Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to elucidate the role of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in regulating apoptosis of tubular epithelial cells in a hypoxia–reperfusion model.
Methods
A hypoxia–reperfusion model was established with NRK-52E cells to assess apoptosis and cell cycle progression after the addition of NGAL. We investigated the expression of four apoptosis factors, Bcl-2, Bax, Fas and FasL, as well as the expression level of two NGAL receptors, 24p3R and megalin, by both Western blot and real-time PCR.
Results
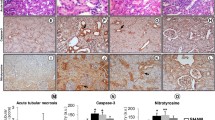
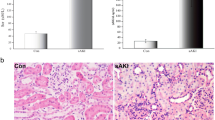
NGAL induced cell proliferation and reduced apoptosis by regulating four apoptosis factors Bcl-2, Bax, Fas and FasL. Western blot demonstrated that the two NGAL receptors, 24p3R and megalin, were increased after hypoxia–reperfusion, which was reduced by exogenous NGAL. Moreover, overexpression of the two receptors induced the expression of the anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2 and reduced the expression of pro-apoptotic Bax, Fas and FasL.
Conclusions
These findings indicate that NGAL reduces apoptosis by regulating the four apoptosis factors Bcl-2, Bax, Fas and FasL through its two receptors 24p3R and megalin. These results also suggest that ectopic expression of NGAL in renal cells might provide a therapeutic strategy in ischemia–reperfusion by reducing apoptosis and promoting renal cell proliferation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
El Sabbahy M, Vaidya VS (2011) Ischemic kidney injury and mechanisms of tissue repair. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 3(5):606–618. doi:10.1002/wsbm.133
Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A (2009) Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 54(6):1012–1024. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.07.020
Kanbay M, Kasapoglu B, Perazella MA (2010) Acute tubular necrosis and pre-renal acute kidney injury: utility of urine microscopy in their evaluation—a systematic review. Int Urol Nephrol 42(2):425–443. doi:10.1007/s11255-009-9673-3
Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, Ronco C (2005) Ending supportive therapy for the kidney I (2005) acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 294(7):813–818. doi:10.1001/jama.294.7.813
Mehta RL, Pascual MT, Soroko S, Savage BR, Himmelfarb J, Ikizler TA, Paganini EP, Chertow GM (2004) Spectrum of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit: the PICARD experience. Kidney Int 66(4):1613–1621. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00927.xKID927
Supavekin S, Zhang W, Kucherlapati R, Kaskel FJ, Moore LC, Devarajan P (2003) Differential gene expression following early renal ischemia/reperfusion. Kidney Int 63(5):1714–1724. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00928.x
Waikar SS, Bonventre JV (2008) Biomarkers for the diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract 109(4):c192–c197. doi:10.1159/000142928
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J, Mori K, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2005) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 365(9466):1231–1238. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)74811-X
Devarajan P, Mishra J, Supavekin S, Patterson LT, Steven Potter S (2003) Gene expression in early ischemic renal injury: clues towards pathogenesis, biomarker discovery, and novel therapeutics. Mol Genet Metab 80(4):365–376
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2003) Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14(10):2534–2543
Mishra J, Mori K, Ma Q, Kelly C, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2004) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a novel early urinary biomarker for cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Am J Nephrol 24(3):307–315. doi:10.1159/000078452
Mishra J, Mori K, Ma Q, Kelly C, Yang J, Mitsnefes M, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2004) Amelioration of ischemic acute renal injury by neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(12):3073–3082. doi:10.1097/01.ASN.0000145013.44578.45
Mori K, Lee HT, Rapoport D, Drexler IR, Foster K, Yang J, Schmidt-Ott KM, Chen X, Li JY, Weiss S, Mishra J, Cheema FH, Markowitz G, Suganami T, Sawai K, Mukoyama M, Kunis C, D’Agati V, Devarajan P, Barasch J (2005) Endocytic delivery of lipocalin–siderophore–iron complex rescues the kidney from ischemia–reperfusion injury. J Clin Investig 115(3):610–621. doi:10.1172/JCI23056
Schmidt-Ott KM, Mori K, Kalandadze A, Li JY, Paragas N, Nicholas T, Devarajan P, Barasch J (2006) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin-mediated iron traffic in kidney epithelia. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 15(4):442–449. doi:10.1097/01.mnh.0000232886.81142.58
Devarajan P (2008) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL): a new marker of kidney disease. Scand J Clin Lab Investig Suppl 241:89–94. doi:10.1080/00365510802150158
Basile DP, Liapis H, Hammerman MR (1997) Expression of bcl-2 and bax in regenerating rat renal tubules following ischemic injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 272(5 Pt 2):F640–F647
Ortiz A, Lorz C, Egido J (1999) The Fas ligand/Fas system in renal injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14(8):1831–1834
Watkins MT, Haudenschild CC, al-Badawi H, Velazquez FR, Larson DM (1995) Immediate responses of endothelial cells to hypoxia and reoxygenation: an in vitro model of cellular dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 268(2 Pt 2):H749–H758
Tominaga K, Kondo C, Johmura Y, Nishizuka M, Imagawa M (2004) The novel gene fad104, containing a fibronectin type III domain, has a significant role in adipogenesis. FEBS Lett 577(1–2):49–54. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.09.062
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C (T) method. Nat Protoc 3(6):1101–1108. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Devireddy LR, Gazin C, Zhu X, Green MR (2005) A cell-surface receptor for lipocalin 24p3 selectively mediates apoptosis and iron uptake. Cell 123(7):1293–1305. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.027
Hvidberg V, Jacobsen C, Strong RK, Cowland JB, Moestrup SK, Borregaard N (2005) The endocytic receptor megalin binds the iron transporting neutrophil-gelatinase-associated lipocalin with high affinity and mediates its cellular uptake. FEBS Lett 579(3):773–777. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.12.031
Chen Z, Chua CC, Ho YS, Hamdy RC, Chua BH (2001) Overexpression of Bcl-2 attenuates apoptosis and protects against myocardial I/R injury in transgenic mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280(5):H2313–H2320
Kirshenbaum LA, de Moissac D (1997) The bcl-2 gene product prevents programmed cell death of ventricular myocytes. Circulation 96(5):1580–1585
Schmidt-Ott KM, Mori K, Li JY, Kalandadze A, Cohen DJ, Devarajan P, Barasch J (2007) Dual action of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. J Am Soc Nephrol 18(2):407–413. doi:10.1681/ASN.2006080882
Yang J, Goetz D, Li JY, Wang W, Mori K, Setlik D, Du T, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Strong R, Barasch J (2002) An iron delivery pathway mediated by a lipocalin. Mol Cell 10(5):1045–1056
Yang J, Mori K, Li JY, Barasch J (2003) Iron, lipocalin, and kidney epithelia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285(1):F9–F18. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00008.2003
Ferris CD, Jaffrey SR, Sawa A, Takahashi M, Brady SD, Barrow RK, Tysoe SA, Wolosker H, Baranano DE, Dore S, Poss KD, Snyder SH (1999) Haem oxygenase-1 prevents cell death by regulating cellular iron. Nat Cell Biol 1(3):152–157. doi:10.1038/11072
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau, bureau-level research project Grant (No. 20114331) and the Advanced Medical Cooperation Project of Songjiang Health Bureau of Shanghai (2011).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zang, X., Zheng, F., Hong, Hj. et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin protects renal tubular epithelial cells in hypoxia–reperfusion by reducing apoptosis. Int Urol Nephrol 46, 1673–1679 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0749-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0749-3