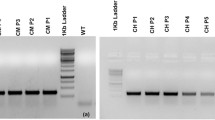
Abstract
An attractive objective in tree breeding is to reduce the content of lignin or alter its composition, in order to facilitate delignification in pulping. This has been achieved in transgenic angiosperm tree species. In this study we show for the first time that changes in lignin content and composition can be achieved in a conifer by taking a transgenic approach. Lignin content and composition have been altered in five-year-old transgenic plants of Norway spruce (Picea abies [L.] Karst) expressing the Norway spruce gene encoding cinnamoyl CoA reductase (CCR) in antisense orientation. The asCCR plants had a normal phenotype but smaller stem widths compared to the transformed control plants. The transcript abundance of the sense CCR gene was reduced up to 35% relative to the transformed control. The corresponding reduction in lignin content was up to 8%, which is at the lower limit of the 90–99% confidence intervals reported for natural variation. The contribution of H-lignin to the non-condensed fraction of lignin, as judged by thioacidolysis, was reduced up to 34%. The H-lignin content was strongly correlated with the total lignin content. Furthermore, the kappa number of small-scale Kraft pulps from one of the most down-regulated lines was reduced 3.5%. The transcript abundances of the various lignin biosynthetic genes were down-regulated indicating co-regulation of the biosynthetic pathway.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anterola AM, Jeon J-H, Davin LB, Lewis NG (2002) Transcriptional control of monolignol biosynthesis in Pinus taeda. J Biol Chem 277:18272–18280
Anterola AM, Lewis NG (2002) Trends in lignin modification: a comprehensive analysis of the effects of genetic manipulations/mutations on lignification and vascular integrity. Phytochemistry 61:221–294
Baucher M, Halpin C, Petit-Conil M, Boerjan W (2003) Lignin: genetic engineering and impact on pulping. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 38:305–350
Bigras FJ, Ryyppö A, Lindström A, Stattin E (2001) Cold acclimation and deacclimation of shoots and roots of conifer seedlings. In: Bigras FJ, Colombo SJ (eds) Conifer cold hardiness. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 57–88
Boerjan W, Ralph J, Baucher M (2003) Lignin biosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:519–546
Brukhin V, Clapham D, Elfstrand M, von Arnold S (2000) Basta tolerance as a selectable and screening marker for transgenic plants of Norway spruce. Plant Cell Rep 19:899–903
Chabannes M, Barakate A, Lapierre C, Marita JM, Ralph J, Pean M, Danoun S, Halpin C, Grima-Pettenati J, Boudet AM (2001) Strong decrease in lignin content without significant alteration of plant development is induced by simultaneous down-regulation of cinnamoyl CoA reductase (CCR) and cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD) in tobacco plants. Plant J 28:257–270
Chang S, Ouryear J, Cairney J (1993) A simple and efficient method for isolating RNA from pine trees. Plant Mol Biol Rep 11:113–116
Clapham DH, Demel P, Elfstrand M, Koop H-U, Sabala I, von Arnold S (2000) Gene transfer by particle bombardment to embryogenic cultures and of Picea abies and the production of transgenic plantlets. Scand J For Res 15:151–160
Christensen AH, Quail PH (1996) Ubiquitin promoter-based vectors for high-level expression of selectable and/or screenable marker genes in monocotyledonous plants. Transgen Res 5:213–218
Dence CW (1992) The determination of lignin. In: Lin SY, Dence CW (eds) Methods in lignin chemistry. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 33–61
Dimmel DR, MacKay JJ, Althen EM, Parks C, Sederoff RR (2001) Pulping and bleaching of CAD-deficient wood. J Wood Chem Technol 21:1–17
Elfstrand M, Fossdal CG, Sitbon F, Olsson O, Lönneborg A, von Arnold S (2001) Overexpression of the endogenous peroxidase-like gene spi 2 in transgenic Norway spruce plants results in increased total peroxidase activity and reduced growth. Plant Cell Rep 20:596–603
Gentle A, Anastasopoulos F, McBrien NA (2001) High-resolution semiquantitative real-time PCR without the use of a standard curve. BioTechniques 31:502–508
Gindl W (2002) Comparing mechanical properties of normal and compression wood in Norway spruce: the role of lignin in compression parallel to the grain. Holzforschung 56:395–401
Goujon T, Ferret V, Mila I, Pollet B, Ruel K, Burlat V, Joseleau JP, Barriere Y, Lapierre C, Jouanin L (2003) Down-regulation of the AtCCR1 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana: effects on phenotype lignins and cell wall degradability. Planta 217:218–228
Goujon T, Sibout R, Eudes A, MacKay J, Juanin L (2003) Genes involved in the biosynthesis of lignin precursors in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 41:677–687
Hannrup B, Cahalan C, Chantre G, Grabner M, Karlsson B, Le Bayon I, Jones GL, Müller U, Pereira H, Rodrigues JC, Rosner S, Rozenberg P, Wilhelmsson L, Wimmer R (2004) Genetic parameters of growth and wood quality traits in Picea abies. Scand J For Res 19:14–29
Halpin C (2004) Investigating and manipulating lignin biosynthesis in the postgenomic era. In: Callow JA (ed) Advances in botanical research, vol 41. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 63–106
Hatfield R, Fukushima RS (2005) Can lignin be accurately measured? Crop Sci 45:832–839
Högberg KA, Bozhkov PV, Grönroos R, von Arnold S (2001) Critical factors affecting ex vitro performance of somatic embryo plants of Picea abies. Scand J For Res 16:295–304
Högberg KA, Ekberg I, Norell L, von Arnold S (1998) Integration of somatic embryogenesis in a tree breeding programme: a case study with Picea abies. Can J For Res 28:1536–1545
Humphreys JM, Chapple C (2002) Rewriting the lignin roadmap. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:224–229
Klimaszewska K, Lachance D, Pelletier G, Lelu MA, Seguin A (2001) Regeneration of transgenic Picea glauca, P. mariana and P. abies after cocultivation of embyrogenic tissue with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. In vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 37:748–755
Lacombe E, Hawkins S, Doorsselaere JV, Piquemal J, Goffner D, Poeydomenge O, Boudet AM (1997) Cinnamoyl CoA reductase the first committed enzyme of the lignin branch biosynthetic pathway: cloning expression and phylogenetic relationships. Plant J 11:429–441
Lange BM, Lapierre C, Sandemann H (1995) Elicitor-induced spruce stress lignin. Plant Physiol 108:1277–1287
Li L, Cheng X, Lu S, Nakatsubu T, Umezawa T, Chiang V (2005) Clarification of cinnamoyl co-enzyme A reductase catalysis in monolignol biosynthesis of aspen. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1073–1082
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantification PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lopes MH, Neto CP, Barros AS, Rutledge D, Delgadillo I, Gil AM (2000) Quantitation of aliphatic suberin in Quercus suber L cork by FTIR spectroscopy and solid-state C-13-NMR spectroscopy. Biopolymers 57:344–351
Lüderitz T, Grisebach H (1981) Enzymic synthesis of lignin precursors. Comparison of cinnamoyl-CoA reductase and cinnamyl alcohol: NADP+ dehydrogenase from spruce (Picea abies L.) and soybean (Glycine max L.). Eur J Biochem 119:115–124
O’Connell A, Holt K, Piquemal J, Grima-Pettenati J, Boudet A, Pollet B, Lapierre C, Petit-Conil M, Schuch W, Halpin C (2002) Improved paper pulp from plants with suppressed cinnamoyl-CoA reductase or cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase. Transgenic Res 11:495–503
Peter G, Neale D (2004) Molecular basis for the evolution of xylem lignification. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:737–742
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45
Pinçon G, Chabannes M, Lapierre C, Pollet B, Ruel K, Joseleau JP, Boudet AM, Legrand M (2001) Simultaneous down-regulation of caffeic/5-hydroxy ferulic acid-O-methyltransferase I and cinnamoyl-Coenzyme A reductase in the progeny from a cross between tobacco lines homozygous for each transgene. Consequences for plant development and lignin synthesis. Plant Physiol 126:145–155
Piquemal J, Lapierre C, Myton K, O’Connell A, Schuch W, Grima-Pettenati J, Boudet AM (1998) Down-regulation of cinnamoyl-CoA reductase induces significant changes of lignin profiles in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant J 13:71–83
Preston CM, Forrester PD (2004) Chemical and carbon-13 cross-polarization magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance characterization of logyard fines from British Columbia. J Environ Qual 33:767–777
Raes J, Rohde A, Christensen JH, Van der Peer Y, Boerjan W (2003) Genome-wide characterization of the lignification toolbox in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 133:1051–1071
Ralph J, Hatfield RD, Piquemal J, Yahiaoui N, Pean M, Lapierre C, Boudet AM (1998) NMR characterization of altered lignins extracted from tobacco plants down-regulated for lignification enzymes cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase and cinnamoyl-CoA reductase. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 95:12803–12808
Rogers LA, Campbell MM (2004) The genetic control of lignin deposition during plant growth and development. New Phytol 164:17–30
Saka S, Goring DAI (1985) Localization of lignins in wood cell walls. In: Higuchi T (ed) Biosynthesis and biodegradation of wood components. Academic, Orlando, pp 51–62
Sederoff RR, MacKay JJ, Ralph J, Hatfield RD (1999) Unexpected variation in lignin. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:145–152
Silva JCE, Wellendorf H, Pereira H (1998) Clonal variation in wood quality and growth in young sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis (Bong) Carr): estimation of quantitative genetic parameters and index selection for improved pulpwood. Silvae Genet 47:20–33
Sperisen C, Gugerli F, Büchler U, Mátyás G (2000) Comparison of two rapid DNA extraction protocols for gymnosperms for amplification in population genetic and phylogenetic studies. For Genet 7:133–136
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A and Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:research 00341–003411
Wadenbäck J, Clapham D, Gellerstedt G, von Arnold S (2004) Variation in content and composition of lignin in young wood of Norway spruce. Holzforschung 58:107–115
Wenck AR, Quinn M, Whetten RW, Pullman G, Sederoff R (1999) High-efficiency Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Norway spruce (Picea abies) and loblolly pine (Pinus taeda). Plant Mol Biol 39:407–416
Wu RL, Remington DL, MacKay JJ, McKeand SE, O’Malley DM (1999) Average effect of a mutation in lignin biosynthesis in loblolly pine. Theor Appl Genet 99:705–710
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Hartmut Weichert for his care of the plants, Kristen Aaltonen, Andrea Majtnerová, Chip Frazier and Annika Wåhlström for scientific assistance, and Inger Ekberg, Emma Gabrielsson and Andreas Helmersson for valuable advice. The work was supported by grants from the Swedish Foundation for International Cooperation in Research and Higher Education and from the Swedish Research Council for Environment, Agricultural Sciences and Spatial Planning.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wadenbäck, J., von Arnold, S., Egertsdotter, U. et al. Lignin biosynthesis in transgenic Norway spruce plants harboring an antisense construct for cinnamoyl CoA reductase (CCR). Transgenic Res 17, 379–392 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-007-9113-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-007-9113-z