Abstract
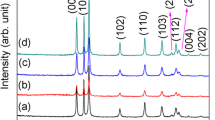
Different nanostructures such as flower-like, rod-like, and snowflake-like of ZnO have been synthesized by varying the amount of agarose using sonochemical method. It is found that morphology is governed by amount of agarose as well as ultrasonic treatment. Three amounts of agarose 0.01, 0.1, and 1.00 g are used to investigate its effect on ZnO. X-ray diffraction (XRD) confirmed the formation of single phase with hexagonal structure. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed flower-like, rod-like, and snowflake-like morphology for 1.00, 0.1, and 0.01 g agarose, respectively. UV/Visible absorption study showed blue shift at band-edge absorption in comparison to bulk ZnO. Photoluminescence spectra showed band-edge emission at 399 nm for lowest amount of agarose which quenched on increasing the agarose amount. These findings show a better and more environment friendly procedure for production of ZnO of readily adjustable morphology.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Djurisic AB, Leung YH (2006) Small 2:944
Li JY, Tompa GS, Liang S, Gorla C, Lu C (1997) J Vac Sci Technol A 15:1663
Mason TJ (ed) (1990) Sonochemistry: the uses of ultrasound in chemistry. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Zheng Y, Yu X, Xu X, Jin D, Yue L (2010) Ultrason Sonochem 17:7
Mazloumi M, Zanganeh S, Kajbafvala A, Ghariniyat P, Taghavi S, Lak A, Mohajerani M, Sadrnezhaad SK (2009) Ultrason Sonochem 16:11
Jia X, Fan H, Zhang F, Qin L (2010) Ultrason Sonochem 17:284
Araki C (1966) Proc Int Seaweed Symp 5:3
Fatin-Rouge N, Milton A, Buffle J, Goulet RR, Tessier A (2003) J Phys Chem B 107:12126
Liu JC, He F, Durham E, Zhao D, Roberts CB (2008) Langmuir 24:328
Zhou JF, Zhou MF, Caruso RA (2006) Langmuir 22:3332
Suslick KS (1988) Ultrasound: its chemical, physical and biological effects. VCH, Weinheim
Suslick KS (1990) Science 247:439
Rees DA (1972) J Biochem 126:257
Arnott S, Fulmer A, Scott WE, Dea ICM, Moorhouse R, Rees DA (1974) J Mol Biol 90:269
Griess GA, Moreno ET, Easom RA, Serwer P (1989) Biopolymers 28:1475
Xiong JY, Narayanan J, Liu XY, Chong TK, Chen SB, Chung TS (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:5638
Mishra P, Yadav RS, Pandey AC (2010) Ultrason Sonochem 17(3):560
Yadav RS, Mishra P, Pandey AC (2008) Ultrason Sonochem 15(5):863
Yadav RS, Pandey AC (2009) Struct Chem 20:1093
Xing YJ, Xi ZH, Xue ZQ, Zhang XD, Song JH, Wang RM, Xu J, Song Y, Zhang SL, Yu DP (2003) Appl Phys Lett 83:1689
Fan XM, Lian JS, Zhao L, Liu Y (2005) Appl Surf Sci 252:420
Tatsumi T, Fujita M, Kawamoto N, Sasajima M, Horikoshi Y (2004) Jpn J Appl Phys 43:2602
Wei X, Ban B, Xue C, Chen C, Liu M (2006) Jpn J Appl Phys 45:8586
Garcia RB, Vidal RRL (2000) Polim Cienc Tecnol 10:155
Nakamoto K (1978) Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and co-ordination compounds. Chichester, Wiley
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful to all the scientific members of Nanotechnology Application Centre, University of Allahabad, Allahabad, India. First author wishes to express her gratitude to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) New Delhi, India, for award of Junior Research Fellowship (JRF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, P., Yadav, R.S. & Pandey, A.C. Controlled growth of flower-like, rod-like, and snowflake-like ZnO nanostructures using agarose as biotemplate and its photoluminescence property. Struct Chem 22, 1281–1286 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-011-9822-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-011-9822-z