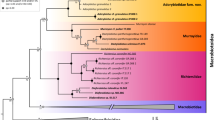
Abstract
Previous phylogenetic analyses of the Acanthocephala have demonstrated that the families Rhadinorhynchidae Lühe, 1912 and Transvenidae Pichelin & Cribb, 2001 are sister clades. However, a recent study found that the Rhadinorhynchidae is paraphyletic, due to the basal position of Rhadinorhynchus biformis Smales, 2014 relative to the Rhadinorhynchidae + Transvenidae. We reassess these relationships with new single-gene and concatenated phylogenetic analyses utilising cox1 mtDNA, 18S rDNA and 28S rDNA, including recently available sequences. Although topologies differed among single-gene analyses, the overall results support R. biformis as representative of a lineage distinct from those of the Rhadinorhynchidae and Transvenidae. Examination of additional specimens of R. biformis allowed us to identify morphological characters that further support this hypothesis. These results lead us to propose transfer of R. biformis to a new genus (Spinulacorpus n. g.) and family (Spinulacorpidae n. fam.) to resolve the paraphyly of the Rhadinorhynchidae.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdou, N. E., & Mahfouz, M. E. (2006). Ultrastructural and genetic diversity studies of two Sclerocollum (Acanthocephala) species infecting siganid and lutianid fishes from the Red Sea, Egypt. Journal of the Egyptian Society of Parasitology, 36, 1035–1056.
Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W., & Lipman, D. J. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology, 215, 403–410.
Amin, O. M., Heckmann, R. A., Dallarés, S., Constenla, M., & Ha, N. V. (2019). Morphological and molecular description of Rhadinorhynchus laterospinosus Amin, Heckmann & Ha, 2011 (Acanthocephala, Rhadinorhynchidae) from marine fish off the Pacific coast of Vietnam. Parasite, 26, 1–14.
Amin, O. M., Heckmann, R. A., Dallarés, S., Constenla, M., & Ha, N. V. (2020). Morphological and molecular description of Rhadinorhynchus hiansi Soota and Bhattacharya, 1981 (Acanthocephala: Rhadinorhynchidae) from marine fish off the Pacific Coast of Vietnam. Journal of Parasitology, 106, 56–70.
Bao, M., Roura, A., Mota, M., Nachón, D., Antunes, C., Cobo, F., et al. (2015). Macroparasites of allis shad (Alosa alosa) and twaite shad (Alosa fallax) of the Western Iberian Peninsula Rivers: ecological, phylogenetic and zoonotic insights. Parasitology Research, 114, 3721–3739.
Betancur-R, R., Li, C., Munroe, T. A., Ballesteros, J. A., & Ortí, G. (2013). Addressing gene tree discordance and non-stationarity to resolve a multi-locus phylogeny of the flatfishes (Teleostei: Pleuronectiformes). Systematic Biology, 62, 763–785.
Braicovich, P. E., Lanfranchi, A. L., Farber, M. D., Marvaldi, A., Luque, J. L., & Timi, J. T. (2014). Genetic and morphological evidence reveals the existence of a new family, genus and species of Echinorhynchida (Acanthocephala). Folia Parasitologica, 61, 377–384.
Chaudhary, A., Amin, O. M., Heckmann, R., & Singh, H. S. (2020). The molecular phylogeny of Pararhadinorhynchus magnus Ha, Amin, Ngo, Heckmann, 2018 (Acanthocephala: Rhadinorhynchidae) from Scatophagus argus (Linn.) (Scatophagidae) in Vietnam. Acta Parasitologica (in press https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-020-00191-5).
Collins, T. M., Fedrigo, O., & Naylor, G. J. (2005). Choosing the best genes for the job: The case for stationary genes in genome-scale phylogenetics. Systematic Biology, 54, 493–500.
Edgar, R. C. (2004). MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research, 32, 1792–1797.
Edmonds, S. J. (1973). Australian Acanthocephala No. 14. On two species of Pararhadinorhynchus, one new. Transactions of the Royal Society of Australia, 97, 19–21.
García-Varela, M., Cummings, M. P., Pérez-Ponce de León, G., Gardner, S. L., & Laclette, J. P. (2002). Phylogenetic analysis based on 18S ribosomal RNA gene sequences supports the existence of class Polyacanthocephala (Acanthocephala). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 23, 288–292.
García-Varela, M., & Nadler, S. A. (2005). Phylogenetic relationships of Palaeacanthocephala (Acanthocephala) inferred from SSU and LSU rDNA gene sequences. Journal of Parasitology, 91, 1401–1409.
García-Varela, M., & Nadler, S. A. (2006). Phylogenetic relationships among Syndermata inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial gene sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 40, 61–72.
Gregori, M., Aznar, F. J., Abollo, E., Roura, A., González, A. F., & Pascual, S. (2013). Nyctiphanes couchii as intermediate host for Rhadinorhynchus sp. (Acanthocephala, Echinorhynchidae) from NW Iberian Peninsula waters. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 105, 9–20.
Guindon, S., Dufayard, J.-F., Lefort, V., Anisimova, M., Hordijk, W., & Gascuel, O. (2010). New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Systematic Biology, 59, 307–321.
Gupta, V., & Fatma, S. (1980). On three new species of acanthocephalan parasites of marine fishes of Mandapam, Tamil Nadu. Indian Journal of Helminthology, 31, 45–53.
Ha, N. V., Amin, O. M., Ngo, H. D., & Heckmann, R. A. (2018). Descriptions of acanthocephalans, Cathayacanthus spinitruncatus (Rhadinorhynchidae) male and Pararhadinorhynchus magnus n. sp. (Diplosentidae), from marine fish of Vietnam, with notes on Heterosentis holospinus (Arhythmacanthidae). Parasite, 25, 35.
Huston, D. C., Cribb, T. H., & Smales, L. R. (2020). Molecular characterisation of acanthocephalans from Australian marine teleosts: Proposal of a new family, synonymy of another and transfer of taxa between orders. Systematic Parasitology, 97, 1–23.
ICZN. (2012). International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature: Amendment of articles 8, 9, 10, 21 and 78 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature to expand and refine methods of publication. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature, 69, 161–169.
Johston, T. H., & Edmonds, S. J. (1947). Australian Acanthocephala No. 5. Transactions of the Royal Society of South Australia, 71, 13–19.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., & Tamura, K. (2016). MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 1870–1874.
Lanfear, R., Calcott, B., Ho, S. Y. W., & Guindon, S. (2012). PartitionFinder: Combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 29, 1695–1701.
Lanfear, R., Frandsen, P. B., Wright, A. M., Senfeld, T., & Calcott, B. (2017). PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 772–773.
Li, L., Chen, H.-X., & Yang, Y. (2018). Morphological and molecular study of Neorhadinorhynchus nudus (Harada, 1938) (Acanthocephala: Cavisomidae) from Auxis thazard Lacepede (Perciformes: Scombridae) in the South China Sea. Acta Parasitologica, 63, 479–485.
Li, L., Wayland, M. T., Chen, H.-X., & Yang, Y. (2019). Remarkable morphological variation in the proboscis of Neorhadinorhynchus nudus (Harada, 1938) (Acanthocephala: Echinorhynchida). Parasitology, 146, 348–355.
Lisitsyna, O. I., Kudlai, O., Cribb, T. H., & Smit, N. J. (2019). Three new species of acanthocephalans (Palaeacanthocephala) from marine fishes collected off the East Coast of South Africa. Folia Parasitologica, 66, 012.
Maddison, W. P., & Maddison, D. R. (2019). Mesquite: A modular system for evolutionary analysis. Version 3.31.
Miller, M. A., Pfeiffer, W., & Schwartz, T. (2010). Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In: Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, pp. 1–8.
Near, T. J., Garey, J. R., & Nadler, S. A. (1998). Phylogenetic relationships of the Acanthocephala inferred from 18S ribosomal DNA sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 10, 287–298.
Pichelin, S., & Cribb, T. H. (2001). The status of the Diplosentidae (Acanthocephala: Palaeacanthocephala) and a new family of acanthocephalans from Australian wrasses (Pisces: Labridae). Folia Parasitologica, 48, 289–303.
Pichelin, S., Smales, L. R., & Cribb, T. H. (2016). A review of the genus Sclerocollum Schmidt & Paperna, 1978 (Acanthocephala: Cavisomidae) from rabbitfishes (Siganidae) in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Systematic Parasitology, 93, 101–114.
Rodríguez-Ezpeleta, N., Brinkmann, H., Roure, B., Lartillot, N., Lang, B. F., & Philippe, H. (2007). Detecting and overcoming systematic errors in genome-scale phylogenies. Systematic Biology, 56, 389–399.
Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D. L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., et al. (2012). MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61, 539–542.
Schmidt, G. D., & Paperna, I. (1978). Sclerocollum rubrimaris gen. et sp. n. (Rhadinorhynchidae: Gorgorhynchinae), and other Acanthocephala of marine fishes from Israel. Journal of Parasitology, 64, 846–850.
Sharifdini, M., Amin, O. M., & Heckmann, R. A. (2020). The molecular profile of Paratrajectura longcementglandatus Amin, Heckmann et Ali, 2018 (Acanthocephala: Transvenidae) from percid fishes in the marine waters of Iran and Iraq. Helminthologia, 57, 1–11.
Smales, L. R. (2014). The genus Rhadinorhynchus (Acanthocephala: Rhadinorhynchidae) from marine fish in Australia with the description of four new species. Acta Parasitologica, 59, 721–736.
Stamatakis, A. (2014). RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, 30, 1312–1313.
Steinauer, M. L., Garcia-Vedrenne, A. E., Weinstein, S. B., & Kuris, A. M. (2019). Acanthocephalan parasites of the oarfish, Regalecus russelii (Regalecidae), with a description of a new species of Gymnorhadinorhynchus (Acanthocephala: Gymnorhadinorhynchidae). Journal of Parasitology, 105, 124–132.
Stöver, B. C., & Müller, K. F. (2010). TreeGraph 2: Combining and visualizing evidence from different phylogenetic analyses. BMC Bioinformatics, 11, 7.
Swofford, D. L. (2002) PAUP: Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony, version 4.0. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA.
Tan, G., Muffato, M., Ledergerber, C., Herrero, J., Goldman, N., Gil, M., et al. (2015). Current methods for automated filtering of multiple sequence alignments frequently worsen single-gene phylogenetic inference. Systematic Biology, 64, 778–791.
Towns, J., Cockerill, T., Dahan, M., Foster, I., Gaither, K., Grimshaw, A., et al. (2014). XSEDE: Accelerating scientific discovery. Computing in Science & Engineering, 16, 62–74.
Wang, Y., Wang, P., & Wu, D. (1993). On some Echinorhynchoidea parasites from marine fishes of Fujian Province, China. Wuyi Science Journal, 10, 29–39.
Xia, X. (2017). DAMBE6: New tools for microbial genomics, phylogenetics, and molecular evolution. Journal of Heredity, 108, 431–437.
Xia, X., & Lemey, P. (2009). Assessing substitution saturation with DAMBE. In: Lemey P., Salemi M. & Vandamme A.-M. (Eds) The phylogenetic handbook: a practical approach to DNA and protein phylogeny, Vol. 2. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 615–630
Xia, X., Xie, Z., Salemi, M., Chen, L., & Wang, Y. (2003). An index of substitution saturation and its application. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 26, 1–7.
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff of the Moreton Bay Research Station (University of Queensland) for their ongoing support of our work and the past and present members of the Marine Parasitology Laboratory (UQ) for assisting with collections over the years. We thank Drs Storm Martin and Tom Cribb for reading and providing comments on early drafts of the manuscript.
Funding
Collections within Moreton Bay were part of a larger effort to characterise the metazoan parasite fauna of fishes from that region and were funded by an ABRS grant (RF215-40) awarded to Drs Thomas Cribb and Scott Cutmore (University of Queensland).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted in compliance with all institutional, national and international guidelines on the care and use of animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as 4264FE4D-E886-4EED-BB8C-BC45A9C5696A. This article was published as an Online First article on the online publication date shown on this page. The article should be cited by using the doi number. This is the Version of Record.
This article is part of the Topical Collection Acanthocephala.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huston, D.C., Smales, L.R. Proposal of Spinulacorpus biforme (Smales, 2014) n. g., n. comb. and the Spinulacorpidae n. fam. to resolve paraphyly of the acanthocephalan family Rhadinorhynchidae Lühe, 1912. Syst Parasitol 97, 477–490 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-020-09923-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-020-09923-7