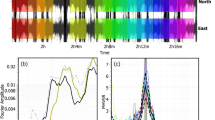
Abstract
InSight’s Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) provides a unique and unprecedented opportunity to conduct the first geotechnical survey of the Martian soil by taking advantage of the repeated seismic signals that will be generated by the mole of the Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP3). Knowledge of the elastic properties of the Martian regolith have implications to material strength and can constrain models of water content, and provide context to geological processes and history that have acted on the landing site in western Elysium Planitia. Moreover, it will help to reduce travel-time errors introduced into the analysis of seismic data due to poor knowledge of the shallow subsurface. The challenge faced by the InSight team is to overcome the limited temporal resolution of the sharp hammer signals, which have significantly higher frequency content than the SEIS 100 Hz sampling rate. Fortunately, since the mole propagates at a rate of \(\sim1~\mbox{mm}\) per stroke down to 5 m depth, we anticipate thousands of seismic signals, which will vary very gradually as the mole travels.
Using a combination of field measurements and modeling we simulate a seismic data set that mimics the InSight HP3-SEIS scenario, and the resolution of the InSight seismometer data. We demonstrate that the direct signal, and more importantly an anticipated reflected signal from the interface between the bottom of the regolith layer and an underlying lava flow, are likely to be observed both by Insight’s Very Broad Band (VBB) seismometer and Short Period (SP) seismometer. We have outlined several strategies to increase the signal temporal resolution using the multitude of hammer stroke and internal timing information to stack and interpolate multiple signals, and demonstrated that in spite of the low resolution, the key parameters—seismic velocities and regolith depth—can be retrieved with a high degree of confidence.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Aki, P.G. Richards, Quantitative Seismology, 2nd edn. (University Science Books, Sausalito, 2002)
V. Ansan, T. Dezert (the DLT group), Western Elysium Planitia, what is regional geology telling us about sub-surface? in InSight Science Team Presentation, Zurich, Switzerland, September 5–9, 2015 (2015)
S. Bonnefoy-Claudet, C. Cornou, P.Y. Bard, F. Cotton, P. Moczo, J. Kristek, D. Fäh, H/V ratio: a tool for site effects evaluation. Results from 1-D noise simulations. Geophys. J. Int. 167, 827–837 (2006). doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03154.x
D.C. Catling et al., A lava sea in the northern plains of Mars: circumpolar Hesperian oceans reconsidered, in 42nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, abs.# 2529 (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, 2011)
D.C. Catling et al., Does the Vastitas Borealis formation contain oceanic or volcanic deposits? in Third Conference on Early Mars, abs.# 7031, Lake Tahoe, NV, May 21–25, 2012 (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, 2012)
C. Charalambous, On the evolution of particle fragmentation with applications to planetary surfaces. PhD thesis, Imperial College London (2014)
G. Dal Moro, Joint analysis of Rayleigh-wave dispersion and HVSR of lunar seismic data from the Apollo 14 and 16 sites. Icarus 254, 338–349 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2015.03.017
P. Delage, F. Karakostas, A. Dhemaied, M. Belmokhtar, P. Lognonné, M. Golombek, E. De Laure, K. Hurst, J.C. Dupla, S. Keddar, Y.J. Cui, B. Banerdt, An investigation of the mechanical properties of some Martian regolith simulants with respect to the surface properties at the InSight mission landing site. Space Sci. Rev. (2017). doi:10.1007/s11214-017-0339-7
D. Fäh, M. Wathelet, M. Kristekova, H. Havenith, B. Endrun, G. Stamm, V. Poggi, J. Burjanek, C. Cornou, Using ellipticity information for site characterization, NERIES JRA4 “Geotechnical Site Characterisation”, task B2, D4—final report (2009). http://www.neries-eu.org/main.php/JRA4_TaskB2_D4_Final_Report.pdf?fileitem=10272807
M.P. Golombek et al., Geology of the Gusev cratered plains from the Spirit rover traverse. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 110, E02S07 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JE002503
M.P. Golombek, A.F.C. Haldemann, R.A. Simpson, R.L. Fergason, N.E. Putzig, R.E. Arvidson, J.F. Bell III., M.T. Mellon, Martian surface properties from joint analysis of orbital, Earth-based, and surface observations, in The Martian Surface: Composition, Mineralogy and Physical Properties, ed. by J.F. Bell III. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2008), pp. 468–497. Chap. 21
M.P. Golombek, R.J. Phillips, Mars tectonics, in Planetary Tectonics, ed. by T.R. Watters, R.A. Schultz (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2010), pp. 183–232. Chap. 5
M. Golombek, L. Redmond, H. Gengl, C. Schwartz, N. Warner, B. Banerdt, S. Smrekar, Selection of the InSight landing site: constraints, plans, and progress (expanded abstract), in 44th Lunar and Planetary Science, Abstract #1691 (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, 2013a)
M. Golombek, N. Warner, C. Schwartz, J. Green, Surface characteristics of prospective InSight landing sites in Elysium Planitia (expanded abstract), in 44th Lunar and Planetary Science, Abstract #1696 (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, 2013b)
M. Golombek, N. Warner, N. Wigton, C. Bloom, C. Schwartz, S. Kannan, D. Kipp, A. Huertas, B. Banerdt, Final four landing sites for the InSight geophysical lander (expanded abstract), in 45th Lunar and Planetary Science, Abstract #1499 (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, 2014)
M. Golombek et al., Selection of the InSight landing site. Space Sci. Rev. (2016, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-016-0321-9
J. Grygorczuk, M. Banaszkiewicz, A. Cichocki, M. Ciesielska, M. Dobrowolski, B. Kędziora, J. Krasowski, T. Kuciński, M. Marczewski, M. Morawski, H. Rickman, T. Rybus, K. Seweryn, K. Skocki, T. Spohn, T. Szewczyk, R. Wawrzaszek, Ł. Wiśniewski, Advanced penetrators and hammering sampling devices for planetary body exploration, in Proceedings of the ASTRA Conference ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2011 (2011)
R.B. Herrmann, Computer programs in seismology: an evolving tool for instruction and research. Seismol. Res. Lett. 84, 108–1088 (2013). doi:10.1785/0220110096
M. Hobiger, N. Le Bihan, C. Cornou, P.-Y. Bard, Multicomponent signal processing for Rayleigh wave ellipticity estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 29, 29–39 (2012). doi:10.1109/MSP.2012.2184969
R.D. Holtz, W.D. Kovacs, An Introduction to Geotechnical Engineering (No. Monograph) (1981)
B. Knapmeyer-Endrun et al., Rayleigh wave ellipticity modeling and inversion for shallow structure at the proposed InSight landing site in Elysium Planitia, Mars. Space Sci. Rev. (2016, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-016-0300-1
M. Kristekova, Time-frequency analysis of seismic signals, PhD thesis, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Bratislava, Slovakia (2006)
E. Lunedei, D. Albarello, On the seismic noise wavefield in a weakly dissipative layered Earth. Geophys. J. Int. 177, 1001–1014 (2009). doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.04062.x
P.L. McFadden, B.J. Drummond, S. Kravis, The Nth-root stack: theory, applications, and examples. Geophysics 51(10), 1879–1892 (1986)
H.J. Melosh, Impact Craters: A Geologic Process (Oxford University Press, London, 1989)
K. Mueller, M.P. Golombek, Compressional structures on Mars. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 32, 435–464 (2004)
S. Piqueux, A. Kleinboehl, M.P. Golombek, Thermal inertia mapping using climate sounder measurements, in Fall Meeting, Abstract P32A-4021, American Geophys. Un., San Francisco, CA, Dec. 15–19, 2014 (2014)
A. Pivarunas, N.H. Warner, M.P. Golombek, Onset diameter of rocky ejecta craters in western Elysium Planitia, Mars: constraints for regolith thickness at the InSight landing site (expanded abstract), in 46th Lunar and Planetary Science, Abstract #1129 (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, 2015)
J. Poganski, N.I. Kömle, G. Kargl, H.F. Schweiger, M. Grott, T. Spohn, O. Krömer, C. Krause, T. Wippermann, G. Tsakyridis, M. Fittock, R. Lichtenheldt, C. Vrettos, J.E. Anrade, Extended pile driving model to predict the penetration of the InSight/HP3 mole into the Martian soil. Space Sci. Rev. (2017, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-016-0302-z
M.A. Presley, P.R. Christensen, The effect of bulk density and particle size sorting on the thermal conductivity of particulate materials under Martian atmospheric pressures. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 102(E4), 9221–9229 (1997)
N. Rawlinson, B.L.N. Kennett, Rapid estimation of relative and absolute delay times across a network by adaptive stacking. Geophys. J. Int. 157, 332–340 (2004)
S. Rost, C. Thomas, Array seismology: methods and applications. Rev. Geophys. 40, 1008 (2002)
M. Sambridge, Geophysical inversion with a neighbourhood algorithm I. Searching a parameter space. Geophys. J. Int. 138, 479–494 (1999). doi:10.1046/j.1365-246X.1999.00876.x
J.C. Santamarina, A. Klein, M.A. Fam, Soils and waves: particulate materials behavior, characterization and process monitoring. J. Soils Sediments 1(2), 130 (2001)
J. Schweitzer, J. Fyen, S. Mykkeltveit, S.J. Gibbons, M. Pirli, D. Kühn, T. Kværna, Seismic arrays, in New Manual of Seismological Observatory Practice 2 (NMSOP-2), Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum GFZ, Potsdam, ed. by P. Bormann (2012), pp. 1–80
K. Seweryn, J. Grygorczuk, R. Wawrzaszek, M. Banaszkiewicz, T. Rybus, Low velocity penetrators (LVP) driven by hammering action-definition of the principle of operation based on numerical models and experimental tests. Acta Astronaut. 99, 303–317 (2014)
T. Spohn, M. Grott, J. Knollenberg, T. van Zoest, G. Kargl, S. Smrekar, W. Banerdt, T. Hudson, Insight: measuring the Martian heat flow using the heat flow and physical properties package (HP3). LPI Contrib. 1683, 1124 (2012)
P.M. Shearer, Introduction to Seismology (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2009)
K. Tanaka et al., Geologic map of Mars. US Geol. Surv. Sci. Invest. Map 3292 (2014)
N.A. Teanby, J. Stevanovic, J. Wookey, N. Murdoch, J. Hurley, R. Myhill, N.E. Bowles, S.B. Calcutt, W.T. Pike, Seismic coupling of short-period wind noise through Mars’ regolith for NASA’s InSight lander. Space Sci. Rev. (2016, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-016-0310-z
M. Wathelet, An improved neighborhood algorithm: parameter conditions and dynamic scaling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L09301 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008GL033256
N.H. Warner, M.P. Golombek, C. Bloom, N. Wigton, C. Schwartz, Regolith thickness in western Elysium Planitia: constraints for the InSight mission (expanded abstract), in 45th Lunar and Planetary Science, Abstract #2217 (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, 2014)
N.H. Warner et al., Near surface stratigraphy and regolith production in southwestern Elysium Planitia, Mars: implications for Hesperian-Amazonian terrains and the InSight lander mission. Space Sci. Rev. (2017, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-017-0352-x
N.R. Wigton, N. Warner, M. Golombek, Terrain mapping of the InSight landing region: Western Elysium Planitia, Mars (expanded abstract), in 45th Lunar and Planetary Science, Abstract #1234 (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, 2014)
D.M. Wood, Geotechnical Modelling, vol. 1 (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kedar, S., Andrade, J., Banerdt, B. et al. Analysis of Regolith Properties Using Seismic Signals Generated by InSight’s HP3 Penetrator. Space Sci Rev 211, 315–337 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0391-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0391-3