Abstract
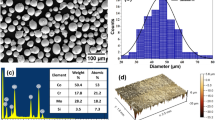
Monodisperse hard carbon spheres (HCSs) with different size from 300 nm to 1 μm were hydrothermally synthesized and characterized. The tribological performance of green water-based HCSs lubricant systems were studied between glass lens and silicon wafer at various normal loads and concentration on a universal micro-tribotester. The coefficient of friction (COF) increased with the particle size and an average COF of about 0.03 was measured when lubricated by 300 nm HCSs suspensions, whereas for 1-μm-sized carbon sphere, the average COF was 0.059 for the particle concentration of 1 mg/ml. For a given size of particles, the COF first decreases with increasing concentration, but the trend reverses after a critical concentration as adding more particles in the confined space block their movement causing higher COF. The wear life of the 1 μm HCSs lubricant was also evaluated at constant load of 2 N for the total shearing length of 8 m. A very low COF of 0.01 was stably achieved for the lubricant with 4 mg/ml HCSs suspension.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jost, H.P.: Economic impact of tribology. ASME J. Mech. Eng. 97 (1974)
Bhushan, B.: Nanotribology and Nanomechanics: An Introduction. Springer, New Yark (2008)
Jeng, Y.R., Huang, Y.H., Tsai, P.C., Hwang, G.L.: Tribological properties of carbon nanocapsule particles as lubricant additive. J. Tribol. 136, 0418011–0418019 (2014)
Miura, K., Kamiya, S., Sasaki, N.: C60 molecular bearings. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 055509 (2003)
Asaka, K., Miyazawa, K., Kizuk, T.: The toughness of multiwall carbon nanocapsules. Nanotechnology 20, 385705 (2009)
Jaekeun, L., Sangwon, C., Yujin, H., Han-Jong, C., Changgun, L., Youngmin, C., et al.: Application of fullerene-added nano-oil for lubrication enhancement in friction surfaces. Tribol. Int. 42, 440–447 (2009)
Feng, B.: Relation between the structure of C60 and its lubricity: a review. Lubr. Sci. 9, 181–183 (1997)
Ohmae, N.: Humidity effects on tribology of advanced carbon materials. Tribol. Int. 39, 1497–1502 (2006)
Berman, D., Erdemir, A., Sumant, A.V.: Reduced wear and friction enabled by graphene layers on sliding steel surfaces in dry nitrogen. Carbon 59, 167–175 (2013)
Berman, D., Erdemir, A., Sumant, A.V.: Few layer graphene to reduce wear and friction on sliding steel surfaces. Carbon 54, 454–459 (2013)
Lee, C.G., Hwang, Y.J., Choi, Y.M., Lee, J.K., Choi, C., Oh, J.M.: A study on the tribological characteristics of graphite nano-lubricants. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 10, 85–90 (2009)
Liu, D.E., Xie, G.X., Guo, D., Cui, Z.Y., Si, L.N., Wan, C.L., Zou, W., Luo, J.B.: Tunable lubricity of aliphatic ammonium graphite intercalation compounds at the micro/nanoscale. Carbon 115, 574–583 (2017)
Xie, G.X., Forslund, M., Pan, J.S.: Direct electrochemical synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (rGO)/copper composite films and their electrical/electroactive properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6, 7444–7455 (2014)
Berman, D., Deshmukh, S.A., Sankaranarayanan, S.K., Erdemir, A., Sumant, A.V.: Extraordinary macroscale wear resistance of one atom thick graphene layer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 6640–6646 (2014)
Egberts, P., Han, G.H., Liu, X.Z., Johnson, A.C., Carpick, R.W.: Frictional behavior of atomically thin sheets: hexagonal-shaped graphene islands grown on copper by chemical vapor deposition. ACS Nano 8, 5010–5021 (2014)
Liu, S.W., Wang, H.P., Xu, Q., Ma, T.B., Yu, G., Zhang, C.H., et al.: Robust microscale superlubricity under high contact pressure enabled by graphene-coated microsphere. Nat. Commun. 8, 14029 (2017). doi:10.1038/ncomms14029
Salomon, G., Gee, A.W.J.D., Zaat, J.H.: Methanol-chemical factors in Mos2-film lubrication. Wear 7, 87–101 (1964)
Zhang, L., Chen, L., Wa, H., Chen, J., Zhou, H.: Synthesis and tribological properties of stearic acid-modified anatase (TiO2) nanoparticles. Tribol. Lett. 41, 409–416 (2011)
Padgurskas, J., Rukuiza, R., Prosycevas, I.: Tribological properties of lubricant additives of Fe, Cu and co nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 60, 224–232 (2013)
Yu, H.L., Xu, Y., Shi, P.J., Xu, B.S., Wang, X.L., Liu, Q., et al.: Characterization and nano-mechanical properties of tribofilms using Cu nanoparticles as additives. Surf. Coat. Technol. 203, 28–34 (2008)
Qui, S.Q., Dong, J.X., Cheng, G.X.: A review of ultrafine particles as antiwear additives and friction modifiers in lubricating oils. Lubr. Sci. 11–3, 217–226 (1999)
Vilt, S.G., Martin, N., McCabe, C., Jennings, G.K.: Frictional performance of silica microspheres. Tribol. Int. 44, 180–186 (2011)
Rapoport, L., Leshchinsky, V., Lvovsky, M., Nepomnyashchy, O., Volovik, Y., Tenne, R.: Mechanism of friction of fullerenes. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 54, 171–176 (2002)
Beerschwinger, U., Reuben, R.L., Yang, S.J.: Frictional study of micromotor bearings. Sens. Actuators, A 63, 229–241 (1997)
Waits, C.M., Geil, B., Ghodssi, R.: Encapsulated ball bearings for rotary micromachines. J. Micromech. Microeng. 17, 224–229 (2007)
Sinha, S.K., Pang, R., Tang, X.S.: Application of micro-ball bearing on Si for high rolling life-cycle. Tribol. Int. 43, 178–187 (2010)
Alazemi, A.A., Etacheri, V., Dysart, A.D., Stacke, L.E., Pol, V.G., Sadeghi, F.: Ultrasmooth submicrometer carbon spheres as lubricant additives for friction and wear reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 5514–5521 (2015)
Sevilla, M., Fuertes, A.B.: Chemical and structural properties of carbonaceous products obtained by hydrothermal carbonization of saccharides. Chem. Eur. J. 15, 4195–4203 (2009)
Shin, Y., Wang, L.Q., Bae, I.T., Arey, B.W., Exarhos, G.J.: Hydrothermal syntheses of colloidal carbon spheres from cyclodextrins. J. Phys. Chem. C 12, 14236–14239 (2008)
Cheng, G.G., Jiang, S.Y., Khosla, T., Pesika, N.S., Ding, J.N., Zhang, Y.H., et al.: Synthesis of hard carbon iron microspheres and their aqueous based tribological performance under magnetic field. Tribol. Lett. 64, 48 (2016)
Mistry, K.K., Pol, V.G., Thackeray, M.M., Wen, J.G., Miller, D.J., Erdemir, A.: Synthesis and tribology of micro-carbon sphere additives for enhanced lubrication. Tribol. Trans. 58, 474–480 (2015)
Baptista, Frederico R., Belhout, S.A., Giordani, S., Quinn, S.J.: Recent developments in carbon nanomaterial sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 4433–4453 (2015)
Sun, X., Li, Y.: Colloidal carbon spheres and their core/shell structures with noble-metal nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 597–601 (2004)
Banyay, M., Sarkar, M., Gräslund, A.: A library of IR bands of nucleic acids in solution. Biophys. Chem. 104, 477–488 (2003)
Li, M., Li, W., Liu, S.: Hydrothermal synthesis, characterization, and KOH activation of carbon spheres from glucose. Carbohyd. Res. 346, 999–1004 (2011)
Cai, S.B., Bhushan, B.: Meniscus and viscous forces during separation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces with liquid-mediated contacts. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 61, 78–106 (2008)
Rymuza, Z., Pytko, S.: The effect of scale in tribological testing. J Mater. Res. Technol. 1, 13–20 (2012)
Dennis, J.S., Jin, K., John, V.T., Pesika, N.S.: Carbon microspheres as ball bearings in aqueous-based lubrication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 3, 2215–2218 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grand No. 51675236), Training Program of the Major Research Plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grand No. 91648109), the Tribology Science Fund of State Key Laboratory of Tribology (SKLTKF14A01) and the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (2016M600366).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, G., Dong, L., Kamboj, L. et al. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Monodisperse Hard Carbon Spheres and Their Water-Based Lubrication. Tribol Lett 65, 141 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-017-0923-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-017-0923-8