Abstract
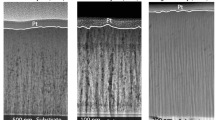
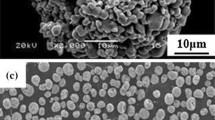
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) coatings have been prepared via nitrogen (N2) spray deposition, a process which deliberately impinges particulates of MoS2 onto a substrate yielding a preferential basally oriented state. Adherent and highly oriented 100- to 300-nm-thick coatings were produced. These coatings exhibited lower initial friction coefficients than sputtered films in dry and humid environments. Such reductions likely stem from a higher degree of basal plane orientation throughout the film as confirmed by XRD. Initial friction in humid air for sprayed coatings (µ = 0.10) was half that of sputtered coatings (µ = 0.21), showing the ability of oriented surface films to produce a low shear strength interface. Aging of these coatings in a humid nitrogen environment also showed the propensity for the films to resist poisoning of their structure which could otherwise result in degraded tribological performance. These results also support the hypothesis that water vapor does not contribute to the oxidation of MoS2.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleischauer, P.D.: Effects of crystallite orientation on environmental stability and lubrication properties of sputtered MoS2 thin films. ASLE Trans. 27, 82–88 (1984)
Lince, J.R., Fleischauer, P.D.: Crystallinity of rf-sputtered MoS2 films. J. Mater. Res. 2, 827–838 (1987)
Holinski, R., Gänsheimer, J.: A study of the lubricating mechanism of molybdenum disulfide. Wear 19, 329–342 (1972)
Singer, I.L., Washington, D.C.: Solid lubricating films for extreme environments. MRS Proc. 140, 215–226 (1988)
Johnston, R.R.M., Moore, A.J.W.: The burnishing of molybdenum disulphide on to metal surfaces. Wear 7, 498–512 (1964)
Salomon, G., De Gee, A.W.J., Zaat, J.H.: Mechano-chemical factors in MoS2-film lubrication. Wear 7, 87–101 (1964)
Winer, W.O.: Molybdenum disulfide as a lubricant: a review of the fundamental knowledge. Wear 10, 422–452 (1967)
Make, D.D., Gao, C., Bredell, L., Kuhhnann-wilsdorf, D.: Micromechanics of MoS2 lubrication. Wear 164, 480–491 (1993)
Rapoport, L., Moshkovich, A., Perfilyev, V., Lapsker, I., Halperin, G., Itovich, Y., Etsion, I.: Friction and wear of MoS2 films on laser textured steel surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 202, 3332–3340 (2008)
Hilton, M.R., Bauer, R., Fleischauer, P.D.: Tribological performance and deformation of sputter-deposited MoS2 solid lubricant films during sliding wear and indentation contact. Thin Solid Films 188, 219–236 (1990)
Spalvins, T.: Structure of sputtered molybdenum disulfide films at various substrate temperatures. ASLE Trans. 17, 1–7 (1974)
Panitz, J., Pope, L.E., Hills, C.R., Lyons, J.E., Staley, D.J.: A statistical study of the combined effects of substrate temperature, bias, annealing and a Cr3Si2 undercoating on the tribological properties of rf sputtered MoS2 coatings. Thin Solid Films 154, 323–332 (1987)
Panitz, J.K.G., Pope, L.E., Lyons, J.E., Staley, D.J.: The tribological properties of MoS2 coatings in vacuum, low relative humidity, and high relative humidity environments. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 6, 1166–1170 (1988)
Bertrand, P.A.: Orientation of rf-sputter-deposited MoS2 films. J. Mater. Res. 4, 180–184 (1989)
Muratore, C., Voevodin, A.A.: Control of molybdenum disulfide basal plane orientation during coating growth in pulsed magnetron sputtering discharges. Thin Solid Films 517, 5605–5610 (2009)
Vierneusel, B., Schneider, T., Tremmel, S., Wartzack, S., Gradt, T.: Humidity resistant MoS2 coatings deposited by unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 235, 97–107 (2013)
Moser, J., Liao, H., Levy, F.: Texture characterisation of sputtered MoS2 thin films by cross-sectional TEM analysis. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 23, 624–626 (1990)
Scharf, T.W., Kotula, P.G., Prasad, S.V.: Friction and wear mechanisms in MoS2/Sb2O3/Au nanocomposite coatings. Acta Mater. 58, 4100–4109 (2010)
Hilton, M.R., Bauer, R., Didziulis, S.V., Dugger, M.T., Keem, J.M., Scholhamer, J.: Structural and tribological studies of MoS2 solid lubricant films having tailored metal-multilayer nanostructures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 53, 13–23 (1992)
Niederhauser, P., Hintermann, H.E., Maillat, M.: Moisture-resistant MoS2-based composite lubricant films. Thin Solid Films 108, 209–218 (1983)
Zabinski, J.S., Donley, M.S., Walck, S.D., Schneider, T.R., Mcdevitt, N.T.: The effects of dopants on the chemistry and tribology of sputter-deposited MoS2 films. Tribol. Trans. 38, 894–904 (1995)
Martin, J.M., Donnet, C., Le Mogne, T., Epicier, T.: Superlubricity of molybdenum disulphide. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 48, 10583–10586 (1993)
Fleischauer, P.D., Hilton, M.R.: Applications of space tribology in the USA. Tribol. Int. 23, 135–139 (1990)
Khare, H.S., Burris, D.L.: The effects of environmental water and oxygen on the temperature-dependent friction of sputtered molybdenum disulfide. Tribol. Lett. 52, 485–493 (2013)
Khare, H.S., Burris, D.L.: Surface and subsurface contributions of oxidation and moisture to room temperature friction of molybdenum disulfide. Tribol. Lett. 53, 329–336 (2014)
Dudder, G.J., Zhao, X., Krick, B., Sawyer, W.G., Perry, S.S.: Environmental effects on the tribology and microstructure of MoS2–Sb2O3–C films. Tribol. Lett. 42, 203–213 (2011)
Ross, S., Sussman, A.: Surface oxidation of molybdenum disulfide. J. Phys. Chem. 59, 889–892 (1955)
Johnston, R.M., Moore, A.J.W.: Water adsorption on molybdenum disulfide containing surface contaminants. J. Phys. Chem. 68, 3399–3406 (1964)
Haltner, A.J., Oliver, C.S.: Effect of water vapor on friction of molybdenum disulfide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 5, 348–355 (1966)
Pritchard, C., Midgley, J.W.: The effect of humidity on the friction and life of unbonded molybdenum disulphide films. Wear 13, 39–50 (1969)
Zhao, X., Perry, S.S.: The role of water in modifying friction within MoS2 sliding interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2, 1444–1448 (2010)
Uemura, M., Saito, K., Nakao, K.: A mechanism of vapor effect on friction coefficient of molybdenum disulfide. Tribol. Trans. 33, 551–556 (1990)
Hilton, M.R., Fleischauer, P.D.: Structural studies of sputter-deposited MoS2 solid lubricant films. MRS Proc. 140, 227–238 (1988)
Fleischauer, P.D., Bauer, R.: The influence of surface chemistry on MoS2 transfer film formation. ASLE Trans. 30, 160–166 (1987)
Aouadi, S.M., Paudel, Y., Luster, B., Stadler, S., Kohli, P., Muratore, C., Hager, C., Voevodin, A.A.: Adaptive Mo2N/MoS2/Ag tribological nanocomposite coatings for aerospace applications. Tribol. Lett. 29, 95–103 (2007)
Baker, C.C., Chromik, R.R., Wahl, K.J., Hu, J.J., Voevodin, A.A.: Preparation of chameleon coatings for space and ambient environments. Thin Solid Films 515, 6737–6743 (2007)
Voevodin, A.A., Zabinski, J.S.: Nanocomposite and nanostructured tribological materials for space applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 65, 741–748 (2005)
Zabinski, J.S., Bultman, J.E., Sanders, J.H., Hu, J.J.: Multi-environmental lubrication performance and lubrication mechanism of MoS2/Sb2O3/C composite films. Tribol. Lett. 23, 155–163 (2006)
Prasad, S.V., McDevitt, N.T., Zabinski, J.S.: Tribology of tungsten disulfide–nanocrystalline zinc oxide adaptive lubricant films from ambient to 500 °C. Wear 237, 186–196 (2000)
Hu, J.J., Bultman, J.E., Zabinski, J.S.: Microstructure and lubrication mechanism of multilayered MoS2/Sb2O3 thin films. Tribol. Lett. 21, 169–174 (2006)
Seitzman, L.E., Singer, I.L., Bolster, R.N., Gossett, C.R.: Effect of a titanium nitride interlayer on the endurance and composition of a molybdenum disulfide coating prepared by ion-beam-assisted deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 51, 232–236 (1992)
Seitzman, L.E., Bolster, R.N., Singer, I.L., Wegand, J.C.: Relationship of endurance to microstructure of IBAD MoS2 coatings. Tribol. Trans. 38, 445–451 (1995)
Stewart, T.B., Fleischauer, P.D.: Chemistry of sputtered molybdenum disulfide films. Inorg. Chem. 21, 2426–2431 (1982)
Fleischauer, P.D.: Fundamental aspects of the electronic structure, materials properties and lubrication performance of sputtered MoS2 films. Thin Solid Films 154, 309–322 (1987)
Krick, B.A., Vail, J.R., Persson, B.N.J., Sawyer, W.G.: Optical in situ micro tribometer for analysis of real contact area for contact mechanics, adhesion, and sliding experiments. Tribol. Lett. 45, 185–194 (2011)
Colbert, R.S., Krick, B.A., Dunn, A.C., Vail, J.R., Argibay, N., Sawyer, W.G.: Uncertainty in pin-on-disk wear volume measurements using surface scanning techniques. Tribol. Lett. 42, 129–131 (2011)
Schmitz, T.L., Action, J.E., Burris, D.L., Ziegert, J.C., Sawyer, W.G.: Wear-rate uncertainty analysis. J. Tribol. 126, 802 (2004)
Burris, D.L., Sawyer, W.G.: Addressing practical challenges of low friction coefficient measurements. Tribol. Lett. 35, 17–23 (2009)
Stoyanov, P., Chromik, R.R., Goldbaum, D., Lince, J.R., Zhang, X.: Microtribological performance of Au–MoS2 and Ti–MoS2 coatings with varying contact pressure. Tribol. Lett. 40, 199–211 (2010)
Singer, I.L., Bolster, R.N., Wegand, J., Fayeulle, S., Stupp, B.C.: Hertzian stress contribution to low friction behavior of thin MoS2 coatings. Appl. Phys. Lett. 57, 995–997 (1990)
Scharf, T.W., Prasad, S.V.: Solid lubricants: a review. J. Mater. Sci. 48, 511–531 (2013)
Archard, J.F., Hirst, W.: The wear of metals under unlubricated conditions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 236, 397–410 (1956)
De Gee, A.W.J., Salomon, G., Zaat, J.H., Gee, D.A.W.J., Salomon, G., Zaat, J.H.: On the Mechanisms of MoS2-film failure in sliding friction. ASLE Trans. 8, 156–163 (1965)
Ripoll, M.R., Simič, R., Brenner, J., Podgornik, B.: Friction and lifetime of laser surface-textured and MoS2-coated Ti6Al4V under dry reciprocating sliding. Tribol. Lett. 51, 261–271 (2013)
Gardos, M.N.: The synergistic effects of graphite on the friction and wear of MoS2 films in air. Tribol. Trans. 31, 214–227 (1988)
Spalvins, T.: Morphological and frictional behavior of sputtered MoS2 films. Thin Solid Films 96, 17–24 (1982)
Spalvins, T.: Lubrication with sputtered MoS2 films: principles, operation, and limitations. JMEP 1, 347–351 (1991)
Fleischauer, P.D., Bauer, R.: Chemical and structural effects on the lubrication properties of sputtered MoS2 films. Tribol. Trans. 31, 239–250 (1988)
Cizaire, L., Vacher, B., Le Mogne, T., Martin, J.M., Rapoport, L., Margolin, A., Tenne, R.: Mechanisms of ultra-low friction by hollow inorganic fullerene-like MoS2 nanoparticles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 160, 282–287 (2002)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Sandia National Laboratories staff members Paul Kotula for acquisition of TEM images, Michael Rye for FIB sample preparation, and Bonnie McKenzie for SEM and EDS microscopy. We thank Lehigh University Tribology Lab members Mark Sidebottom and Guosong Zeng for discussions and help in setting up instrumentation. Sandia National Laboratories is a multi-mission laboratory managed and operated by Sandia Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Lockheed Martin Corporation, for the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration under contract DE-AC04-94AL85000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curry, J.F., Argibay, N., Babuska, T. et al. Highly Oriented MoS2 Coatings: Tribology and Environmental Stability. Tribol Lett 64, 11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0745-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0745-0