Abstract
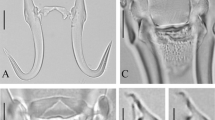
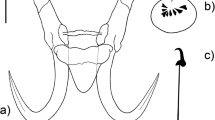
Gyrodactylus jennyae n. sp. is described from the body surface and mouthparts of tadpoles of the bullfrog Rana catesbeiana Shaw imported presumably from Missouri, USA, into a federal government facility in Moncton, New Brunswick, Canada. Its morphology resembles most closely that of G. chologastris Mizelle, Whittaker & McDougal, 1969 described from two amblyopsids (blind cave fishes) in Kentucky and North Carolina. Both species have long slender hamuli, a ventral bar with a relatively long membrane and small anterolateral processes, a cirrus with two rows of small spines and marginal hooks with a well-developed sickle heel and short handle. The two species differ morphologically; G. jennyae has a marginal hook sickle with a more pronounced heel than that found in G. chologastris. A BLAST search using a 945 base pair sequence that included the nuclear ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacers 1 and 2 and the 5.8S rRNA gene from G. jennyae n. sp. showed that the overall similarity with other Gyrodactylus sequences on GenBank was relatively low. The ITS1 region was similar to that of G. misgurni Ling, 1962; however, no ITS2 and 5.8S rRNA sequences are available for that species. A separate search using 5.8S sequences revealed that G. markakulensis Gvosdev, 1950 and G. laevis Malmberg, 1957 were the closest to G. jennyae (1 and 2 bp differences, respectively). These species are parasites of cyprinids (or their predators) and are similar to G. jennyae and G. chologastris in having a double row of small hooks on the cirrus and overall similar morphologies of the haptoral hard parts. There are now five species of Gyrodactylus described exclusively from amphibians and this appears to have involved at least three separate host-switches from fishes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S. F., Madden, T. L., Schäffer, A. A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W., et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 3389–3402.
Andrews, K. D., Lampley, R. L., Gillman, M. A., Corey, D. T., Ballard, S. R., Blasczyk, M. J., et al. (1992). Helminths of Rana catesbeiana in southern Illinois with a checklist of helminths in bullfrogs of North America. Transactions of the Illinois State Academy of Sciences, 85, 147–172.
Bakke, T. A., Cable, J., & Harris, P. D. (2007). The biology of gyrodactylid monogeneans: The “Russian-doll killers”. Advances in Parasitology, 64, 161–376.
Bakke, T. A., Harris, P. D., & Cable, J. (2002). Host specificity dynamics: Observations on gyrodactylid monogeneans. International Journal for Parasitology, 31, 281–308.
Barber, I. (2007). Parasites, behaviour and welfare in fish. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 104, 251–264.
Cable, J., Harris, P. D., & Tinsley, R. C. (1997). Melanin deposition in the gut of the monogenean Macrodactylus polypteri Malmberg 1957. International Journal for Parasitology, 27, 1323–1331.
Cone, D. K., & Dechtiar, A. O. (1984). Gyrodactylus fryi n sp. (Monogenea) from Esox masquinongy Mitchill in Ontario. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 62, 1089–1090.
Crawshaw, G. J. (1997). Disease in Canadian amphibian populations. Herpetological Conservation, 1, 258–270.
Dodd, K. C. Jr., Gunzburger, M. S., Barichivich, W. J., & Staiger, J. S. (2004). Southeast amphibian research and monitoring initiative (National Wildlife Refuges Summary Report for 2004). United States Geological Survey. Gainsville, FL: Florida Integrated Science Center. http://armi.usgs.gov/SEARMI2004Report.pdf.
Geets, A., Appleby, C., & Ollivier, F. (1999). Host-dependent and seasonal variation in opisthaptoral hard parts of Gyrodactylus cf. arcuatus from three Pomatoschistus spp. and G. arcuatus from Gasterosteus arculeatus: A multivariate approach. Parasitology, 119, 27–40.
Green, D. E., & Dodd, C. K., Jr. (2007). Presence of amphibian chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis and other amphibian pathogens at warm-water fish hatcheries in southeastern North America. Herpetological Conservation and Biology, 2, 43–47.
Gunzburger, M. S., Dodd, C. K. Jr., Barichivich, W. J., & Staiger, J. S. (2005). Southeast amphibian research and monitoring initiative (2005 Annual Report). United States Geological Survey. Gainsville, FL: Florida Integrated Science Center. http://fl.biology.usgs.gov/armi/2005_Annual_Report/2005_annual_report.html.
Herman, C. A. (1992). Endocrinology. In M. E. Feder & W. W. Burggren (Eds.), Environmental physiology of the amphibians (pp. 40–54). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Huyse, T., Audenaert, V., & Volckaert, F. A. M. (2003). Speciation and host–parasite relationships in the parasite genus Gyrodactylus (Monogenea, Platyhelminthes) infecting gobies of the genus Pomatoschistus (Gobiidae, Teleostei). International Journal for Parasitology, 33, 1679–1689.
Leblanc, J., Hansen, H., Burt, M., & Cone, D. (2006). Gyrodactylus neili n. sp. (Monogenea: Gyrodactylidae), a parasite of chain pickerel Esox niger Lesueur (Esocidae) from freshwaters of New Brunswick, Canada. Systematic Parasitology, 65, 43–48.
Malmberg, G. (1970). The excretory systems and the marginal hooks as a basis for the systematics of Gyrodactylus (Trematoda, Monogenea). Arkiv För Zoologie, 23, 1–237.
Malmberg, G. (1993). Gyrodactilidae et gyrodactylose des salmonidae. Bulletin Français de la Pêche et de la Pisciculture, 328, 5–46.
Matějusová, I., Gelnar, M., McBeath, A. J. A., Collins, C. M., & Cunningham, C. O. (2001). Molecular markers for gyrodactylids (Gyrodactylidae: Monogenea) from five fish families (Teleostei). International Journal for Parasitology, 31, 738–745.
Mizelle, J. D., Kritsky, D. C., & Bury, R. B. (1968). Studies on the monogenetic trematodes. XLI. Gyrodactylus ensatus sp. n., the first species of the genus described from Amphibia. Journal of Parasitology, 54, 281–282.
Mizelle, J. D., Kritsky, D. C., & McDougal, H. D. (1969). Studies on monogenetic trematodes. XLII. New species of Gyrodactylus from Amphibia. Journal of Parasitology, 55, 740–741.
Nieto, N. C., Camann, M. A., Foley, J. E., & Reiss, J. O. (2007). Disease associated with integumentary and cloacal parasites in tadpoles of northern red-legged frog Rana aurora aurora. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 78, 61–71.
Prudhoe, S., & Bray, R. A. (1982). Platyhelminth parasites of the Amphibia. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 217 pp.
Stuart, S. N., Chanson, J. S., Cox, N. A., Young, B. E., Rodrigues, A. S. L., Fischman, D. L., et al. (2004). Status and trends of amphibian declines and extinctions worldwide. Science, 306, 1783–1786.
Stunkard, H. W., & Dunihue, F. W. (1933). Gyrodactylus as a parasite of the tadpoles of Rana catesbeiana. Journal of Parasitology, 20, 137.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2007). MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1596–1599.
Vojtkova, L. (1989). The occurrence of the representatives of the class Monogenea in amphibians in Europe. Scripta Facultatis Scientarium Naturalium Universitatis Purkynianae Brunensis, 19, 331–338.
Volgar-Pastukhova, L. G. (1959). Parasitic fauna of the Anura in the Danube delta. In Y. I. Polyanksy (Ed.), Ecological parasitology (pp. 58–95). Leningrad: Leningradskogo Universiteta. (In Russian).
Wootton, D. M., Ryan, K. A., Demaree, R. S., & Critchfield, R. L. (1993). A new species of Gyrodactylus (Monogenea: Monopisthocotylea) on tadpoles of Rana catesbeiana from California, U.S.A. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 112, 230–233.
You, P., Easy, R. H., & Cone, D. K. (2008). Gyrodactylus parvae n. sp. (Monogenea) from the fins and body surface of Pseudorasbora parva (Cyprinidae) in central China. Comparative Parasitology, 75, 28–32.
Ziętara, M., Huyse, T., Lumme, J., & Volckaert, F. A. M. (2002). Deep divergence among subgenera of Gyrodactylus inferred from rDNA ITS region. Parasitology, 124, 39–52.
Ziętara, M. S., & Lumme, J. (2002). Speciation by host switch and adaptive radiation in a fish parasite genus Gyrodactylus (Monogenea, Gyrodactylidae). Evolution, 56, 2445–2458.
Zug, G. R. (1993). Herpetology: An introductory biology of amphibians and reptiles. San Diego, California: Academic Press, 527 pp.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly funded by the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada through Discovery Grants awarded to D.K.C. and J.D.M., an NSERC Postgraduate Scholarship (PGS M) awarded to L.P., and funds from the Pesticide Science Fund (PSF, Environment Canada) to D.J.M. and Bruce Pauli. T.H. is funded through a postdoctoral grant of the Research Foundation—Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen). The authors thank Dr Eric Hoberg for arranging loan of museum material, Dr David E. Green for sharing field data and Dr Rodney Bray for sharing records. Ken Doe and Paula Jackman (Environment Canada) are gratefully acknowledged for providing the tadpoles, as is Bruce Pauli (Environment Canada) for coordinating the PSF project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paetow, L., Cone, D.K., Huyse, T. et al. Morphology and molecular taxonomy of Gyrodactylus jennyae n. sp. (Monogenea) from tadpoles of captive Rana catesbeiana Shaw (Anura), with a review of the species of Gyrodactylus Nordmann, 1832 parasitising amphibians. Syst Parasitol 73, 219–227 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-009-9183-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-009-9183-9