Abstract
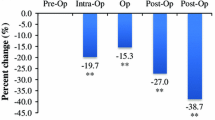
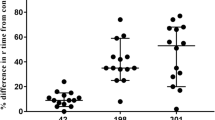
Factor Xa inhibitors (FXaI) apixaban and rivaroxaban are used for thromboprophylaxis after major elective orthopaedic surgery. Because few patient sample studies exist, we postoperatively assessed patients undergoing unilateral total hip arthroplasty, including 22 treated with apixaban (2.5 mg BID) and 20 treated with rivaroxaban (10 mg OD). We collected blood samples before and 3 h after drug intake at 4 time points, preoperatively, as well as on day 1, week 1 (day 2–8) and day 28 post-operation. APTT and PT were immediately analysed. Calibrated anti-FXa activity, Russel’s Viper Venom Time (RVVT) and thrombin generation (TG; Calibrated Automated Thrombogram®) captured the effects of FXaI on coagulation and TG. APTT and PT remained within the reference interval throughout, and did not correlate with FXaI levels (PT R2 = 0.44, APTT R2 = 0.07). Mean apixaban concentration at the peak varied by eightfold (19–153 ng/mL), but rivaroxaban only by 1.5-fold (111–183 ng/mL). Rivaroxaban, but not apixaban prolonged RVVT at peak levels. Both FXaIs had a prolonged lag time of TG (p < 0.001). Rivaroxaban decreased ETP peak at all time points and reached a minimum at day 28 (540 nM/min at rivaroxaban 184 ng/mL, p < 0.001), while rivaroxaban trough levels were low and ETP values normal. However, with apixaban, after an initial decrease, ETP did not differ between peak and trough levels until decreasing on day 28 at peak (990 nM/min at apixaban 112 ng/mL, p = 0.005). In conclusion, due to different dosing and pharmacology rivaroxaban and apixaban distinctly inhibited TG under postoperative conditions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eriksson BI, Borris LC, Friedman RJ, Haas S, Huisman MV, Kakkar AK, Bandel TJ, Beckmann H, Muehlhofer E, Misselwitz F, Geerts W, RECORD1 Study Group (2008) Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip arthroplasty. N Engl J Med 358:2765–2775. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0800374
Lassen MR, Gallus A, Raskob GE, Pineo G, Chen D, Ramirez LM, ADVANCE-3 Investigators (2010) Apixaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip replacement. N Engl J Med 363:2487–2498. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1006885
Salmela B, Joutsi-Korhonen L, Armstrong E, Lassila R (2012) Active online assessment of patients using new oral anticoagulants: bleeding risk, compliance, and coagulation analysis. Semin Thromb Hemost 38:23–30. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1300948
Cuker A (2016) Laboratory measurement of the non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants: selecting the optimal assay based on drug, assay availability, and clinical indication. J Thromb Thrombolysis 41:241–247. doi:10.1007/s11239-015-1282-7
Siegal DM, Curnutte JT, Connolly SJ, Lu G, Conley PB, Wiens BL, Mathur VS, Castillo J, Bronson MD, Leeds JM, Mar FA, Gold A, Crowther MA (2015) Andexanet Alfa for the reversal of factor Xa inhibitor activity. N Engl J Med 373:2413–2424. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1510991
Hillarp A, Baghaei F, Fagerberg Blixter I, Gustafsson KM, Stigendal L, Sten-Linder M, Strandberg K, Lindahl TL (2011) Effects of the oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban on commonly used coagulation assays. J Thromb Haemost 9:133–139. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04098.x
Douxfils J, Chatelain C, Chatelain B, Dogne JM, Mullier F (2013) Impact of apixaban on routine and specific coagulation assays: a practical laboratory guide. Thromb Haemost 110:283–294. doi:10.1160/TH12-12-0898
Helin TA, Pakkanen A, Lassila R, Joutsi-Korhonen L (2013) Laboratory assessment of novel oral anticoagulants: method suitability and variability between coagulation laboratories. Clin Chem 59:807–814. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2012.198788
Hillarp A, Gustafsson KM, Faxalv L, Strandberg K, Baghaei F, Fagerberg Blixter I, Berndtsson M, Lindahl TL (2014) Effects of the oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor apixaban on routine coagulation assays and anti-FXa assays. J Thromb Haemost 12:1545–1553. doi:10.1111/jth.12649
Triplett DA (2000) Use of the dilute Russell viper venom time (dRVVT): its importance and pitfalls. J Autoimmun 15:173–178. doi:10.1006/jaut.2000.0414
Favaloro EJ, Lippi G, Koutts J (2011) Laboratory testing of anticoagulants: the present and the future. Pathology 43:682–692. doi:10.1097/PAT.0b013e32834bf5f4
Tripodi A, Padovan L, Veena C, Scalambrino E, Testa S, Peyvandi F (2015) How the direct oral anticoagulant apixaban affects thrombin generation parameters. Thromb Res 135:1186–1190. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2015.03.032
Wan H, Yang Y, Zhu J, Wu S, Zhou Z, Huang B, Wang J, Shao X, Zhang H (2016) An in-vitro evaluation of direct thrombin inhibitor and factor Xa inhibitor on tissue factor-induced thrombin generation and platelet aggregation: a comparison of dabigatran and rivaroxaban. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. doi:10.1097/MBC.0000000000000509
Martin-Fernandez L, Ziyatdinov A, Carrasco M, Millon JA, Martinez-Perez A, Vilalta N, Brunel H, Font M, Hamsten A, Souto JC, Soria JM (2016) Genetic determinants of thrombin generation and their relation to venous thrombosis: results from the GAIT-2 Project. PLoS ONE 11:e0146922. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0146922
Lutsey PL, Folsom AR, Heckbert SR, Cushman M (2009) Peak thrombin generation and subsequent venous thromboembolism: the Longitudinal Investigation of Thromboembolism Etiology (LITE) study. J Thromb Haemost 7:1639–1648. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03561.x
Ay C, Dunkler D, Simanek R, Thaler J, Koder S, Marosi C, Zielinski C, Pabinger I (2011) Prediction of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer by measuring thrombin generation: results from the Vienna Cancer and Thrombosis Study. J Clin Oncol 29:2099–2103. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.32.8294
EMA. Eliquis Summary of Product Characteristics. EMEA/H/C/002148-R/0034 2011
EMA. Xarelto Summary of Product Characteristics. EMEA/H/C/000944-IB/0040/G 2009
Freyburger G, Macouillard G, Khennoufa K, Labrouche S, Molimard M, Sztark F (2015) Rivaroxaban and apixaban in orthopaedics: is there a difference in their plasma concentrations and anticoagulant effects? Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 26:925–933. doi:10.1097/MBC.0000000000000371
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Verzeroli C, Giaccherini C, Masci G, Santoro A, De Braud F, Celio L, Labianca R, Mandalà M, Merelli B, Tondini C, Gasparini G, Sarmiento R, Tartari C, Piras F, Gamba S, Rio F, Milesi V, Tessarolo S, Vignoli A, Russo L (2015) Measurement of thrombin generation is a positive predictive biomarker of v enous thromboembolism (VTE) in metastatic cancer patients enrolled in the Hypercan Study. Blood 126:654
Virtanen L, Salmela B, Leinonen J, Lemponen M, Huhtala J, Joutsi-Korhonen L, Lassila R (2014) Laboratory-monitored fondaparinux and coagulation activity in association with total hip replacement. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 25:597–603. doi:10.1097/MBC.0000000000000116
Mjaaland KE, Kivle K, Svenningsen S, Pripp AH, Nordsletten L (2015) Comparison of markers for muscle damage, inflammation, and pain using minimally invasive direct anterior versus direct lateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. J Orthop Res 33:1305–1310. doi:10.1002/jor.22911
Mueck W, Schwers S, Stampfuss J (2013) Rivaroxaban and other novel oral anticoagulants: pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects, specific patient populations and relevance of coagulation monitoring. Thromb J 11:10-9560-11-10. doi:10.1186/1477-9560-11-10
Thordardottir S, Vikingsdottir T, Bjarnadottir H, Jonsson H Jr, Gudbjornsson B (2016) Activation of complement following total hip replacement. Scand J Immunol. doi:10.1111/sji.12411
Hankey GJ, Stevens SR, Piccini JP, Lokhnygina Y, Mahaffey KW, Halperin JL, Patel MR, Breithardt G, Singer DE, Becker RC, Berkowitz SD, Paolini JF, Nessel CC, Hacke W, Fox KA, Califf RM, ROCKET AF Steering Committee and Investigators (2014) Intracranial hemorrhage among patients with atrial fibrillation anticoagulated with warfarin or rivaroxaban: the rivaroxaban once daily, oral, direct factor Xa inhibition compared with vitamin K antagonism for prevention of stroke and embolism trial in atrial fibrillation. Stroke 45:1304–1312. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.004506
Bytniewski P, Machala W, Romanowski L, Wisniewski W, Kosowski K (2014) The dynamics of D-dimer level fluctuation in patients after the cemented and cementless total hip and total knee replacement. J Orthop Surg Res 9:89-014-0089-0. doi:10.1186/s13018-014-0089-0
Dahl OE, Harenberg J, Wexels F, Preissner KT (2015) Arterial and venous thrombosis following trauma and major orthopedic surgery: molecular mechanisms and strategies for intervention. Semin Thromb Hemost 41:141–145. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1544230
Warwick D, Rosencher N (2010) The ‘‘critical thrombosis period’’ in major orthopedic surgery: when to start and when to stop prophylaxis. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 16:394–405. doi:10.1177/1076029609355151
Hemker HC, Al Dieri R, De Smedt E, Beguin S (2006) Thrombin generation, a function test of the haemostatic-thrombotic system. Thromb Haemost 96:553–561
Ratzinger F, Lang M, Belik S, Jilma-Stohlawetz P, Schmetterer KG, Haslacher H, Perkmann T, Quehenberger P (2016) Lupus-anticoagulant testing at NOAC trough levels. Thromb Haemost 116:235–240. doi:10.1160/TH16-02-0081
Helin TA, Pakkanen A, Lassila R, Joutsi-Korhonen L (2016) Effects of apixaban on prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time and anti-Xa assays: a European survey. Clin Chem Lab Med. doi:10.1515/cclm-2016-0742
Al Dieri R, Bloemen S, Kelchtermans H, Wagenvoord R, Hemker HC (2013) A new regulatory function of activated factor V: inhibition of the activation by tissue factor/factor VII(a) of factor X. J Thromb Haemost 11:503–511. doi:10.1111/jth.12126
Long AT, Kenne E, Jung R, Fuchs TA, Renne T (2016) Contact system revisited: an interface between inflammation, coagulation, and innate immunity. J Thromb Haemost 14:427–437. doi:10.1111/jth.13235
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the Helsingin ja Uudenmaan Sairaanhoitopiiri (Grant No. TYH 2015312). The authors sincerely acknowledge the contributions of Jaana Leiviskä, PhD, and Jari Leinonen, PhD, for implementing the rivaroxaban and apixaban calibrated anti-Xa assays, and laboratory technician Marja Lemponen is acknowledged for performing the coagulation analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration as well as its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helin, T.A., Virtanen, L., Manninen, M. et al. Effects of thromboprophylactic doses of apixaban and rivaroxaban on coagulation and thrombin generation in association with total hip replacement. J Thromb Thrombolysis 43, 562–569 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-017-1492-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-017-1492-2