Abstract
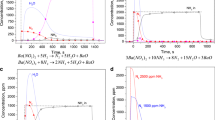
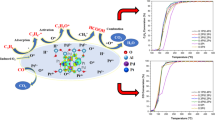
The overall NSR operation was tested over a bimetallic Pt/Rh–BaO lean NO x trap (LNT) catalyst in the range of 473–673 K with simulated diesel exhausts and compared to monometallic 1 wt% Pt/BaO/γ-Al2O3 and 0.5 wt% Rh/BaO/γ-Al2O3 samples. The results showed the beneficial effect of the simultaneous presence of 0.5 wt% Pt and 0.25 wt% Rh on the catalytic performance under lean-burn conditions at low temperatures. It was observed that both Pt/BaO/γ-Al2O3 and Rh/BaO/γ-Al2O3, which both were mildly aged, have limited NO x reduction capacity at 473 K. However, combining Pt and Rh in the NO x storage catalyst assisted the NO x reduction process to occur at lower temperatures (473 K). One possible reason could be that the combined Pt and Rh sample was more resistant to aging. In addition, the NO2-TPD data showed that the presence of Rh into the Pt/BaO/γ-Al2O3 system has a considerable effect on the spill-over process of NO x , accelerating the release of NO x at lower temperatures. These results were in a good agreement with the observed higher rate of oxygen release of the bimetallic Pt/Rh catalyst, leaving a significant number of noble metal sites available for adsorption at lower temperatures than that of the monometallic Pt sample. The superior NSR performance of the bimetallic Pt/Rh/BaO/γ-Al2O3 catalyst under lean-burn conditions suggested the existence of synergetic promotion effect between the Pt and Rh components, increasing the NO x reduction efficiency in comparison with that of the monometallic Pt and Rh–BaO LNT catalysts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matsumoto SI (2000) CATTECH 4:102–109
Epling WS, Campbell LE, Yezerets A, Currier NW, Parks JE (2004) Catal Rev 46:163–245
Roy S, Baiker A (2009) Chem Rev 109:4054–4091
Olsson L, Fridell E (2002) J Catal 210:340–353
Forzatti P, Lietti L, Gabrielli N (2010) Appl Catal B 99:145–155
Breen JP, Burch R, Fontaine-Gautrelet C, Hardacre C, Rioche C (2008) Appl Catal B 81:150–159
Breen JP, Rioche C, Burch R, Hardacre C, Meunier FC (2007) Appl Catal B 72:178–186
Abdulhamid H, Fridell E, Skoglundh M (2006) Appl Catal B 62:319–328
Amberntsson A, Fridell E, Skoglundh M (2003) Appl Catal B 46:429–439
Büchel R, Pratsinis SE, Baiker A (2012) Appl Catal B 113–114:160–171
Andonova S, Marchionni V, Borelli M, Nedyalkova R, Lietti L, Olsson L (2013) Appl Catal B 132–133:266–281
Lindholm A, Currier NW, Li J, Yezerets A, Olsson L (2008) J Catal 258:273–288
Burch R, Daniells ST, Breen JP, Hu P (2004) J Catal 224:252–260
Tanaka S-i, Yuzaki K, Ito S-i, Uetsuka H, Kameoka S, Kunimori K (2000) Catal Today 63:413–418
Olsson L, Persson H, Fridell E, Skoglundh M, Andersson B (2001) J Phys Chem B 105:6895–6906
Scotti A, Nova I, Tronconi E, Castoldi L, Lietti L, Forzatti P (2004) Ind Eng Chem Res 43:4522–4534
Acknowledgments
This study has been performed at the Competence Centre for Catalysis in collaboration with Politecnico di Milano. KCK is financially supported by Chalmers University of Technology, the Swedish Energy Agency and the member companies: AB Volvo, Volvo Car Corporation, Scania CV AB, SAAB Powertrain, Haldor Topsoe A/S and The Swedish Space Corporation. We would like to acknowledge the Swedish Energy Agency, Swedish Science Council, Swedish foundation for strategic research (F06-0006) and Chalmers Initiative Transport, for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andonova, S., Marchionni, V., Lietti, L. et al. Enhanced Low Temperature NO x Reduction Performance Over Bimetallic Pt/Rh–BaO Lean NO x Trap Catalysts. Top Catal 56, 68–74 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-013-9931-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-013-9931-6