Abstract
Background
We evaluated antitumoral effect of combined chemotherapy and interleukin-12 (IL-12) gene therapy in in vitro and in vivo experimental urothelial bladder cancer (UBC) model.
Materials and methods
EJ UBC cells were transfected with recombinant IL-12 genes using a liposomal transfection agent. Pirarubicin (THP) was added to the experimental samples at a final concentration of 20 mg/l. Four groups were assigned in vitro: untreated cells, transfected cells, untransfected cells plus THP and transfected cells plus THP. Death rates (DR) and cellular micromorphologic changes were evaluated. Bladder tumor model was established by subcutaneous injection of EJ cells to the nude mice. Four groups were assigned in vivo: control group; THP group; IL-12 gene group and IL-12 gene plus THP group. After injection of combined THP and IL-12 gene therapy, tumor size and IL-12 levels were evaluated.
Results
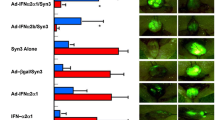
In vitro study: DR in the THP + IL-12 gene therapy group (58.2 ± 15.8%) was significantly higher than transfected group (12.2 ± 5.6%; P = 0.01) and untransfected cells plus THP group (33.4 ± 7.8; P = 0.046). A higher amount of apoptotic changes and necrosis on transmission electron microscope analysis were observed in transfected cells plus THP group. In vivo study: A significant tumor attenuation was found in IL-12 gene in combination with THP group when compared with any other groups that were treated without Il-12 or THP (P < 0.05). IL-12 levels in serum were significant high in IL-12 gene groups (P < 0.01).
Conclusion
The combination of THP chemotherapy and IL-12 gene therapy showed an additive antitumoral effect on bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Further investigation should be focused on high-level transgene protocols in vivo.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolenz C, Cao Y, Fernández Arancibia M et al (2006) Intravesical mitomycin C for superficial transitional cell carcinoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 6:1273–1282
Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Oosterlinck W et al (2006) Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol 49:466–475
Sylvester RJ, Oosterlinck W, van der Meijden AP (2004) A single immediate postoperative instillation of chemotherapy decreases the risk of recurrence in patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer: a meta-analysis of published results of randomized clinical trials. J Urol 171:2186–2190
Akagashi K, Tanda H, Kato S, Ohnishi S et al (2006) Recurrence pattern for superficial bladder cancer. Int J Urol 13(6):686–691
O’Donnell MA, Luo Y, Hunter SE et al (2004) Interleukin-12 immunotherapy of murine transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: dose dependent tumor eradication and generation of protective immunity. J Urol 171:1330–1335
Loskog AS, Fransson ME, Totterman TT (2005) AdCD40L gene therapy counteracts T regulatory cells and cures aggressive tumors in an orthotopic bladder cancer model. Clin Cancer Res 15:8816–8821
Siemens DR, Austin JC, Hedican SP et al (2000) Viral vector delivery in solid-state vehicles: gene expression in a murine prostate cancer model. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:403–412
Chuang TF, Lee SC, Kw Liao et al (2009) Electroporation-mediated IL-12 gene therapy in a transplantable canine cancer model. Int J Cancer 125:698–707
Carrion R, Seigne J (2002) Surgical management of bladder carcinoma. Cancer Control 9:284–292
von der Maase H, Sengelov L, Roberts JT (2005) Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:4602–4608
Koya MP, Simon MA, Soloway MS (2006) Complications of intravesical therapy for urothelial cancer of the bladder. J Urol 175:2004–2010
Manetti R, Parronchi P, Giudizi MG et al (1993) Natural killer cell stimulatory factor (interleukin 12 [IL-12]) induces T helper type 1 (Th1)-specific immune responses and inhibits the development of IL-4-producing Th cells. J Exp Med 177:1104–1199
Trinchieri G (2003) Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 3:133–146
Colombo MP, Trinchieri G (2002) Interleukin-12 in anti-tumor immunity and immunotherapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13:155–168
Gollob JA, Mier JW, Veenstra K et al (2000) Phase I trial of twice-weekly intravenous interleukin 12 in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer or malignant melanoma: ability to maintain IFN- γ induction is associated with clinical response. Clin Cancer Res 6:1678–1692
Del Vecchio M, Bajetta E, Canova S et al (2007) Interleukin-12: biological properties and clinical application. Clin Cancer Res 13:4677–4685
Shiratori I, Suzuki Y, Oshiumi H et al (2007) Recombinant interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 antitumor therapy in a guinea-pig hepatoma cell implant model. Cancer Sci 98:1936–19422
Teicher BA, Ara G, Buxton D et al (1997) Optimal scheduling of interleukin 12 and chemotherapy in the murine MB-49 bladder carcinoma and B16 melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 3:1661–1667
Brunda MJ, Luistro L, Warrier RR et al (1993) Antitumor and antimetastatic activity of interleukin 12 against murine tumor. J Exp Med 197:1223–1230
Weiss GR, O’Donnell MA, Loughlin K et al (2003) Phase 1 study of the intravesical administration of recombinant human interleukin-12 in patients with recurrent superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Immunother 26:343–348
Wang H, Yang G, Timme TL et al (2007) IL-12 gene-modified bone marrow cell therapy suppresses the development of experimental metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 14:819–827
Horinaga M, Harsch KM, Fukuyama R et al (2005) Intravesical interleukin-12 gene therapy in an orthotopic bladder cancer model. Urology 66:461–466
Tan J, Newton CA, Djeu JY et al (1996) Injection of complementary DNA encoding interleukin-12 inhibits tumor establishment at a distant site in a murine renal carcinoma model. Cancer Res 56:3399–3403
Tsai YS, Shiau AL, Chen YF et al (2010) Enhancement of antitumor activity of gammaretrovirus carrying IL-12 gene through genetic modification of envelope targeting HER2 receptor: a promising strategy for bladder cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 17:37–48
Zaharoff DA, Hoffman BS, Hooper HB et al (2009) Intravesical Immunotherapy of superficial bladder cancer with Chitosan/Interleukin-12. Cancer Res 69:6192–6199
Leist M, Jaattela M (2001) Triggering of apoptosis by cathepsins. Cell Death Differ 8:324–326
Khan T, Hixon JA, Stauffer JK et al (2006) Therapeutic modulation of Akt activity and antitumor efficacy of interleukin-12 against orthotopic murine neuroblastoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:190–202
Loeffler M, Kroemer G (2000) The mitochondrion in cell death control: certainties and incognita. Exp Cell Res 256:19–26
Kaufmann SH, Earnshwa WC (2000) Induction of apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp Cell Res 256:42–49
Acknowledgments
The part of experiments in vivo was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC: 30901481).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wanpeng Liu and Yanwei Cao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Cao, Y., Fernández, M.I. et al. Additive antitumoral effect of interleukin-12 gene therapy and chemotherapy in the treatment of urothelial bladder cancer in vitro and in vivo. Int Urol Nephrol 43, 721–727 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-010-9866-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-010-9866-9