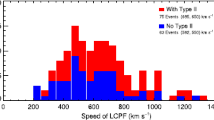
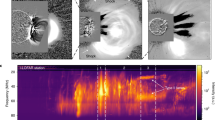
Abstract
The basic idea of the paper is to present transparently and confront two different views on the origin of large-scale coronal shock waves, one favoring coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and the other one preferring flares. For this purpose, we first review the empirical aspects of the relationship between CMEs, flares, and shocks (as manifested by radio type II bursts and Moreton waves). Then, various physical mechanisms capable of launching MHD shocks are presented. In particular, we describe the shock wave formation caused by a three-dimensional piston, driven either by the CME expansion or by a flare-associated pressure pulse. Bearing in mind this theoretical framework, the observational characteristics of CMEs and flares are revisited to specify advantages and drawbacks of the two shock formation scenarios. Finally, we emphasize the need to document clear examples of flare-ignited large-scale waves to give insight on the relative importance of flare and CME generation mechanisms for type II bursts/Moreton waves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, M.D.: 2003, A search for CMEs associated with big flares. Solar Phys. 218, 261 – 279. doi:10.1023/B:SOLA.0000013039.69550.bf.
Asai, A., Yokoyama, T., Shimojo, M., Shibata, K.: 2004, Downflow motions associated with impulsive nonthermal emissions observed in the 2002 July 23 solar flare. Astrophys. J. 605, L77 – L80. doi:10.1086/420768.
Aschwanden, M.J.: 2004, Physics of the Solar Corona. An Introduction, Springer, Berlin.
Attrill, G.D.R., Harra, L.K., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Démoulin, P.: 2007, Coronal “wave”: magnetic footprint of a coronal mass ejection? Astrophys. J. 656, L101 – L104. doi:10.1086/512854.
Balasubramaniam, K.S., Pevtsov, A.A., Neidig, D.F.: 2007, Are Moreton waves coronal phenomena? Astrophys. J. 658, 1372 – 1379. doi:10.1086/512001.
Bárta, M., Vršnak, B., Karlický, M.: 2008, Dynamics of plasmoids formed by the current sheet tearing. Astron. Astrophys. 477, 649 – 655. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078266.
Bárta, M., Karlický, M., Vršnak, B., Goossens, M.: 2007, MHD waves and shocks generated during magnetic field reconnection. Cent. Eur. Astrophys. Bull. 31, 165 – 180.
Benz, A.O., Brajša, R., Magdalenić, J.: 2007, Are there radio-quiet solar flares? Solar Phys. 240, 263 – 270. doi:10.1007/s11207-007-0365-9.
Biesecker, D.A., Myers, D.C., Thompson, B.J., Hammer, D.M., Vourlidas, A.: 2002, Solar phenomena associated with “EIT waves”. Astrophys. J. 569, 1009 – 1015. doi:10.1086/339402.
Cane, H.V., Erickson, W.C.: 2005, Solar type II radio bursts and IP type II events. Astrophys. J. 623, 1180 – 1194. doi:10.1086/428820.
Cane, H.V., Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Howard, R.A.: 1987, Energetic interplanetary shocks, radio emission, and coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 92, 9869 – 9874.
Chen, P.F.: 2006, The relation between EIT waves and solar flares. Astrophys. J. 641, L153 – L156. doi:10.1086/503868.
Chen, P.F., Fang, C., Shibata, K.: 2005, A full view of EIT waves. Astrophys. J. 622, 1202 – 1210. doi:10.1086/428084.
Cho, K.S., Moon, Y.J., Dryer, M., Shanmugaraju, A., et al.: 2005, Examination of type II origin with SOHO/LASCO observations. J. Geophys. Res. (Space Phys.) 110, A12101. doi:10.1029/2004JA010744.
Cho, K.S., Lee, J., Moon, Y.J., Dryer, M., et al.: 2007, A study of CME and type II shock kinematics based on coronal density measurement. Astron. Astrophys. 461, 1121 – 1125. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20064920.
Ciaravella, A., Raymond, J.C., Kahler, S.W., Vourlidas, A., Li, J.: 2005, Detection and diagnostics of a coronal shock wave driven by a partial-halo coronal mass ejection on 28 June 2000. Astrophys. J. 621, 1121 – 1128. doi:10.1086/427619.
Cliver, E.W., Webb, D.F., Howard, R.A.: 1999, On the origin of solar metric type II bursts. Solar Phys. 187, 89 – 114.
Cliver, E.W., Nitta, N.V., Thompson, B.J., Zhang, J.: 2004, Coronal shocks of November 1997 revisited: The CME type II timing problem. Solar Phys. 225, 105 – 139. doi:10.1007/s11207-004-3258-1.
Cliver, E.W., Laurenza, M., Storini, M., Thompson, B.J.: 2005, On the origins of solar EIT waves. Astrophys. J. 631, 604 – 611. doi:10.1086/432250.
Dauphin, C., Vilmer, N., Krucker, S.: 2006, Observations of a soft X-ray rising loop associated with a type II burst and a coronal mass ejection in the 03 November 2003 X-ray flare. Astron. Astrophys. 455, 339 – 348. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054535.
Delaboudinière, J.P., Artzner, G.E., Brunaud, J., Gabriel, A.H., et al.: 1995, EIT: Extreme-ultraviolet imaging telescope for the SOHO mission. Solar Phys. 162, 291 – 312.
Delannée, C., Aulanier, G.: 1999, CME associated with transequatorial loops and a bald patch flare. Solar Phys. 190, 107 – 129.
Dodson, H.W.: 1949, Position and development of the solar flares of 8 and 10 May 1949. Astrophys. J. 110, 382 – 386.
Fletcher, L., Hannah, I.G., Hudson, H.S., Metcalf, T.R.: 2007, A TRACE white light and RHESSI hard X-ray study of flare energetics. Astrophys. J. 656, 1187 – 1196. doi:10.1086/510446.
Forbes, T.G.: 1988, Shocks produced by impulsively driven reconnection. Solar Phys. 117, 97 – 121.
Forbes, T.G., Priest, E.R.: 1983, A numerical experiment relevant to line-tied reconnection in two-ribbon flares. Solar Phys. 84, 169 – 188.
Gallagher, P.T., Lawrence, G.R., Dennis, B.R.: 2003, Rapid acceleration of a coronal mass ejection in the low corona and implications for propagation. Astrophys. J. 588, L53 – L56. doi:10.1086/375504.
Gary, G.A.: 2001, Plasma beta above a solar active region: Rethinking the paradigm. Solar Phys. 203, 71 – 86.
Gary, D.E., Dulk, G.A., House, L., Illing, R., et al.: 1984, Type II bursts, shock waves, and coronal transients – The event of 29 June 1980, 0233 UT. Astron. Astrophys. 134, 222 – 233.
Gilbert, H.R., Holzer, T.E.: 2004, Chromospheric waves observed in the He i spectral line (λ=10 830 Å): A closer look. Astrophys. J. 610, 572 – 587. doi:10.1086/421452.
Gilbert, H.R., Thompson, B.J., Holzer, T.E., Burkepile, J.T.: 2001, A comparison of CME-associated atmospheric waves observed in coronal (19.5 nm) and chromospheric (He i 1083 nm and H-alpha 656 nm) lines. AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, B746.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2006, Coronal Mass Ejections and Type II Radio Bursts, Washington DC American Geophysical Union Geophysical Monograph Series 165, 207–220.
Gopalswamy, N., Raulin, J.P., Kundu, M.R., Nitta, N., et al.: 1995, VLA and YOHKOH observations of an M1.5 flare. Astrophys. J. 455, 715 – 732. doi:10.1086/176618.
Gopalswamy, N., Kaiser, M.L., Thompson, B.J., Burlaga, L.F., et al.: 2000, Radio-rich solar eruptive events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 1427 – 1430.
Gopalswamy, N., Aguilar-Rodriguez, E., Yashiro, S., Nunes, S., et al.: 2005, Type II radio bursts and energetic solar eruptions. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A12 S07. doi:10.1029/2005JA011158.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., et al.: 2008, Radio-quiet fast and wide coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 674, 560 – 569.
Harrison, R.A., Bryans, P., Simnett, G.M., Lyons, M.: 2003, Coronal dimming and the coronal mass ejection onset. Astron. Astrophys. 400, 1071 – 1083. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20030088.
Harvey, G.A.: 1965, 2800 Megacycle per second radiation associated with type II and type IV solar radio bursts and the relation with other phenomena. J. Geophys. Res. 70, 2961.
Holman, G.D., Pesses, M.E.: 1983, Solar type II radio emission and the shock drift acceleration of electrons. Astrophys. J. 267, 837 – 843. doi:10.1086/160918.
Hudson, H.S., Warmuth, A.: 2004, Coronal loop oscillations and flare shock waves. Astrophys. J. 614, L85 – L88. doi:10.1086/425314.
Hudson, H.S., Khan, J.I., Lemen, J.R., Nitta, N.V., Uchida, Y.: 2003, Soft X-ray observation of a large-scale coronal wave and its exciter. Solar Phys. 212, 121 – 149. doi:10.1023/A:1022904125479.
Karlický, M.: 1984, Narrowband dm-spikes as indication of flare mass ejection. Solar Phys. 92, 329 – 342.
Karlický, M.: 1988, Response of the current sheet to a time-limited enhancement of electrical resistivity. Bull. Astron. Inst. Czechoslov. 39, 13 – 23.
Khan, J.I., Aurass, H.: 2002, X-ray observations of a large-scale solar coronal shock wave. Astron. Astrophys. 383, 1018 – 1031. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20011707.
Klassen, A., Aurass, H., Klein, K.L., Hofmann, A., Mann, G.: 1999, Radio evidence on shock wave formation in the solar corona. Astron. Astrophys. 343, 287 – 296.
Klein, K.L., Khan, J.I., Vilmer, N., Delouis, J.M., Aurass, H.: 1999, X-ray and radio evidence on the origin of a coronal shock wave. Astron. Astrophys. 346, L53 – L56.
Kołomański, S., Tomczak, M., Ronowicz, P., Karlický, M., Aurass, H.: 2007, Flare-associated X-ray plasma ejections and radio drifting structures. Cent. Eur. Astrophys. Bull. 31, 125 – 134.
Landau, L.D., Lifshitz, E.M.: 1987, Fluid Mechanics, 2nd edn., Oxford, Pergamon Press.
Leblanc, Y., Dulk, G.A., Vourlidas, A., Bougeret, J.L.: 2001, Tracing shock waves from the corona to 1 AU: Type II radio emission and relationship with CMEs. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 25301 – 25312. doi:10.1029/2000JA000260.
Liu, C., Lee, J., Yurchyshyn, V., Deng, N., et al.: 2007, The eruption from a sigmoidal solar active region on 13 May 2005. Astrophys. J. 669, 1372 – 1381. doi:10.1086/521644.
Magdalenić, J., Vršnak, B., Pohjolainen, S., Temmer, M., Aurass, H., Lehtinen, N.: 2008, Multi-wavelength study of coronal waves associated with the CME-flare event of 24 December 1996. Solar Phys. doi:10.1007/s11207-008-9220-x. This issue.
Mancuso, S., Raymond, J.C.: 2004, Coronal transients and metric type II radio bursts. I. Effects of geometry. Astron. Astrophys. 413, 363 – 371. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20031510.
Mancuso, S., Raymond, J.C., Kohl, J., Ko, Y.K., Uzzo, M., Wu, R.: 2002, UVCS/SOHO observations of a CME-driven shock: Consequences on ion heating mechanisms behind a coronal shock. Astron. Astrophys. 383, 267 – 274. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20011721.
Mann, G.: 1995, Simple magnetohydrodynamic waves. J. Plasma Phys. 53, 109 – 125.
Mann, G., Klassen, A.: 2005, Electron beams generated by shock waves in the solar corona. Astron. Astrophys. 441, 319 – 326. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20034396.
Maričić, D., Vršnak, B., Stanger, A.L., Veronig, A.: 2004, Coronal mass ejection of 15 May 2001: I. Evolution of morphological features of the eruption. Solar Phys. 225, 337 – 353. doi:10.1007/s11207-004-3748-1.
Maričić, D., Vršnak, B., Stanger, A.L., Veronig, A.M., Temmer, M., Roša, D.: 2007, Acceleration phase of coronal mass ejections: II. Synchronization of the energy release in the associated flare. Solar Phys. 241, 99 – 112. doi:10.1007/s11207-007-0291-x.
Michalek, G., Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H.: 2007, Width of radio-loud and radio-quiet CMEs. Solar Phys. 246, 409 – 414. doi:10.1007/s11207-007-9062-y.
Moreton, G.E.: 1960, Hα Observations of flare-initiated disturbances with velocities ≈1000 km s−1. Astron. J. 65, 494 – 495. doi:10.1086/108346.
Moreton, G.E., Ramsey, H.E.: 1960, In: Recent Observations of Dynamical Phenomena Associated with Solar Flares CS-72, Astron. Soc. Pac., San Francisco, 357 – 358.
Moses, D., Clette, F., Delaboudinière, J.P., Artzner, G.E., et al.: 1997, EIT observations of the extreme ultraviolet sun. Solar Phys. 175, 571 – 599. doi:10.1023/A:1004902913117.
Narukage, N., Hudson, H.S., Morimoto, T., Akiyama, S., et al.: 2002, Simultaneous observation of a Moreton wave on 3 November 1997 in Hα and soft X-rays. Astrophys. J. 572, L109 – L112. doi:10.1086/341599.
Nelson, G.J., Melrose, D.B.: 1985, Type II bursts. In: Solar Radiophysics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 333 – 359.
Neupert, W.M.: 1989, Transient coronal extreme ultraviolet emission before and during the impulsive phase of a solar flare. Astrophys. J. 344, 504 – 512. doi:10.1086/167819.
Payne-Scott, R., Yabsley, D.E., Bolton, J.G.: 1947, Relative times of arrival of solar noise on different radio frequencies. Nature 160, 256 – 257.
Pick, M., Malherbe, J.M., Kerdraon, A., Maia, D.J.F.: 2005, On the disk Hα and radio observations of the 28 October 2003 flare and coronal mass ejection event. Astrophys. J. 631, L97 – L100. doi:10.1086/497137.
Plunkett, S.P., Vourlidas, A., Šimberová, S., Karlický, M., Kotrč, P., Heinzel, P., Kupryakov, Y.A., Guo, W.P., Wu, S.T.: 2000, Simultaneous SOHO and ground-based observations of a large eruptive prominence and coronal mass ejection. Solar Phys. 194, 371 – 391.
Pohjolainen, S., Lehtinen, N.J.: 2006, Slow halo CMEs with shock signatures. Astron. Astrophys. 449, 359 – 367. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054118.
Priest, E.R.: 1982, Solar Magneto-Hydrodynamics, Reidel, Dordrecht.
Ramsey, H.E., Smith, S.F.: 1966, Flare-initiated filament oscillations. Astron. J. 71, 197 – 199.
Raymond, J.C., Thompson, B.J., St. Cyr, O.C., Gopalswamy, N., et al.: 2000, SOHO and radio observations of a CME shock wave. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 1439 – 1442. doi:10.1029/1999GL003669.
Reiner, M.J., Kaiser, M.L., Plunkett, S.P., Prestage, N.P., Manning, R.: 2000, Radio tracking of a white-light coronal mass ejection from solar corona to interplanetary medium. Astrophys. J. 529, L53 – L56. doi:10.1086/312446.
Reiner, M.J., Kaiser, M.L., Gopalswamy, N., Aurass, H., et al.: 2001, Statistical analysis of coronal shock dynamics implied by radio and white-light observations. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 25279 – 25290. doi:10.1029/2000JA004024.
Reiner, M.J., Krucker, S., Gary, D.E., Dougherty, B.L., Kaiser, M.L., Bougeret, J.L.: 2007, Radio and white-light coronal signatures associated with the RHESSI hard X-ray event of 23 July 2002. Astrophys. J. 657, 1107 – 1116. doi:10.1086/510827.
Riley, P., Lionello, R., Mikić, Z., Linker, J., et al.: 2007, “Bursty” reconnection following solar eruptions: MHD simulations and comparison with observations. Astrophys. J. 655, 591 – 597. doi:10.1086/509913.
Russell, C.T., Mulligan, T.: 2002, On the magnetosheath thicknesses of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Planet. Space Sci. 50, 527 – 534.
Saito, K.: 1970, A non-spherical axisymmetric model of the solar K corona of the minimum type. Ann. Obs. Astron. Tokyo 12, 53 – 120.
Sedov, L.I.: 1959, Similarity and Dimensional Methods in Mechanics, Academic Press, New York.
Shanmugaraju, A., Moon, Y.J., Vršnak, B.: 2008, Type II radio bursts with high and low starting frequencies. Solar Phys. submitted.
Shanmugaraju, A., Moon, Y.J., Dryer, M., Umapathy, S.: 2003, An investigation of solar maximum metric type II radio bursts: Do two kinds of coronal shock sources exist? Solar Phys. 215, 161 – 184.
Shanmugaraju, A., Moon, Y.J., Cho, K.S., Kim, Y.H., Dryer, M., Umapathy, S.: 2005, Multiple type II solar radio bursts. Solar Phys. 232, 87 – 103. doi:10.1007/s11207-005-1586-4.
Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Michels, D.J.: 1983, Associations between coronal mass ejections and soft X-ray events. Astrophys. J. 272, 349 – 354. doi:10.1086/161298.
Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Howard, R.A., Michels, D.J., Koomen, M.J., et al.: 1985, Coronal mass ejections and interplanetary shocks. J. Geophys. Res. 90, 163 – 175.
Srivastava, N., Schwenn, R., Inhester, B., Martin, S.F., Hanaoka, Y.: 2000, Factors related to the origin of a gradual coronal mass ejection associated with an eruptive prominence on 21 – 22 June 1998. Astrophys. J. 534, 468 – 481. doi:10.1086/308749.
Steinolfson, R.S.: 1984, Type II radio emission in coronal transients. Solar Phys. 94, 193 – 202.
Stewart, R.T., Magun, A.: 1980, Radio evidence for electron acceleration by transverse shock waves in herringbone Type II solar bursts. Proc. Astron. Soc. Aust. 4, 53 – 55.
Subramanian, K.R., Ebenezer, E.: 2006, A statistical study of the characteristics of type II doublet radio bursts. Astron. Astrophys. 451, 683 – 690. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054215.
Švestka, Z., Fritzová-Švestková, L.: 1974, Type II radio bursts and particle acceleration. Solar Phys. 36, 417 – 431. doi:10.1007/BF00151211.
Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M., Vršnak, B., Rybák, J., et al.: 2008, Acceleration in fast halo CMEs and synchronized flare HXR bursts. Astrophys. J. 673, L95 – L98. doi:10.1086/527414.
Thompson, B.J., Cliver, E.W., Nitta, N., Delannée, C., Delaboudinière, J.P.: 2000, Coronal dimmings and energetic CMEs in April – May 1998. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 1431 – 1434. doi:10.1029/1999GL003668.
Thompson, B.J., Plunkett, S.P., Gurman, J.B., Newmark, J.S., St. Cyr, O.C., Michels, D.J.: 1998, SOHO/EIT observations of an Earth-directed coronal mass ejection on 12 May 1997. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2465 – 2468. doi:10.1029/98GL50429.
Uchida, Y.: 1968, Propagation of hydromagnetic disturbances in the solar corona and moreton’s wave phenomenon. Solar Phys. 4, 30 – 44. doi:10.1007/BF00146996.
Uchida, Y.: 1974, Behavior of the flare produced coronal MHD wavefront and the occurrence of type II radio bursts. Solar Phys. 39, 431 – 449.
Volonskaya, N.N., Volonskaya, T.N., Semenov, V.S., Biernat, H.K.: 2003, Enargy and momentum balance in the process of time-dependent magnetic Petschek-type reconnection. Int. J. Geomagn. Aeron. 3, 245 – 253.
Vršnak, B.: 2001, Solar flares and coronal shock waves. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 25291 – 25300. doi:10.1029/2000JA004009.
Vršnak, B., Lulić, S.: 2000, Formation of coronal MHD shock waves – I. The basic mechanism. Solar Phys. 196, 157 – 180.
Vršnak, B., Ruždjak, V., Zlobec, P., Aurass, H.: 1995, Ignition of MHD shocks associated with solar flares. Solar Phys. 158, 331 – 351.
Vršnak, B., Warmuth, A., Brajša, R., Hanslmeier, A.: 2002a, Flare waves observed in Helium i 10 830 Å. A link between Hα Moreton and EIT waves. Astron. Astrophys. 394, 299 – 310. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021121.
Vršnak, B., Magdalenić, J., Aurass, H., Mann, G.: 2002b, Band-splitting of coronal and interplanetary type II bursts. II. Coronal magnetic field and Alfvén velocity. Astron. Astrophys. 396, 673 – 682. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021413.
Vršnak, B., Maričić, D., Stanger, A.L., Veronig, A.: 2004, Coronal mass ejection of 15 May 2001: II. Coupling of the CME acceleration and the flare energy release. Solar Phys. 225, 355 – 378. doi:10.1007/s11207-004-4995-x.
Vršnak, B., Warmuth, A., Temmer, M., Veronig, A., et al.: 2006, Multi-wavelength study of coronal waves associated with the CME-flare event of 3 November 2003. Astron. Astrophys. 448, 739 – 752. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053740.
Vršnak, B., Maričić, D., Stanger, A.L., Veronig, A.M., Temmer, M., Roša, D.: 2007, Acceleration phase of coronal mass ejections: I. Temporal and spatial scales. Solar Phys. 241, 85 – 98. doi:10.1007/s11207-006-0290-3.
Wagner, W.J., MacQueen, R.M.: 1983, The excitation of type II radio bursts in the corona. Astron. Astrophys. 120, 136 – 138.
Warmuth, A., Mann, G.: 2005, A model of the Alfvén speed in the solar corona. Astron. Astrophys. 435, 1123 – 1135. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20042169.
Warmuth, A., Mann, G., Aurass, H.: 2005, First soft X-ray observations of global coronal waves with the GOES solar X-ray imager. Astrophys. J. 626, L121 – L124. doi:10.1086/431756.
Warmuth, A., Vršnak, B., Aurass, H., Hanslmeier, A.: 2001, Evolution of two EIT/Hα Moreton waves. Astrophys. J. 560, L105 – L109. doi:10.1086/324055.
Warmuth, A., Vršnak, B., Magdalenić, J., Hanslmeier, A., Otruba, W.: 2004a, A multiwavelength study of solar flare waves. I. Observations and basic properties. Astron. Astrophys. 418, 1101 – 1115. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20034332.
Warmuth, A., Vršnak, B., Magdalenić, J., Hanslmeier, A., Otruba, W.: 2004b, A multiwavelength study of solar flare waves. II. Perturbation characteristics and physical interpretation. Astron. Astrophys. 418, 1117 – 1129. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20034333.
White, S.M.: 2007, Solar radio bursts and space weather. Asian J. Phys. 16, 189 – 207.
White, S.M., Thompson, B.J.: 2005, High-cadence radio observations of an EIT wave. Astrophys. J. 620, L63 – L66. doi:10.1086/428428.
Wild, J.P., McCready, L.L.: 1950, Observations of the spectrum of high-intensity solar radiation at metre wavelengths. I. The apparatus and spectral types of solar burst observed. Aust. J. Sci. Res. A Phys. Sci. 3, 387 – 398.
Zhang, J.: 2005, A study on the acceleration of coronal mass ejections. In: Dere, K., Wang, J., Yan, Y. (eds.) Coronal and Stellar Mass Ejections, IAU Symp. 226, 65–70.
Zhang, J., Dere, K.P.: 2006, A statistical study of main and residual accelerations of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 649, 1100 – 1109. doi:10.1086/506903.
Zhang, J., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A., Kundu, M.R., White, S.M.: 2001, On the temporal relationship between coronal mass ejections and flares. Astrophys. J. 559, 452 – 462. doi:10.1086/322405.
Zhang, J., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A., Vourlidas, A.: 2004, A study of the kinematic evolution of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 604, 420 – 432. doi:10.1086/381725.
Zhukov, A.N., Auchère, F.: 2004, On the nature of EIT waves, EUV dimmings and their link to CMEs. Astron. Astrophys. 427, 705 – 716. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20040351.
Žic, T., Vršnak, B., Temmer, M., Jacobs, C.: 2008, Cylindrical and spherical pistons as drivers of MHD shocks. Solar Phys. doi:10.1007/s11207-008-9173-0. This issue.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Radio Physics and the Flare-CME Relationship
Guest Editors: Karl-Ludwig Klein and Silja Pohjolainen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vršnak, B., Cliver, E.W. Origin of Coronal Shock Waves. Sol Phys 253, 215–235 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-008-9241-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-008-9241-5