, higher N availability resulted in a significant decrease of N resorption efficiency in photosynthetic tissue of A. distentifolium.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R (1996) Nutrient resorption from senescing leaves of perennials: are there general patterns? J Ecol 84:597–608
Buček A, Štykar J (1993) Dynamics of development of forest phytocenoses in the Kněhyně nature reserve influenced by phytotoxic emission (in Czech). In: Křístek J, Tesař V (eds) The Beskids Bulletin 5, Brno, pp 66–67
Chapin FS III (1980) The mineral nutrition of wild plants. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 11:233–260
Chapin FS III, Moilanen L (1991) Nutritional controls over nitrogen and phosphorus resorption from Alaskan birch leaves. Ecology 72:709–715
de la Cretaz AL, Kelty MJ (2002) Development of tree regeneration in fern-dominated forest understories after reduction of deer browsing. Restor Ecol 10:416–426
den Dubbelden KC, Knops JMH (1993) The effect of competition and slope inclination on aboveground biomass allocation of understorey ferns in subtropical forest. Oikos 67:285–290
Falkengren-Grerup U, Diekmann M (2003) Use of a gradient of N-deposition to calculate effect-related soil and vegetation measures in deciduous forests. For Ecol Manag 180:113–124
Fenn ME, Poth MA, Johnson DW (1996) Evidence for nitrogen saturation in the San Bernardino Mountains in southern California. For Ecol Manag 82:211–230
Fiala K, Tůma I, Holub P, Jandák J (2005) The role of Calamagrostis communities in preventing soil acidification and base cation losses in deforested mountain area affected by acid deposition. Plant Soil 268:35–49
George LO, Bazzaz FA (1999) The fern understory as an ecological filter: emergence and establishment of canopy-tree seedlings. Ecology 80:833–845
Gűsewell S (2004) N:P ratios in terrestrial plants: variation and functional significance. New Phytol 164:243–266
Gűsewell S (2005) Nutrient resorption of wetland graminoids is related to the type of nutrient limitation. Funct Ecol 19:344–354
Hill JD, Silander JA (2001) Distribution and dynamics of two ferns: Dennstaedtia punctilobula (Dennstaedtiacea) and Thelypteris noveboracensis (Thelypteridaceae) in a Northeast mixed hardwoods-hemlock forest. Am J Bot 88:894–902
Holeksa J (2003) Relationship between field-layer vegetation and canopy openings in a Carpathian subalpine spruce forest. Plant Ecol 168:57–67
Hunter JG (1953) The composition of bracken: some major- and trace-element constituents. J Sci Food Agric 4:10–20
Killingbeck KT (1996) Nutrients in senesced leaves: keys to the search for potential resorption and resorption proficiency. Ecology 77:1716–1727
Killingbeck KT, Hammen-Winn SL, Vecchio PG, Goguen ME (2002) Nutrient resorption efficiency and proficiency in fronds and trophopods of a winter-deciduous fern Dennstaedtia punctilobula. Int J Plant Sci 163:99–105
Kobe RK, Lepczyk ChA, Iyer M (2005) Resorption efficiency decreases with increasing green leaf nutrients in a global data set. Ecology 86:2780–2792
Koerselman W, Meuleman AFM (1996) The vegetation N:P ratio: a new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J Appl Ecol 33:1441–1450
McHaffie HS, Legg CJ, Ennos RA (2001) A single gene with pleiotropic effects accounts for the Scottish endemic taxon Athyrium distentifolium var. flexile. New Phytol 152:491–500
Minoletti ML, Boerner REJ (1993) Seasonal photosynthesis, nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics, and resorption in the wintergreen fern Polystichum acrostichoides (Michx.) Schott. Bull Torrey Bot Club 120:397–404
Odland A (1991) A synecological investigation of Athyrium distentifolium-dominated stands in western Norway. Nordic J Bot 11:651–673
Pande K (1998) A study of growth and morphology of Athyrium distentifolium TAUSCH growing in different environmental conditions in the Beskydy mountains. In: Tesař V, Kula E (eds) The Beskids Bulletin 11, Brno, pp 69–74
Richardson SJ, Allen RB, Doherty JE (2008) Shifts in leaf N:P ratio during resorption reflect soil P in temperate rainforest. Funct Ecol 22:738–745
Roem WJ, Berendse F (2000) Soil acidity and nutrient supply ratio as possible factors determining changes in plant species diversity in grassland and heathland communities. Biol Conserv 92:151–161
Ryan DF, Bormann FH (1982) Nutrient resorption in northern hardwood forests. Bioscience 32:29–32
Tessier JT (2001) Vernal photosynthesis and nutrient retranslocation in Dryopteris intermedia. Am Fern J 91:187–196
Tessier JT, Raynal DJ (2003) Use of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in plant tissue as an indicator of nutrient limitation and nitrogen saturation. J Appl Ecol 40:523–534
Thomas SC, Halpern CB, Falk DA, Liguori DA, Austin KA (1999) Plant diversity in managed forests: understory responses to thinning and fertilization. Ecol Appl 9:864–879
Tůma I, Fiala K, Holub P, Pande K (2006) Biomass formation, nutrient uptake and release in fern stands of Athyrium distentifolium on deforested areas affected by pollution: comparison with grass stands. Ekol Bratisl 25:264–279
Tůma I, Fiala K, Holub P (2008) Can stands of Athyrium distentifolium/Opiz/fern reduce leaching of base cations from soil similarly as grass stands do in mountain areas under enhanced nitrogen input? Beskids Bull 1:179–182
Vacek S, Bastl M, Lepš J (1999) Vegetation changes in forests of the Krkonoše Mts. over a period of air pollution stress (1980–1995). Plant Ecol 143:1–11
Wright IJ, Westoby M (2003) Nutrient concentration, resorption and lifespan: leaf traits of Australian sclerophyll species. Funct Ecol 17:10–19
Zelená V (1996) Main types of grass communities of deforested areas in the Beskydy Mts. In: Fiala K (ed) Grass ecosystems of deforested areas in the Beskydy Mts. Preliminary results of ecological studies. Institute of Landscape Ecology AS CR, Brno, pp 39–44
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Grant Agency of the Academy of Science of the Czech Republic (project no. IAA600050616) and by projects No. AV0Z 60050516 and AV0Z 60870520. We are indebted to Prof. J.M. Bernard for his review of the text.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holub, P., Tůma, I. The effect of enhanced nitrogen on aboveground biomass allocation and nutrient resorption in the fern Athyrium distentifolium . Plant Ecol 207, 373–380 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-009-9681-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-009-9681-5