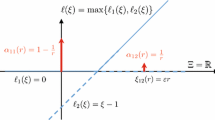
Abstract
This work investigates the problem of construction of designs for estimation and discrimination between competing linear models. In our framework, the unknown signal is observed with the addition of a noise and only a few evaluations of the noisy signal are available. The model selection is performed in a multi-resolution setting. In this setting, the locations of discrete sequential D and A designs are precisely constraint in a small number of explicit points. Hence, an efficient stochastic algorithm can be constructed that alternately improves the design and the model. Several numerical experiments illustrate the efficiency of our method for regression. One can also use this algorithm as a preliminary step to build response surfaces for sensitivity analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato, U., Antoniadis, A., Pensky, M.: Wavelet kernel penalized estimation for non-equispaced design regression. Stat. Comput. 16, 37–55 (2006)
Berlinet, A., Thomas-Agnan, C.: Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces in Probability and Statistics. Kluwer Academic, Boston (2004)
Biswas, A., Chaudhuri, P.: An efficient design for model discrimination and parameter estimation in linear models. Biometrika 89(3), 709–718 (2002)
Blanchard, G., Geman, D.: Sequential testing designs for pattern recognition. Ann. Stat. 33, 1155–1202 (2005)
Box, G.E.P., Draper, N.R.: A basis for the selection of a response surface design. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 54(287), 622–654 (1959)
Busby, D., Farmer, C., Iske, A.: Hierarchical nonlinear approximation for experimental design and statistical data fitting. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 29(1), 49–69 (2007)
Candès, E., Tao, T.: The Dantzig selector: Statistical estimation when p is much smaller than n. Ann. Stat. 35(6), 2313–2351 (2007)
Castaño, D., Kunoth, A.: Adaptive fitting of scattered data by spline wavelets. In: Curve and Surface Fitting, Saint-Malo, 2002, pp. 65–78. Nashboro Press, Brentwood (2003)
Dette, H., Studden, W.J.: The Theory of Canonical Moments with Applications in Statistics, Probability, and Analysis. Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics: Applied Probability and Statistics. Wiley, New York (1997)
Donoho, D.L., Johnstone, I.M.: Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage. Biometrika (1994)
Efron, B., Johnstone, I., Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R.: Least angle regression. Ann. Stat. 32(2), 407–499 (2003)
Fang, Z., Wiens, D.P.: Integer-valued, minimax robust designs for estimation and extrapolation in heteroscedastic, approximately linear models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 95(451), 807–818 (2000)
Fedorov, V.V.: Theory of Optimal Experiments. Academic Press, New York (1969)
Friedman, J.H.: Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines. Ann. Stat. 19, 1–141 (1991)
Geman, S., Geman, D.: Stochastic relaxation, Gibbs distributions and the Bayesian restoration of images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 6(6), 721–741 (1984)
Green, P.J.: Reversible jump Markov chain Monte Carlo computation and Bayesian model determination. Biometrika 82, 711–732 (1995)
Guyon, I., Weston, J., Barnhill, S., Vapnik, V.: Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 46, 389–422 (2002)
Hajeck, B.: Cooling schedules for optimal annealing. Math. Oper. Res. 13, 311–329 (1988)
Hall, P., Marron, J.: Extent to which least-square cross-validation minimises integrated square error in nonparametric density estimation. Probab. Theory Relat. Fields 74, 567–581 (1987)
Karlin, S., Studden, W.J.: Optimal experimental designs. Ann. Math. Stat. 37, 783–815 (1966)
Kerkyacharian, G., Picard, D.: Regression in random design and warped wavelets. Bernoulli 10(6), 1053–1105 (2004)
Khuri, A.I., Cornell, J.A.: Response Surfaces: Designs and Analyses. Marcel Dekker, New York (1987)
Kiefer, J., Wolfowitz, J.: Optimum designs in regression problem. Ann. Math. Stat. 30, 271–294 (1959)
Klinger, A.: Inference in high dimensional generalized linear models based on soft thresholding. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 63(2), 377–392 (2001)
Lai, T.L., Wei, C.Z.: Least square estimates in stochastic regression models with applications to identification and control of dynamic systems. Ann. Stat. 10(1), 154–166 (1982)
Liu, Y., Oyet, A.J.: Exact wavelet designs for discrimination. Sankhya 68(4), 569–586 (2006)
Meyer, Y.: Ondelettes et Opérateurs I. Hermann, Paris (1990)
Meyer, R.K., Nachtsheim, C.J.: The coordinate-exchange algorithm for constructing exact optimal experimental designs. Technometrics 37(1), 60–69 (1995)
Oyet, A.J., Wiens, D.P.: On exact minimax wavelet designs obtained by simulated annealing. Stat. Probab. Lett. 61, 111–121 (2003)
Oyet, A.J., Wiens, D.P.: Exact wavelet designs for discrimination. Sankhya 68(4), 569–586 (2006)
Pronzato, L.: Adaptive optimization and D-optimum experimental design. Ann. Stat. 28(6), 1743–1761 (2000)
Silverman, B.W.: Some aspects of the spline smoothing approach to nonparametric regression curve fitting. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 47, 1–52 (1985)
Tibshirani, R.: Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 58(1), 267–288 (1996)
Wiens, D.P.: Minimax designs for approximately linear regression. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 31, 353–371 (1992)
Zhou, H.: The adaptive Lasso and its Oracle properties. J. Am. Stat. Soc. 101, 1418–1429 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, S., Déjean, S. & Gadat, S. Adaptive sequential design for regression on multi-resolution bases. Stat Comput 22, 753–772 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-011-9267-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-011-9267-7