Abstract
Purpose
The relationship between chronic kidney disease (CKD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in population with diabetes remains controversial. Our current study aimed to explore the association between NAFLD and CKD in population with prediabetes or diabetes.
Methods
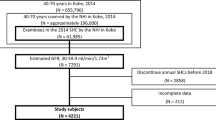
A cross-sectional study was conducted in Zhuhai city from June to October 2012. A total of 190 out of 334 participants with prediabetes or diabetes were enrolled in this study. CKD was defined as estimated GFR <60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 and/or albumin-to-creatinine ratio ≥30 mg/g. NAFLD was diagnosed on the basis of ultrasonographic and excluded fatty liver disease caused by other reasons such as drinking. The association between NAFLD and CKD was then analyzed using SPSS (version 19.0).
Results
Subjects with NAFLD were more likely with a higher urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (P < 0.001). CKD were common among patients with NAFLD than those without NAFLD (P < 0.05). NAFLD was significantly associated with CKD (P < 0.05) in the unadjusted analyses as well as after adjustment for potential confounders. The unadjusted odd ratio and adjusted odd ratio for CKD were 2.25 (95 % CI 1.07–4.77, P = 0.034) and 2.68 (95 % CI 1.12–6.01, P = 0.016). When further adjusted for hypertension, serum high-density lipoprotein and serum fasting glucose, the association of NAFLD with CKD was still significant (OR 2.78, 95 % CI 1.03–7.52, P = 0.044).
Conclusions
Our current study suggests that ultrasound-diagnosed NAFLD is associated with CKD among population with prediabetes or diabetes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcome (KDIGO) CKD work group (2013) KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 3:S1–S150
Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K et al (2013) Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 382:260–272
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K et al (2012) Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet 380:2095–2128
Zhang L, Wang F, Wang L et al (2012) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet 379:815–822
Coresh J, Byrd-Holt D, Astor BC et al (2005) Chronic kidney disease awareness, prevalence, and trends among U.S. adults, 1999 to 2000. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:180–188
Angulo P, Lindor KD (2002) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:186–190
Angulo P (2002) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med 346(16):1221–1231
Zhang H, Han S, Cao P et al (2013) Effects of Chinese wild rice on lipid metabolism and lipotoxicity in rats fed with high fat/cholesterol diet. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 42:190–195
Gaggini M, Morelli M, Buzzigoli E et al (2013) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its connection with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Nutrients 5:1544–1560
Shibata M, Kihara Y, Taguchi M et al (2007) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes in middle-aged Japanese men. Diabetes Care 30:2940–2944
Targher G, Chonchol M, Bertolini L et al (2008) Increased risk of CKD among type 2 diabetics with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:1564–1570
Targher G, Pichiri I, Zoppini G et al (2012) Increased prevalence of chronic kidney disease in patients with Type 1 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver. Diabet Med 29:220–226
Sirota JC, McFann K, Targher G et al (2012) Association between nonalcoholic liver disease and chronic kidney disease: an ultrasound analysis from NHANES 1988-1994. Am J Nephrol 36:466–471
Li Y, Zhao L, Chen Y et al (2013) Association between metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in perimenopausal women. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:3987–3997
Li Y, Zhou C, Shao X et al (2014) Hypertriglyceridemic waist phenotype and chronic kidney disease in a Chinese population aged 40 years and older. PLoS ONE 9(3):e92322. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0092322
Li Y, Chen S, Shao X et al (2014) Association of uric acid with metabolic syndrome in men, premenopausal women and postmenopausal women. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11:2899–2910
Li Y, Chen Y, Liu X et al (2014) Metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in a Southern Chinese population. Nephrology doi: 10.1111/nep.12219. [Epub ahead of print]
Li Y, Zhao L, Liu X et al (2013) Prevalence and distribution of metabolic syndrome in a southern Chinese population. Saudi Med J 34(9):929–936
Genuth S, Alberti KG, Bennett P et al (2003) Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 26:3160–3167
American Diabetes Association (2012) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 35(Suppl 1):S64–S71
Expert Panel on Detection E, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (2001) Executive summary of the third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). JAMA 285:2486–2497
Choe SS, Choi AH, Lee JW et al (2007) Chronic activation of liver X receptor induces beta-cell apoptosis through hyperactivation of lipogenesis: liver X receptor-mediated lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 56:1534–1543
Chang Y, Ryu S, Sung E et al (2008) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease predicts chronic kidney disease in nonhypertensive and nondiabetic Korean men. Metabolism 57:569–576
Zeng MD, Fan JG, Lu LG et al (2008) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases. J Dig Dis 9:108–112
Guo W, Pirtskhalava T, Tchkonia T et al (2007) Aging results in paradoxical susceptibility of fat cell progenitors to lipotoxicity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292:E1041–E1051
Xie Y, Wang M, Zhang Y et al (2013) Serum uric acid and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in non-diabetic Chinese men. PLoS ONE 8:e67152
Zhan YT, Zhang C, Li L et al (2012) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is not related to the incidence of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes. Int J Mol Sci 13:14698–14706
Yasui K, Sumida Y, Mori Y et al (2011) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and increased risk of chronic kidney disease. Metabolism 60:735–739
Ahn AL, Choi JK, Kim MN et al (2013) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic kidney disease in Koreans aged 50 years or older. Korean J Fam Med 34(3):199–205
Targher Giovanni, Chonchol Michel, Zoppini Giacomo et al (2011) Risk of chronic kidney disease in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: is there a link? J Hepatol 54:1020–1029
Navarro-Gonza lez JF, Mora C, Muros M et al (2013) Relationship between inflammation and microalbuminuria in prehypertension. J Hum Hypertens 27:119–125
Saadeh S, Younossi ZM, Remer EM et al (2002) The utility of radiological imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 123:745–750
Webb M, Yeshua H, Zelber-Sagi S et al (2009) Diagnostic value of a computerized hepatorenal index for sonographic quantification of liver steatosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192:909–914
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the following Science Foundation: (1) EU FP7 Program, UroSense, 2011; (2) Guangdong Provincial Science and Technique Program (No. 2011B031800386), 2011.
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yongqiang Li and Shuangshuang Zhu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhu, S., Li, B. et al. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic kidney disease in population with prediabetes or diabetes. Int Urol Nephrol 46, 1785–1791 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0796-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0796-9