Abstract
Purpose
To determine whether perirenal fat is associated with increased urinary albumin excretion and whether perirenal fat affects renal vascular endothelial function in obese rats.
Methods
Wistar rats were randomly divided into normal and obesity group, which were fed with normal and high-fat diet, respectively. Blood and urine samples were collected. Endothelial function of the aorta was determined by measuring endothelium-dependent vasodilatation. Renal tissues were collected for CD34 immunohistochemistry and free fatty acids (FFA) measurement. Levels of glomerular nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) were measured.
Results
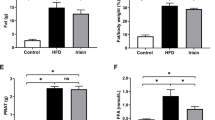
After 24 weeks, plasma FFA, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and malondialdehyde levels were elevated and were significantly higher in renal venous blood than in jugular venous blood in obese rats. Urinary albumin/creatinine ratio, glomerular CD34 expression, glomerular ROS level, and renal cortex FFA levels were higher in obese rats. Endothelial dysfunction was more severe in the infra-renal aorta than in the thoracic aorta in obese rats. Plasma adiponectin and glomerular NO levels were lower in obese rats.
Conclusion
Perirenal fat is associated with increased urinary albumin excretion in obese rats. The mechanism may be renal vascular endothelial dysfunction caused by increased oxidative stress and activation of inflammatory molecular pathways due to elevated FFA and low adiponectin levels.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hurt RT, Frazier TH, McClave SA, Kaplan LM (2011) Obesity epidemic: overview, pathophysiology, and the intensive care unit conundrum. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 35(5 Suppl):4S–13S
Rokholm B, Baker JL, Sorensen TI (2010) The levelling off of the obesity epidemic since the year 1999—a review of evidence and perspectives. Obes Rev 11(12):835–846
Klausen KP, Parving HH, Scharling H, Jensen JS (2009) Microalbuminuria and obesity: impact on cardiovascular disease and mortality. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 71(1):40–45
Kopple JD, Feroze U (2011) The effect of obesity on chronic kidney disease. J Ren Nutr 21(1):66–71
Weisinger JR, Kempson RL, Eldridge FL, Swenson RS (1974) The nephrotic syndrome: a complication of massive obesity. Ann Intern Med 81(4):440–447
Kambham N, Markowitz GS, Valeri AM, Lin J, D’Agati VD (2001) Obesity-related glomerulopathy: an emerging epidemic. Kidney Int 59(4):1498–1509
Foster MC, Hwang SJ, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, DeBoer IH, Robins SJ et al (2011) Association of subcutaneous and visceral adiposity with albuminuria: the Framingham Heart Study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 19(6):1284–1289
Sun X, Han F, Miao W, Hou N, Cao Z, Zhang G (2013) Sonographic evaluation of para- and perirenal fat thickness is an independent predictor of early kidney damage in obese patients. Int Urol Nephrol 45(6):1589–1595
Lamacchia O, Nicastro V, Camarchio D, Valente U, Grisorio R, Gesualdo L et al (2011) Para- and perirenal fat thickness is an independent predictor of chronic kidney disease, increased renal resistance index and hyperuricaemia in type-2 diabetic patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(3):892–898
Han F, Hou N, Miao W, Sun X (2013) Correlation of ultrasonographic measurement of intrarenal arterial resistance index with microalbuminuria in nonhypertensive, nondiabetic obese patients. Int Urol Nephrol 45(4):1039–1045
Sun X, Han F, Yi J, Hou N, Cao Z (2013) The effect of telomerase activity on vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in type 2 diabetes in vivo and in vitro. Mol Med Rep 7(5):1636–1640
Lee RM, Lu C, Su LY, Werstuck G, Gao YJ (2009) Effects of hyperglycemia on the modulation of vascular function by perivascular adipose tissue. J Hypertens 27(1):118–131
Sun X, Yu Y, Han L (2013) High FFA levels related to microalbuminuria and uncoupling of VEGF-NO axis in obese rats. Int Urol Nephrol 45(4):1197–1207
Kono T, Saito M, Kinoshita Y, Satoh I, Shinbori C, Satoh K (2006) Real-time monitoring of nitric oxide and blood flow during ischemia-reperfusion in the rat testis. Mol Cell Biochem 286(1–2):139–145
Asaba K, Tojo A, Onozato ML, Goto A, Quinn MT, Fujita T et al (2005) Effects of NADPH oxidase inhibitor in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 67(5):1890–1898
Pinto-Sietsma SJ, Navis G, Janssen WM, de Zeeuw D, Gans RO, de Jong PE (2003) A central body fat distribution is related to renal function impairment, even in lean subjects. Am J Kidney Dis 41(4):733–741
Bonnet F, Marre M, Halimi JM, Stengel B, Lange C, Laville M et al (2006) Larger waist circumference is a predictive factor for the occurrence of microalbuminuria in a non-diabetic population. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss 99(7–8):660–662
Sharma K (2008) Adiponectin regulates albuminuria and podocyte function in mice. J Clin Investig 118(5):1645
Sharma K (2009) The link between obesity and albuminuria: adiponectin and podocyte dysfunction. Kidney Int 76(2):145–148
Li Y, Sun X, Yu Y (2013) Serum fetuin-A levels related with microalbuminuria in diet-induced obese rats. Biomed Res Int 2013:795103
Kern PA (2003) Adiponectin expression from human adipose tissue relation to obesity, insulin resistance, and tumor necrosis factor-α expression. Diabetes 52(7):1779–1785
Yamauchi T, Kadowaki T (2008) Physiological and pathophysiological roles of adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in the integrated regulation of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Int J Obes (Lond) 32(Suppl 7):S13–S18
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 81300688), Weifang Health Bureau Program (2013082), and the Science and Technology Innovation Fund of Affiliated Hospital of Weifang Medical University (No. K12QC1004).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, N., Han, F., Wang, M. et al. Perirenal fat associated with microalbuminuria in obese rats. Int Urol Nephrol 46, 839–845 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0656-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0656-7